Abstract
Twenty-five patients with late-onset Huntington's disease were studied; motor impairment appeared at age 50 years or later. The average age at onset of chorea was 57.5 years, with an average age at diagnosis of 63.1 years. Approximately 25% of persons affected by Huntington's disease exhibit late onset. A preponderance of maternal transmission was noted in late-onset Huntington's disease. The clinical features resembled those of mid-life onset Huntington's disease but progressed more slowly. Neuropathological evaluation of two cases reveal less severe neuronal atrophy than for mid-life onset disease.
Full text
PDF

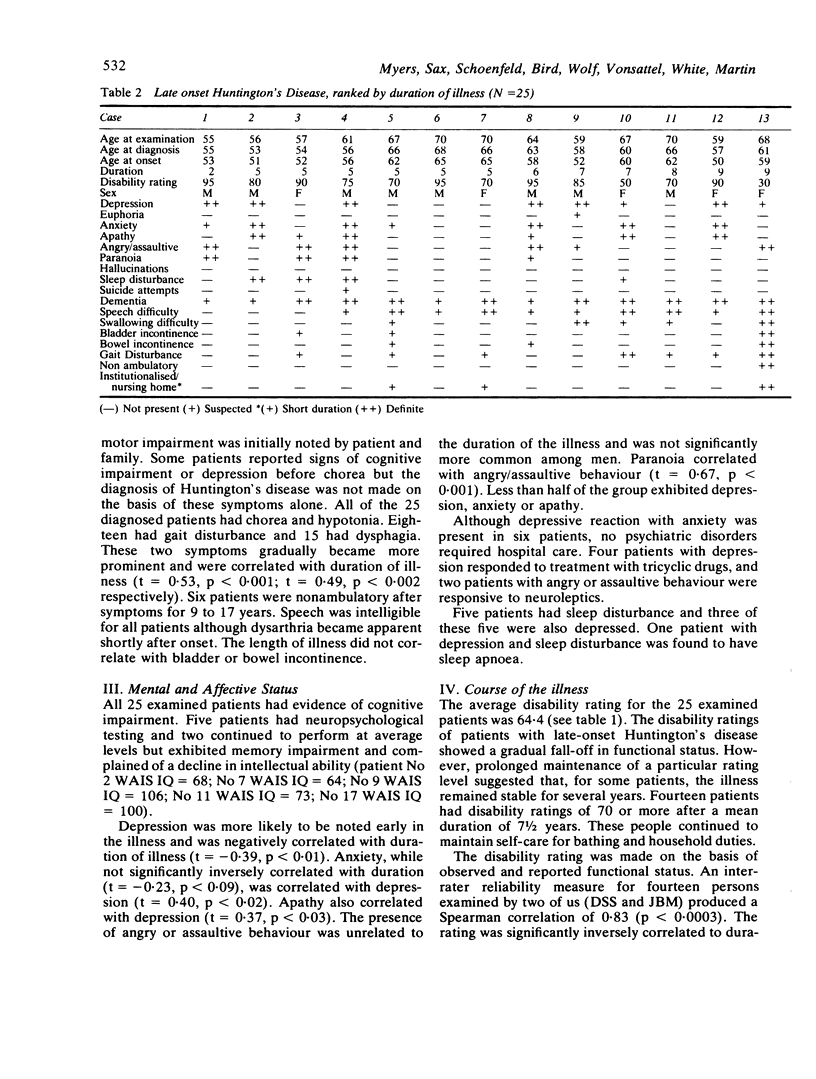
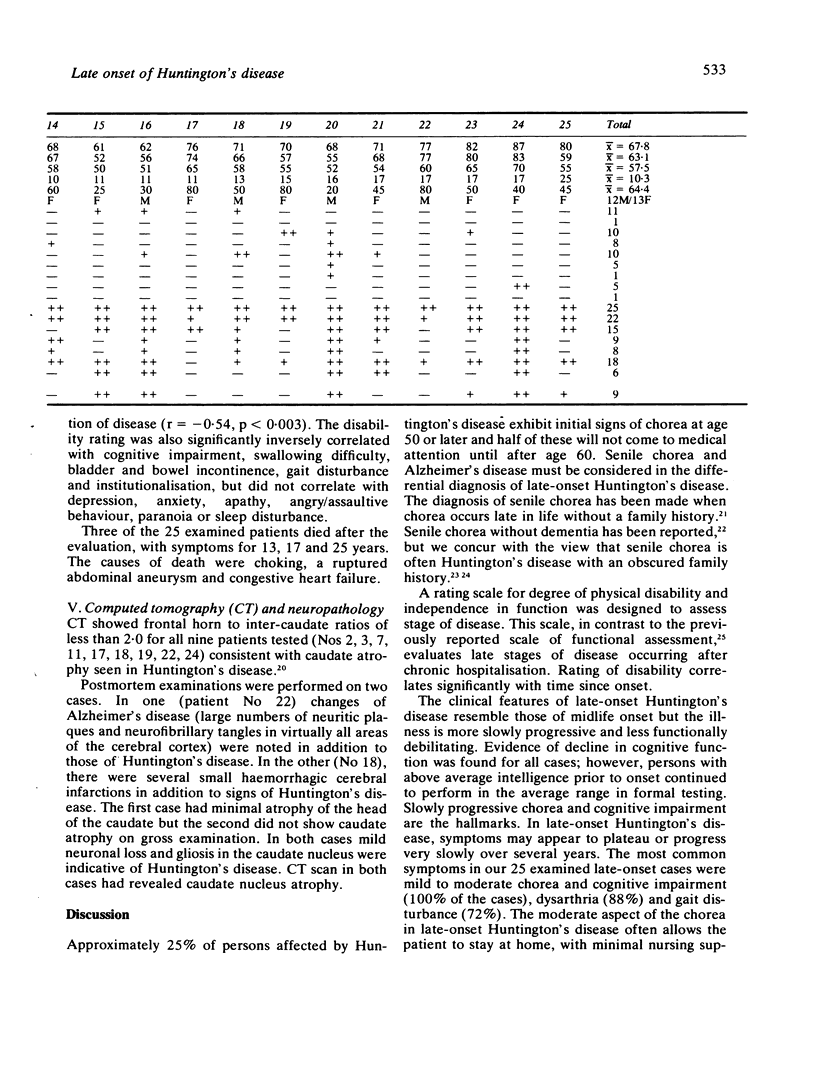

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTENBENDER J. B., QUADFASEL F. A. Rigid and akinetic forms of Huntington's chorea. Arch Neurol. 1962 Oct;7:275–288. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210040027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird E. D., Caro A. J., Pilling J. B. A sex related factor in the inheritance of Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):255–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers R. K., Gilles F. H., Fung C. Huntington's disease in children. Neuropathologic study of four cases. Neurology. 1973 Jun;23(6):561–569. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.6.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein S. E., Franz M. L., Jensen B. A., Chase G. A., Folstein M. F. Conduct disorder and affective disorder among the offspring of patients with Huntington's disease. Psychol Med. 1983 Feb;13(1):45–52. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700050054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Te-Juatco L. Association between age of onset and parental inheritance in Huntington chorea. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):289–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., MacGregor J. M., Saffer D. S., Beighton P. H. The high frequency of juvenile Huntington's chorea in South Africa. J Med Genet. 1982 Apr;19(2):94–97. doi: 10.1136/jmg.19.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVIS G. A. HUNTINGTON'S CHOREA IN CHILDHOOD. Arch Neurol. 1963 Sep;9:244–257. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460090050005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Goldman D., Bird E. D., Sax D. S., Merril C. R., Schoenfeld M., Wolf P. A. Maternal transmission in Huntington's disease. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):208–210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Madden J. J., Teague J. L., Falek A. Factors related to onset age of Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):481–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED T. E., CHANDLER J. H. Huntington's chorea in Michigan. I. Demography and genetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1958 Jun;10(2):201–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sax D. S., O'Donnell B., Butters N., Menzer L., Montgomery K., Kayne H. L. Computed tomographic, neurologic, and neuropsychological correlates of Huntington's disease. Int J Neurosci. 1983;18(1-2):21–36. doi: 10.3109/00207458308985874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulson I. Huntington disease: functional capacities in patients treated with neuroleptic and antidepressant drugs. Neurology. 1981 Oct;31(10):1333–1335. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.10.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsky L., Myers R. H., Walshe T. M. Huntington's disease in monozygotic twins reared apart. J Med Genet. 1983 Dec;20(6):408–411. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.6.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENDT G. G., LANDZETTEL H. J., UNTERREINER I. Das Erkrankungsalter bei der Huntingtonschen Chorea. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1959;9(1):18–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


