Abstract
The hypothesis that migraine is a primary neurological disturbance with secondary vascular manifestations is tested by analysing the five phases of migraine attacks and the eight groups of recognised precipitating factors. Accessory evidence from cerebral blood flow and EEG recordings taken during attacks is also considered. The evidence supports the concept that the sensory cortex and hypothalamus could be initiating sites for migraine attacks, and indicates that a neurological mechanism, suggested by Liveing and Gowers 100 years ago, remains viable and needs to be considered in future research.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam K., Oswald I. Sleep is for tissue restoration. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1977 Jul;11(4):376–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amery W. K. Brain hypoxia: the turning-point in the genesis of the migraine attack? Cephalalgia. 1982 Jun;2(2):83–109. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1982.0202083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller O. Pathogenesis of vascular headache of the migrainous type: the role of impaired central inhibition. Headache. 1975 Oct;15(3):177–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1975.hed1503177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N., Dexter S. L. The site of pain origin during migraine attacks. Cephalalgia. 1981 Sep;1(3):143–147. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1981.0103143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
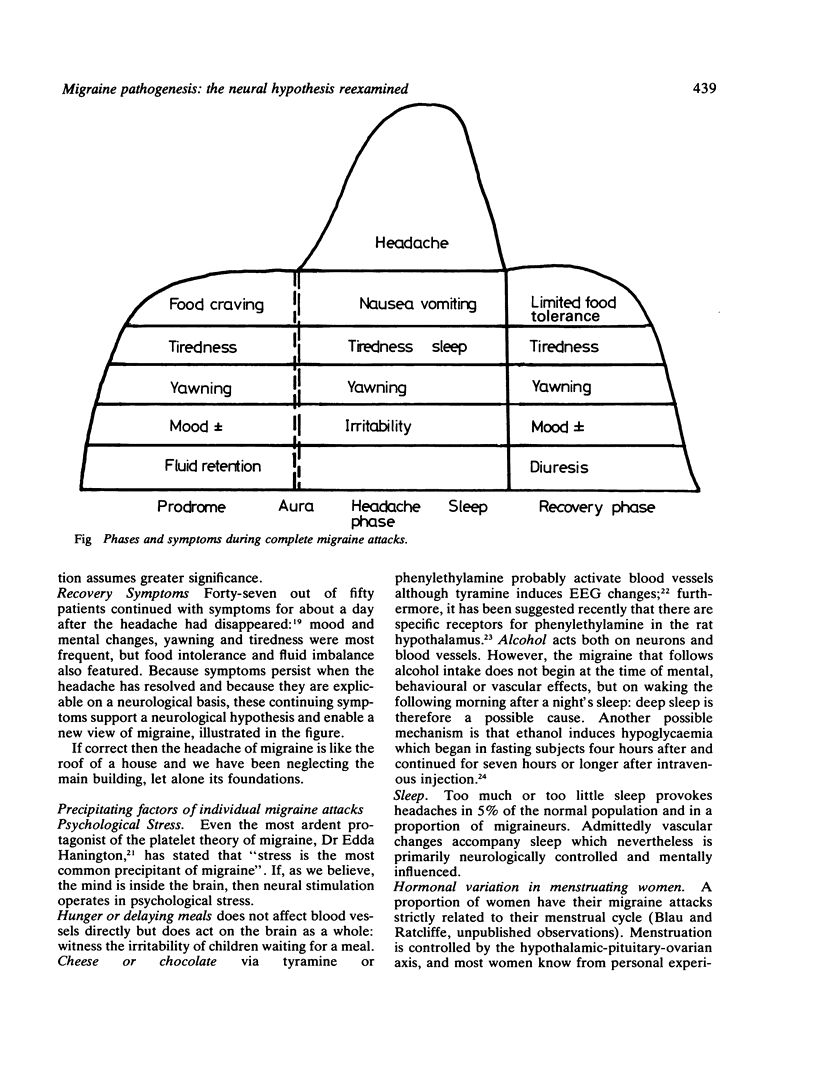
- Blau J. N. Migraine prodromes separated from the aura: complete migraine. Br Med J. 1980 Sep 6;281(6241):658–660. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6241.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N. Migraine: A vasomotor instability of the meningeal circulation. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N. Resolution of migraine attacks: sleep and the recovery phase. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Mar;45(3):223–226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Cerebral ischemia--less familiar types. Clin Neurosurg. 1971;18:267–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S. A basis for migraine therapy- the autonomic theory reappraised. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Apr;54(630):231–243. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.54.630.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennard C., Gawel M., Rudolph N. de M., Rose F. C. Visual evoked potentials in migraine subjects. Res Clin Stud Headache. 1978;6:73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapkin M. L., French J. H., Golden G. S., Rowan A. J. The electroencephalogram in childhood basilar artery migraine. Neurology. 1977 Jun;27(6):580–583. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.6.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. B. Footballer's migraine. Br Med J. 1972 May 6;2(5809):326–327. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5809.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. E., Levine A. S. The central control of appetite. Lancet. 1983 Feb 19;1(8321):398–401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91511-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Rehncrona S., Siesjö B. K. Coupling of cerebral metabolism and blood flow in epileptic seizures, hypoxia and hypoglycaemia. Ciba Found Symp. 1978 Mar;(56):199–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470720370.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J., Tfelt-Hansen P., Henriksen L., Larsen B. The common migraine attack may not be initiated by cerebral ischaemia. Lancet. 1981 Aug 29;2(8244):438–440. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90774-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Hulihan-Giblin B., Skolnick P. (+)-Amphetamine binding to rat hypothalamus: relation to anorexic potency for phenylethylamines. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):487–490. doi: 10.1126/science.7123250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Grubb R. L., Eichling J. O. Central neuroendocrine regulation of brain water permeability. Ciba Found Symp. 1978 Mar;(56):219–235. doi: 10.1002/9780470720370.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. S., Sherrington C. S. On the Regulation of the Blood-supply of the Brain. J Physiol. 1890 Jan;11(1-2):85–158.17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1890.sp000321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Moffett A., Swash M. Observations on the relation of migraine and epilepsy. An electroencephalographic, psychological and clinical study using oral tyramine. Epilepsia. 1972 Jul;13(3):365–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1972.tb04577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens J. Domperidone in the prevention of complete classical migraine. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Mar 27;284(6320):944–944. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6320.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M., Williams K., Leyton M. Observations on the treatment of an acute attack of migraine. Res Clin Stud Headache. 1978;6:141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M., Brown P. M., Juul S. M., Prestwich S. A., Sönksen P. H. Glucose turnover and metabolic and hormonal changes in ethanol-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 14;282(6267):849–853. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6267.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. K., Hassanein R. S., Kodanaz A., Meek J. C. Circadian rhythms of plasma cortisol in migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Aug;42(8):741–748. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.8.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


