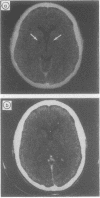
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BICKFORD R. G., BUTT H. R. Hepatic coma: the electroencephalographic pattern. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):790–799. doi: 10.1172/JCI103134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY J. M., WATSON C. W., ADAMS R. D. Significance of the electroencephalographic changes in hepatic coma. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1950;51:161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa K., Kugoh T., Otsuki S., Shinagawa S., Urita M. [A case of the hepatic encephalopathy with unusual episodes of the triphasic spike-wave stupor (author's transl)]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1977 Jun;17(6):391–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplane D., Widlocher D., Pillon B., Baulac M., Binoux F. Comportement compulsif d'allure obsessionnelle par nécrose circonscrite bilatérale pallido-striatale. Encéphalopathie par piqûre de guêpe. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1981;137(4):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardizzi L. R. Computerized tomographic correlate of carbon monoxide poisoning. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jan;36(1):38–39. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500370068016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer E., Khalifeh R. Petit mal status ("spike-wave stupor"). An electro-clinical appraisal. Epilepsia. 1965 Sep;6(3):250–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1965.tb03793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura N., Ikeda H., Kumashiro H., Hosokawa K., Booker H. E. Spike-wave stupor. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1970;24(1):37–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1970.tb01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSER C. M. Electroencephalographic changes and hyperammonemia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Feb;10(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERLOCK S. Hepatic coma. Practitioner. 1963 Jul;191:18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Sakamoto T., Nishide K., Sadamitsu D., Fusamoto H., Yoshioka T., Sugimoto T., Onishi S. Correlation of pathological findings with computed tomographic findings after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 26;308(21):1296–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Takahashi M., Ohashi N., Fusamoto H., Maemura K., Kobayashi H., Yoshioka T., Sugimoto T. Computerised tomography as an indication of long-term outcome after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):783–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Bhagat S. The effect of extraction of the intrafascicular contents of peripheral nerve trunks on perineurial structure. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Aug 7;43(1-2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00685008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]