Abstract
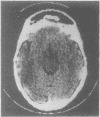
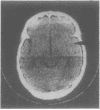
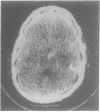
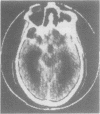
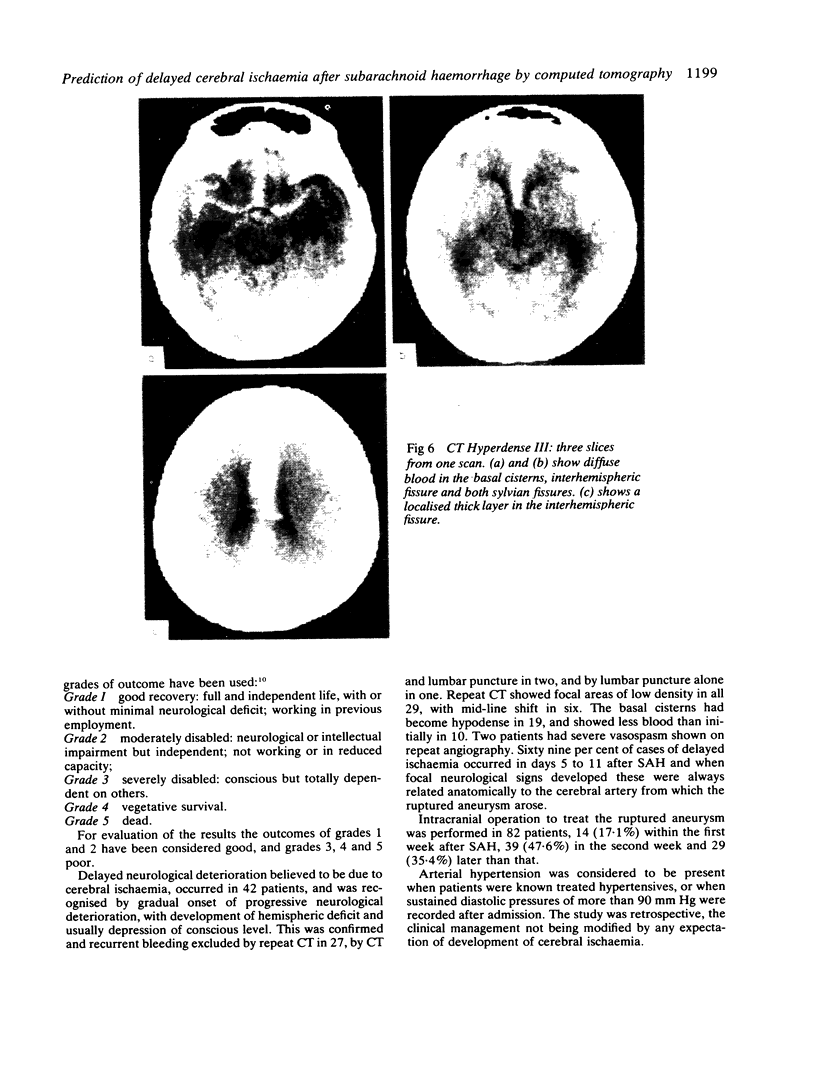
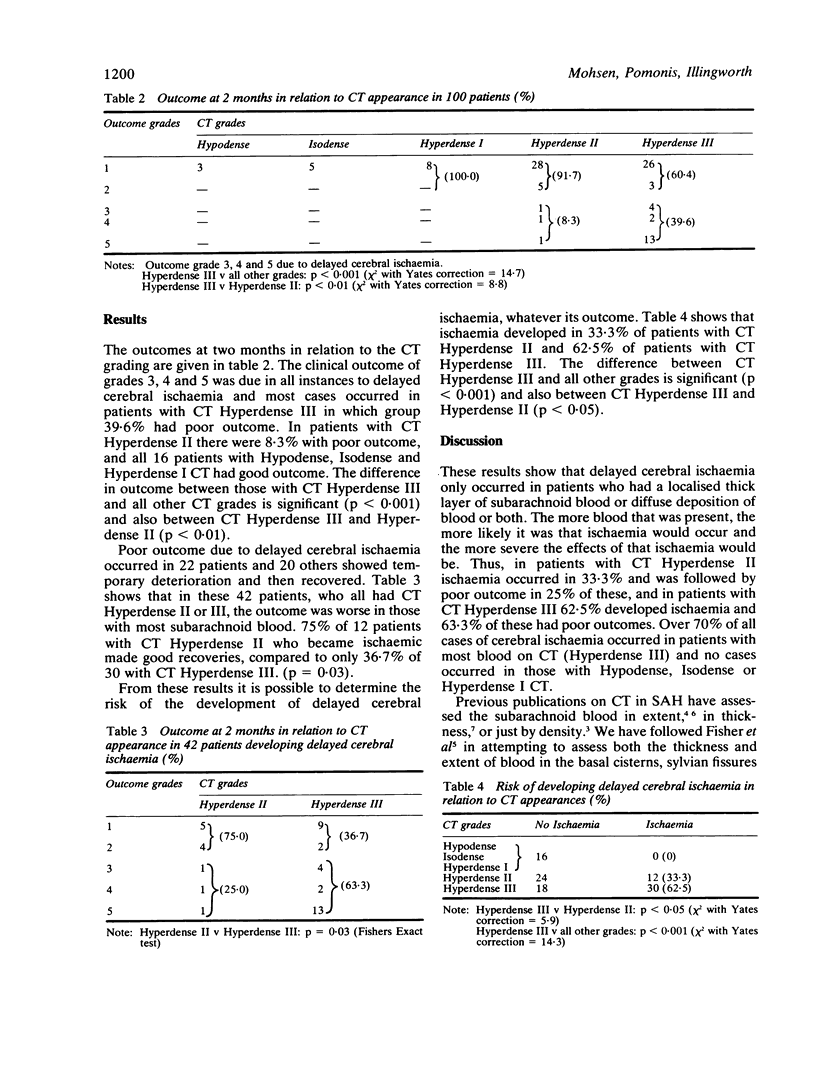
Computed tomography was performed in 100 patients within 4 days of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. The CT appearances have been divided into five grades by the thickness and extent of the subarachnoid blood. Delayed cerebral ischaemia occurred in 62.5% of patients with most blood on CT, in 33.3% of those in the next grade and in none of the other grades with less amounts of blood. The outcome from delayed ischaemia was worse in those with most CT blood.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameen A. A., Illingworth R. Anti-fibrinolytic treatment in the pre-operative management of subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by ruptured intracranial aneurysm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Mar;44(3):220–226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell B. A., Kendall B. E., Symon L. Computed tomography in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Jun;43(6):522–524. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.6.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M., Kistler J. P., Davis J. M. Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery. 1980 Jan;6(1):1–9. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198001000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet. 1975 Mar 1;1(7905):480–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice-Williams R. S. Ruptured intracranial aneurysms: has the incidence of early rebleeding been over-estimated? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;45(9):774–779. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.9.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka H. Report on the cooperative study of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Section VII. I. Evaluation of the conservative management of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1966 Nov;25(5):574–592. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.5.0574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]