Abstract
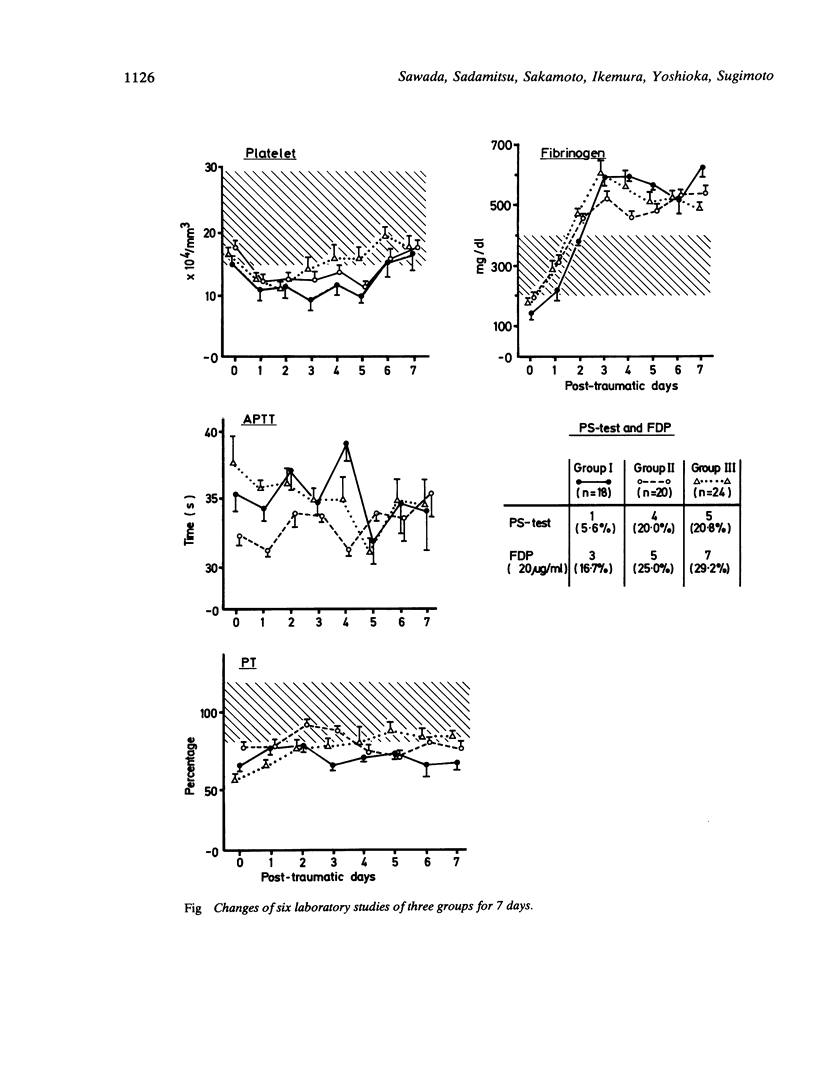
The relationship between delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma and disseminated intravascular coagulation was investigated. Eighteen patients with delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma were selected as the study subjects from 268 consecutive patients with head trauma and compared with another two groups of patients with closed head injury (20 cases) and with multiple injuries (24 cases). All cases had six laboratory studies for disseminated intravascular coagulation for 7 days. The results revealed no different clotting abnormalities among the three groups. From the laboratory point of view, it could be concluded there was no essential relationship between disseminated intravascular coagulation and the appearance of delayed traumatic intracerebral haematoma.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrup T. Assay and content of tissue thromboplastin in different organs. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Nov 15;14(3-4):401–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. R. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1980 Jun;146(6):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strinchini A., Baudo F., Nosari A. M., Panzacchi G., de Cataldo F. Letter: Defibrination and head injury. Lancet. 1974 Oct 19;2(7886):957–957. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sande J. J., Veltkamp J. J., Boekhout-Mussert R. J., Bouwhuis-Hoogerwerf M. L. Head injury and coagulation disorders. J Neurosurg. 1978 Sep;49(3):357–365. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.49.3.0357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


