Abstract
There are essentially no objective neuropathological data on brain atrophy in chronic alcoholic patients despite numerous neuroradiological studies which show a high incidence of shrinkage or atrophy. Therefore measurements were made of the intracranial volume (ICV) and brain volume (BV) in a necropsy study of 25 chronic alcoholic patients and 44 controls. The pericerebral space (PICS) was calculated according to the formula (formula; see text) The PICS will increase in patients with brain atrophy since the ICV remains constant throughout life. The mean PICS value was 8.3% in controls, 11.3% in the alcoholic group, 14.7% in alcoholics with superimposed Wernicke's encephalopathy (thiamine deficiency) and 16.2% in those alcoholics with associated liver disease. Thus there was a statistically significant loss of brain tissue in chronic alcoholic patients which appeared to be more severe in those with associated nutritional vitamin deficiencies or alcoholic liver disease.
Full text
PDF
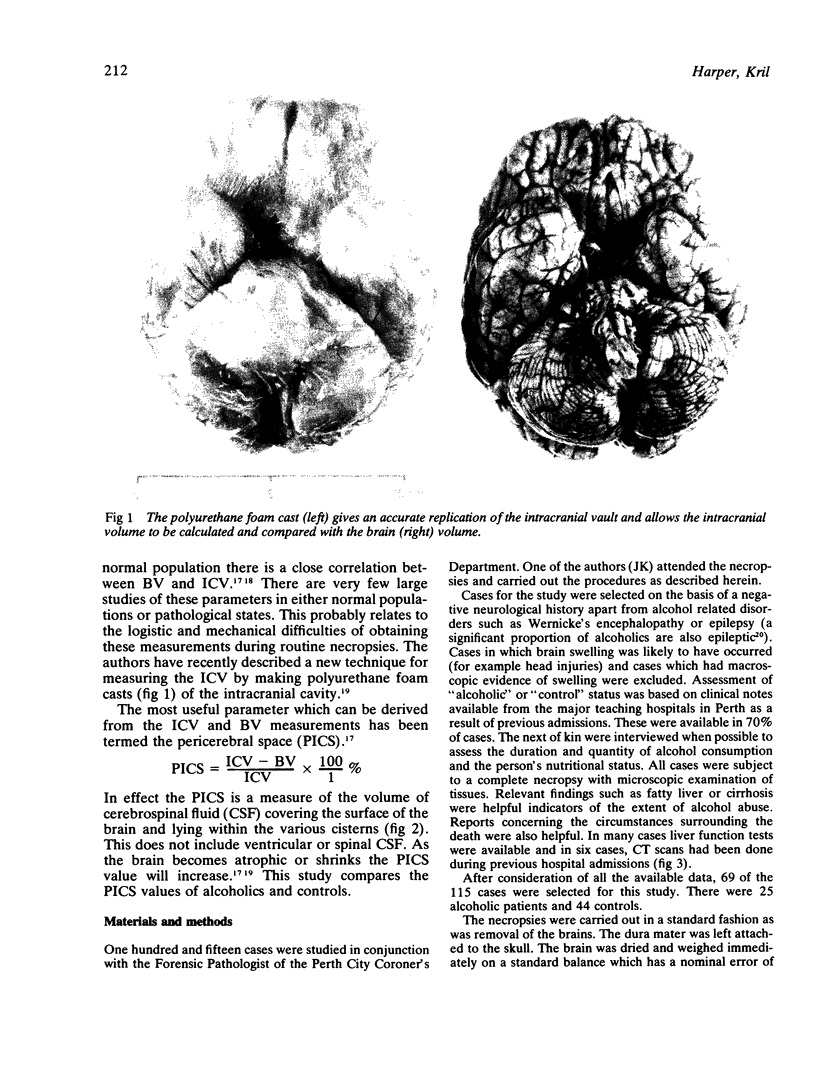
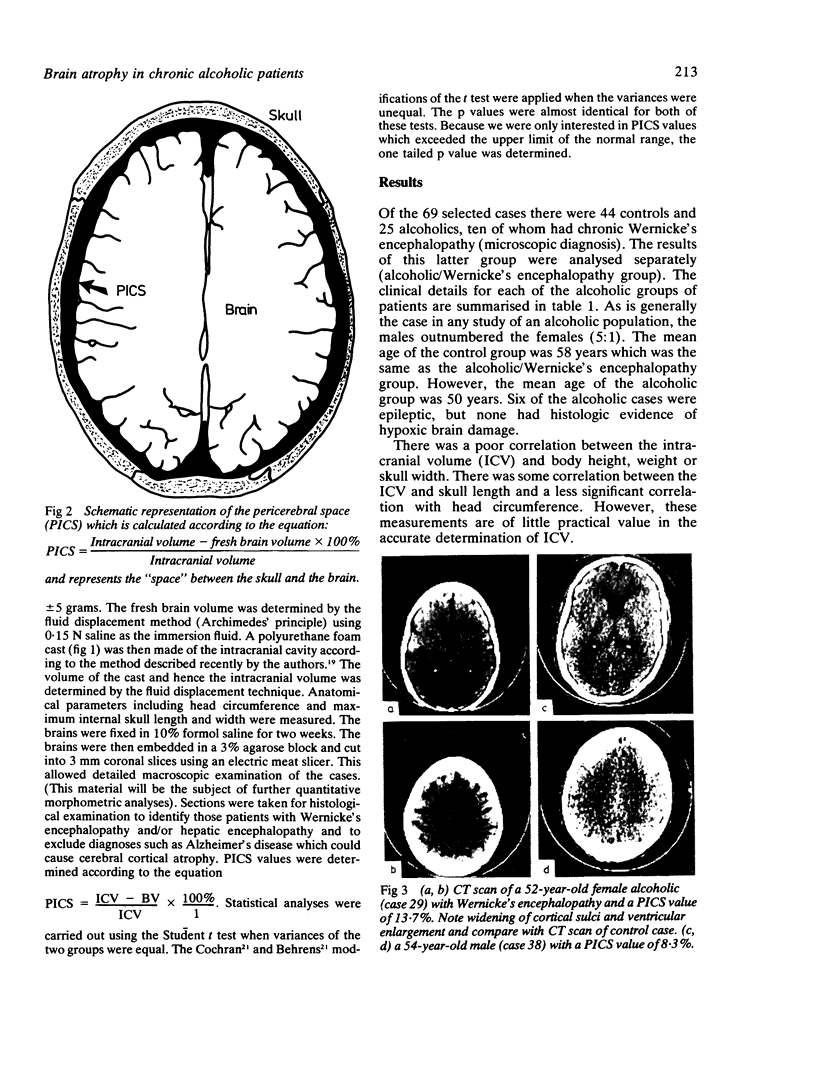
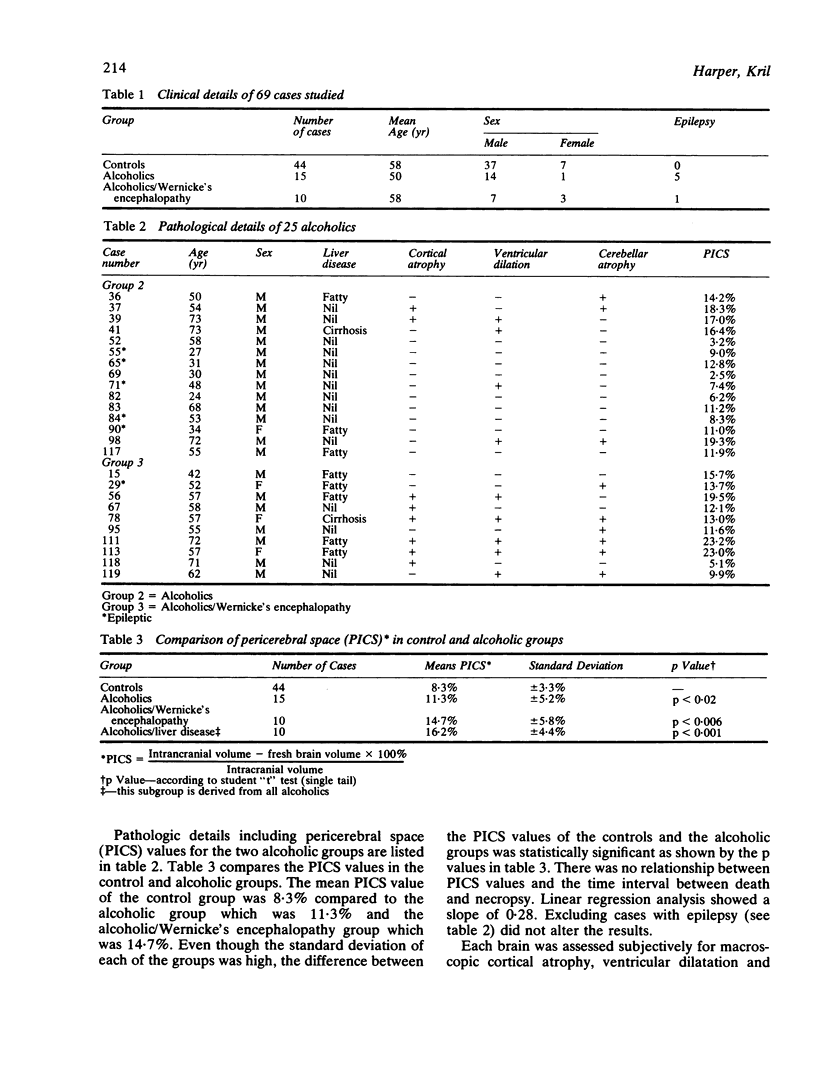



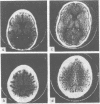
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker W., Aps E. J., Majumdar S. K., Shaw G. K., Thomson A. D. The relationship between brain and liver damage in chronic alcoholic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Nov;45(11):984–987. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.11.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C., Perrett L. Brain damage due to alcohol consumption: an air-encephalographic, psychometric and electroencephalographic study. Br J Addict Alcohol Other Drugs. 1971 Nov;66(3):170–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1971.tb02382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cala L. A., Mastaglia F. L. Computerized axial tomography in the detection of brain damage: 1. Alcohol, nutritional deficiency and drugs of addiction. Med J Aust. 1980 Aug 23;2(4):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlen P. L., Wortzman G., Holgate R. C., Wilkinson D. A., Rankin J. C. Reversible cerebral atrophy in recently abstinent chronic alcoholics measured by computed tomography scans. Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.653357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekaban A. S. Changes in brain weights during the span of human life: relation of brain weights to body heights and body weights. Ann Neurol. 1978 Oct;4(4):345–356. doi: 10.1002/ana.410040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFF H., SEITELBERGER F. Die Alters veränderungen des menschlichen Gehirns. Z Alternsforsch. 1957 Jul;10(4):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C., Kril J., Raven D., Jones N. Intracranial cavity volumes: a new method and its potential applications. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1984 Jan-Feb;10(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1984.tb00337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C. The incidence of Wernicke's encephalopathy in Australia--a neuropathological study of 131 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jul;46(7):593–598. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.7.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard B. M., Anderson J. M. Age, senile dementia and ventricular enlargement. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Jul;44(7):631–635. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.7.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Møller L., Hardt F., Haubek A., Jensen E. Alcohol-induced brain damage and liver damage in young males. Lancet. 1979 Oct 13;2(8146):759–761. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lishman W. A. Cerebral disorder in alcoholism: syndromes of impairment. Brain. 1981 Mar;104(Pt 1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron M. A. The alcoholic brain: CT scan and psychological findings. Psychol Med Monogr Suppl. 1983;3:1–33. doi: 10.1017/s0264180100000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salokangas R. K. Hospital and outpatient care for psychotic patients during the last three decades. Subsequent hospital and outpatient treatment of psychotic patients hospitalized for the first time in 1949--50, 1959--60 or 1969--70. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1980 Jul;62(1):47–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1980.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar M., McCormick W. F. Decrease in ventricular and sulcal size after death. Radiology. 1978 May;127(2):409–411. doi: 10.1148/127.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarter R. E. An analysis of cognitive deficits in chronic alcoholics. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1973 Aug;157(2):138–147. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197308000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D. Alcohol-related structural brain changes. Br Med Bull. 1982 Jan;38(1):87–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torvik A., Lindboe C. F., Rogde S. Brain lesions in alcoholics. A neuropathological study with clinical correlations. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):233–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., Carlen P. L. Relationship of neuropsychological test performance to brain morphology in amnesic and non-amnesic chronic alcoholics. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1980;286:89–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1980.tb08057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P., Kornaczewski A., Rankin J. G., Santamaria J. N. Physical disease in alcoholism. Initial survey of 1,000 patients. Med J Aust. 1971 Jun 5;1(23):1217–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]