Abstract
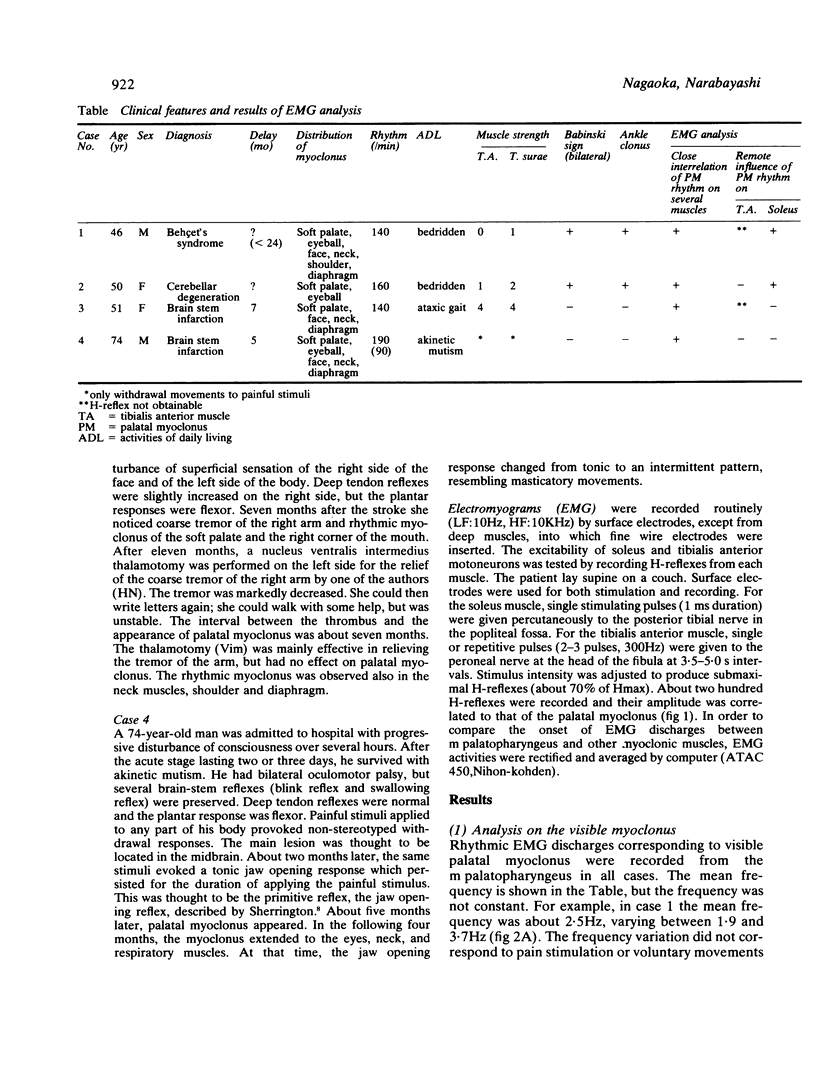
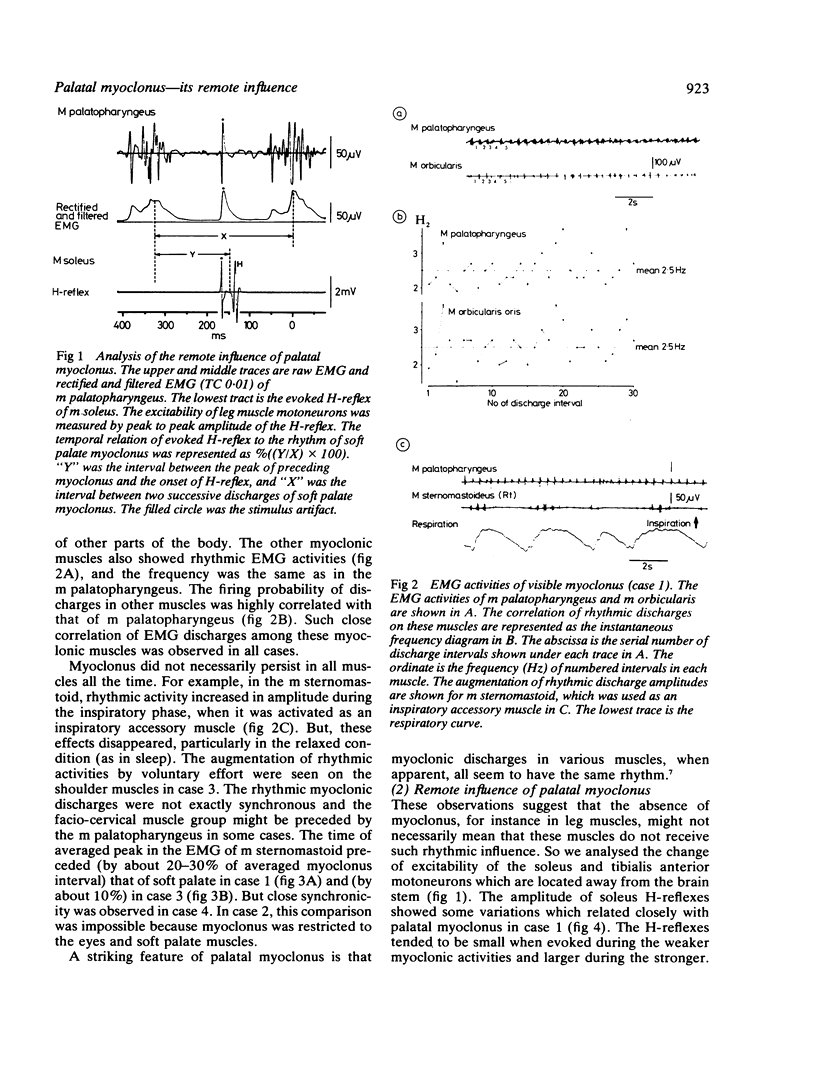
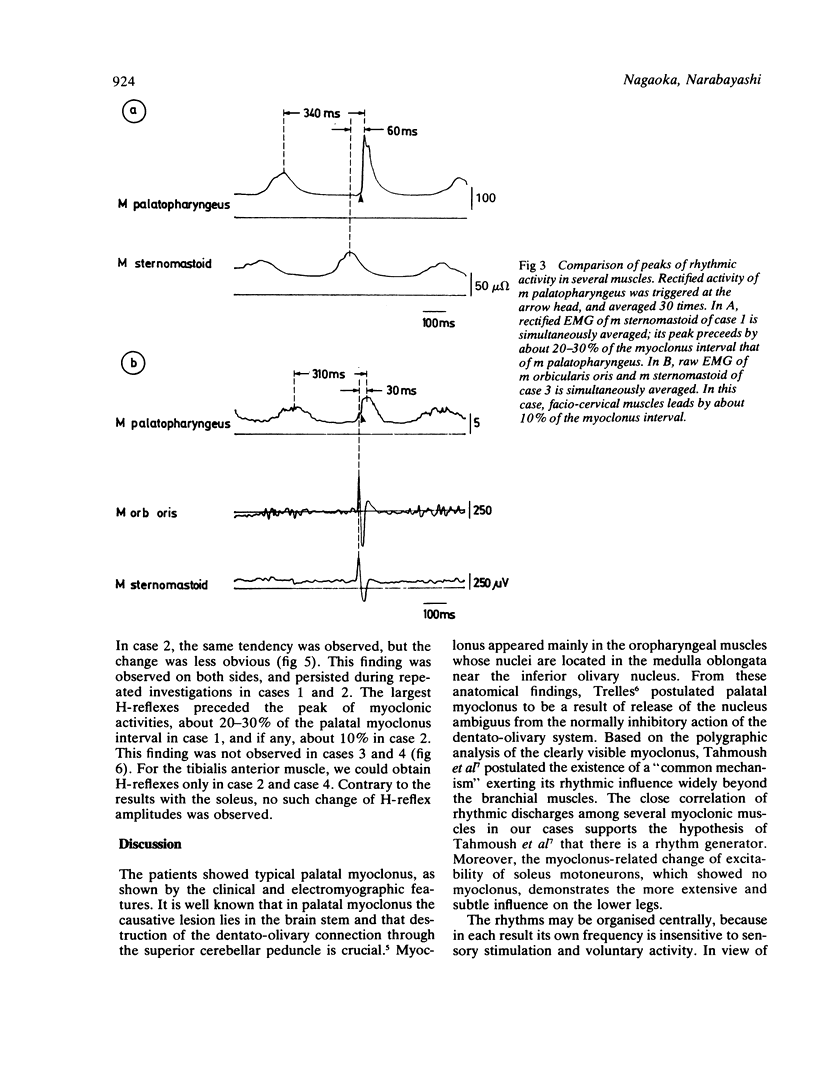
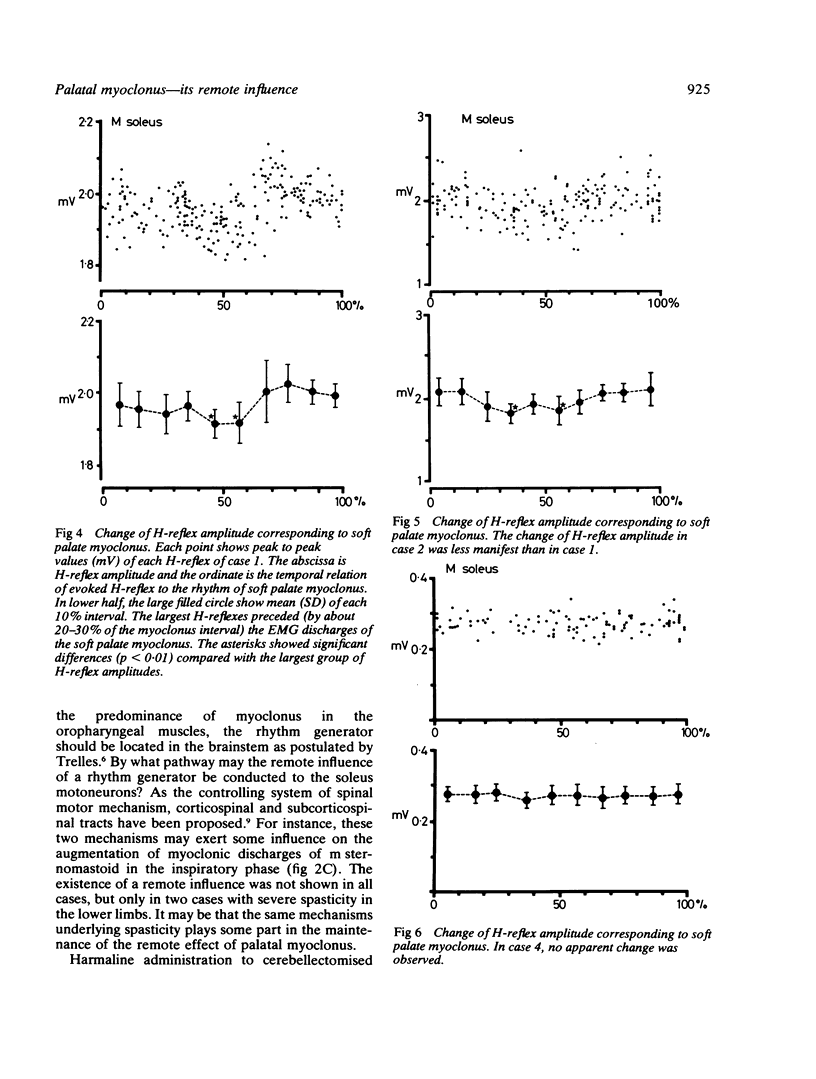
Four patients with palatal myoclonus were examined electromyographically. Surface EMG was recorded simultaneously from several myoclonic muscles and the correlation between their rhythmic discharges was shown. The possible existence of a remote influence of palatal myoclonus was tested by recording soleus and anterior tibial H-reflexes and seeking a correlation of their amplitudes with the rhythm of palatal myoclonus. Two cases, both with additional severe spasticity in the legs, showed rhythmic variation of the soleus H-reflex amplitude corresponding with that of their palatal myoclonus. This suggests that the neural mechanism generating the visible myoclonus has much more extensive effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lapresle J. Rhythmic palatal myoclonus and the dentato-olivary pathway. J Neurol. 1979 Jan 5;220(4):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00314146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. G., Kuypers H. G. The functional organization of the motor system in the monkey. I. The effects of bilateral pyramidal lesions. Brain. 1968 Mar;91(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondot P., Ben Hamida M. Myoclonies du voile et myoclonies squelettiques. Etude clinique et anatomique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1968 Jul;119(1):59–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahmoush A. J., Brooks J. E., Keltner J. L. Palatal myoclonus associated with abnormal ocular and extremity movements. A polygraphic study. Arch Neurol. 1972 Nov;27(5):431–440. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490170063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelles J. O. Les myoclonies vélo-palatines. Considerátions anatomiques et physiopathologiques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1968 Jul;119(1):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



