Abstract
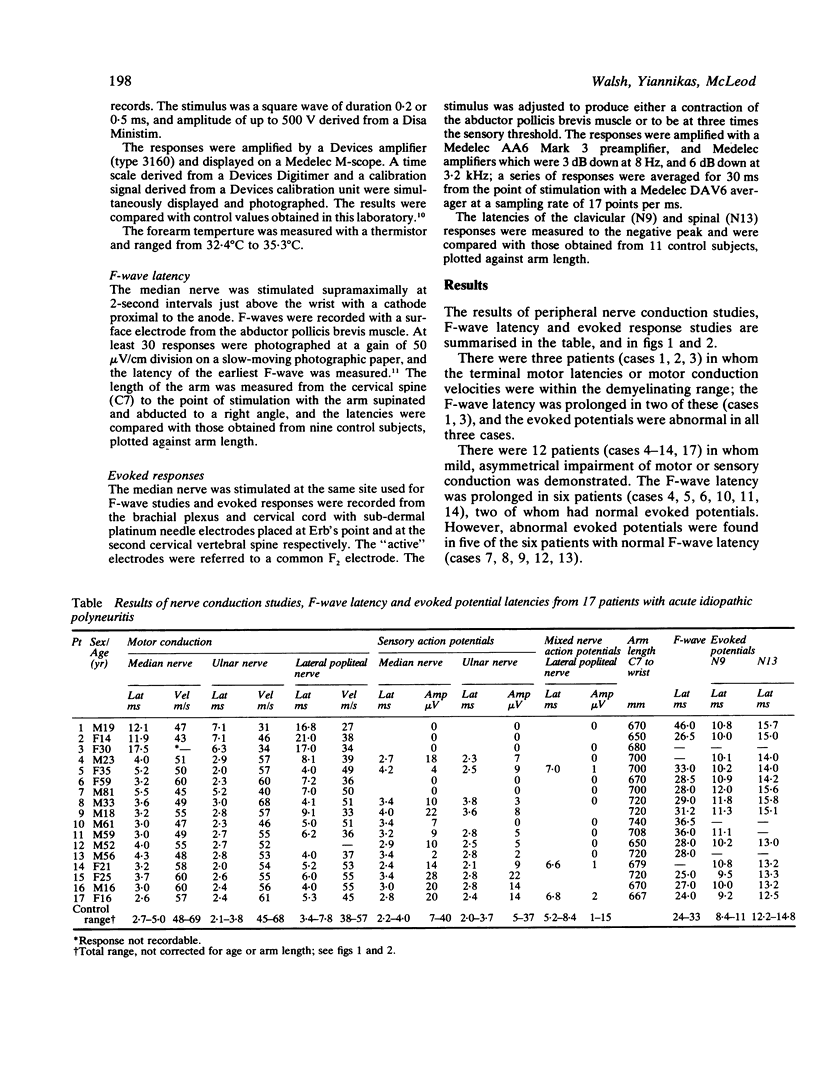
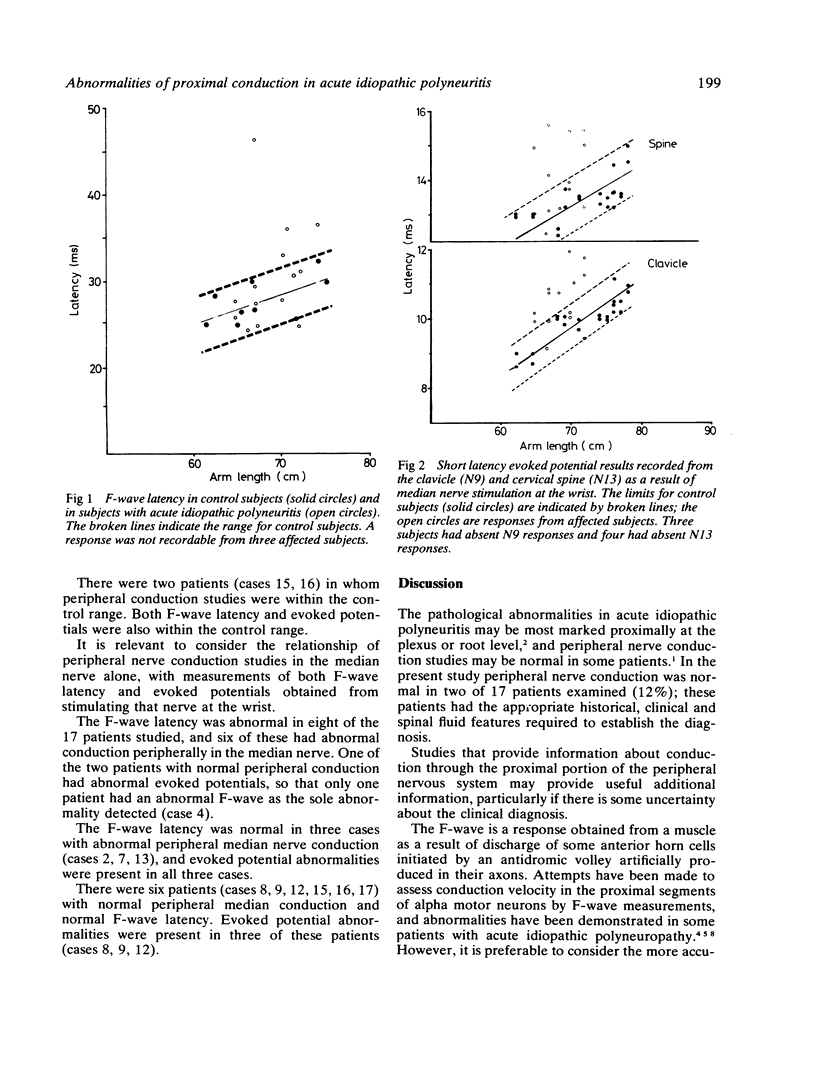
Motor and sensory conduction studies, F-wave latency, and the latency of evoked potentials from the brachial plexus and cervical spine in response to median nerve stimulation were examined in 17 patients with acute idiopathic polyneuropathy. Short latency evoked potentials provided a higher yield of evidence of abnormalities of proximal conduction than did the F-wave latency. Both methods of studying conduction in the proximal segments of a peripheral nerve may be normal, however, in a small number of patients who have significant pathological lesions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Butzer J. F. F-wave conduction velocity in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Assessment of nerve segment between axilla and spinal cord. Arch Neurol. 1975 Aug;32(8):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490500044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. Proximal versus distal slowing of motor nerve conduction velocity in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1978 Apr;3(4):344–350. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D., Ashby P. Conduction velocity in the proximal segments of a motor nerve in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Jun;39(6):538–544. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.6.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman T., Shahani B. T., Young R. R. Late responses as aids to diagnosis in peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Feb;43(2):156–162. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Walsh J. C., Prineas J. W., Pollard J. D. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. A clinical and electrophsiological follow-up study. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):145–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuck R. R., Antony J. H., McLeod J. G. F-wave in experimental allergic neuritis. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. C., McLeod J. G. Alcoholic neuropathy. An electrophysiological and histological study. J Neurol Sci. 1970 May;10(5):457–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff C. H., Gilliatt R. W. F waves in patients with hand wasting caused by a cervical rib and band. Muscle Nerve. 1979 Nov-Dec;2(6):452–457. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. R., Shahani B. T. Clinical value and limitations of f-wave determination. Muscle Nerve. 1978 May-Jun;1(3):248–250. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


