Abstract
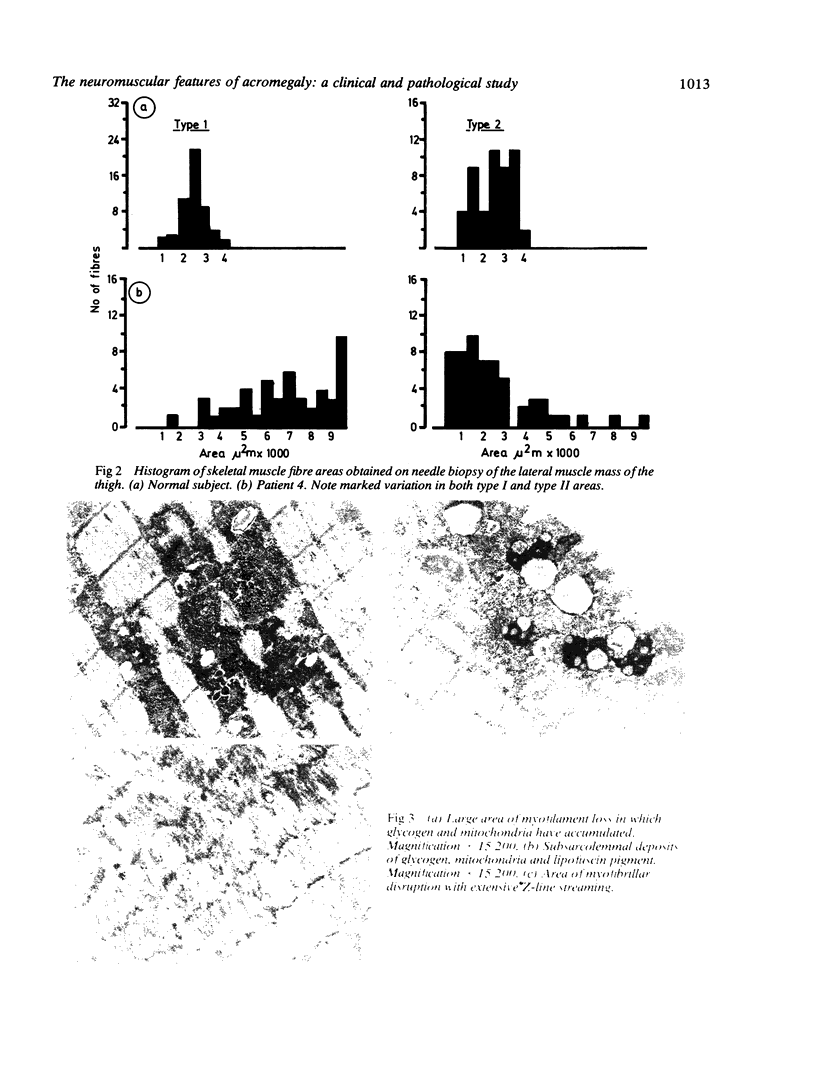
A study of the neuromuscular features of acromegaly was performed in six patients. Clinical assessment was supplemented by quadriceps force measurements, plasma creatine kinase (CK) activities, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies. Muscle mass was measured by urinary creatinine/height indices (CHI) and cross sectional area (CSA) of thighs and calves on computed tomography. Quadriceps force/unit cross sectional area was derived. Needle biopsies of vastus lateralis were studied by histochemical and ultrastructural methods. Mean fibre area (MFA) and fibre type proportions were measured. Most of the subjects studied had muscle pain and proximal muscle weakness confirmed by quadriceps force measurements. This occurred in the absence of muscle wasting, as shown by cross sectional area measurements and normal or raised creatinine/height indices. "Myopathic" features were demonstrated by needle biopsy in half the patients and occasionally by electromyography and raised plasma creatine kinase activity. Abnormalities on needle biopsy included variation in fibre size, type 2 fibre atrophy and large type 1 MFA relative to type 2 MFA. Electronmicroscopy showed the non-specific findings of increased glycogen accumulation, excess lipofuscin pigment and myofilament loss.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L., Sherman M., Scrimshaw N. S. Therapeutic index of nutritional depletion in hospitalized patients. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Oct;141(4):512–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek D. B., Graystone J. E. Insulin and growth hormone: regulators of growth with particular reference to muscle. Kidney Int. 1978 Oct;14(4):317–322. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Gagrat B. M., Wadia N. H., Desai M., Bharucha E. P. Nature of muscular change in osteomalacia: light- and electron-microscope observations. J Pathol. 1975 Dec;117(4):211–228. doi: 10.1002/path.1711170404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Young A., Hosking G. P., Jones D. A. Human skeletal muscle function: description of tests and normal values. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Mar;52(3):283–290. doi: 10.1042/cs0520283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R., Young A., Wiles M. Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in the diagnosis of myopathy and the clinical study of muscle function and repair. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 31;302(5):261–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001313020504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gondring W. H. The carpal tunnel syndrome and acromegaly. J Okla State Med Assoc. 1966 Jun;59(6):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaleeli A. A., Edwards R. H., Gohil K., McPhail G., Rennie M. J., Round J., Ross E. J. Corticosteroid myopathy: a clinical and pathological study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1983 Feb;18(2):155–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1983.tb03198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaleeli A. A., Gohil K., McPhail G., Round J. M., Edwards R. H. Muscle morphology and metabolism in hypothyroid myopathy: effects of treatment. J Clin Pathol. 1983 May;36(5):519–526. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein I., Parker M., Shebert R., Ayyar D. R., Levey G. S. Hypothyroidism presenting as muscle stiffness and pseudohypertrophy: Hoffmann's syndrome. Am J Med. 1981 Apr;70(4):891–894. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. D. Neuromuscular involvement in pituitary gigantism. Br Med J. 1972 May 27;2(5812):499–500. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5812.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L., Barwich D. D., Hall R. Myopathy in acromegaly. Lancet. 1970 Oct 31;2(7679):907–909. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L. Pathological changes in skeletal muscle in acromegaly. Acta Neuropathol. 1973;24(4):273–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00685584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeran R. O., Slavin G., Andrews T. M., Ward P., Mair W. G. Muscle fibre type changes in hypothyroid myopathy. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Aug;28(8):659–663. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.8.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeran R. O., Slavin G., Ward P., Paul E., Mair W. G. Hypothyroid myopathy. A clinical and pathologaical study. J Pathol. 1980 Sep;132(1):35–54. doi: 10.1002/path.1711320105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgar J., Johnson M. A., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on fibre size in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jul;19(3):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Round J. M., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. A flexible microprocessor system for the measurement of cell size. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;35(6):620–624. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.6.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzankoff S. P., Norris A. H. Effect of muscle mass decrease on age-related BMR changes. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Dec;43(6):1001–1006. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.6.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignos P. J., Jr, Greene R. Oxidative respiration of skeletal muscle in experimental corticosteroid myopathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viteri F. E., Alvarado J. The creatinine height index: its use in the estimation of the degree of protein depletion and repletion in protein calorie malnourished children. Pediatrics. 1970 Nov;46(5):696–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Young A., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Muscle relaxation rate, fibre-type composition and energy turnover in hyper- and hypo-thyroid patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Oct;57(4):375–384. doi: 10.1042/cs0570375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]