Abstract
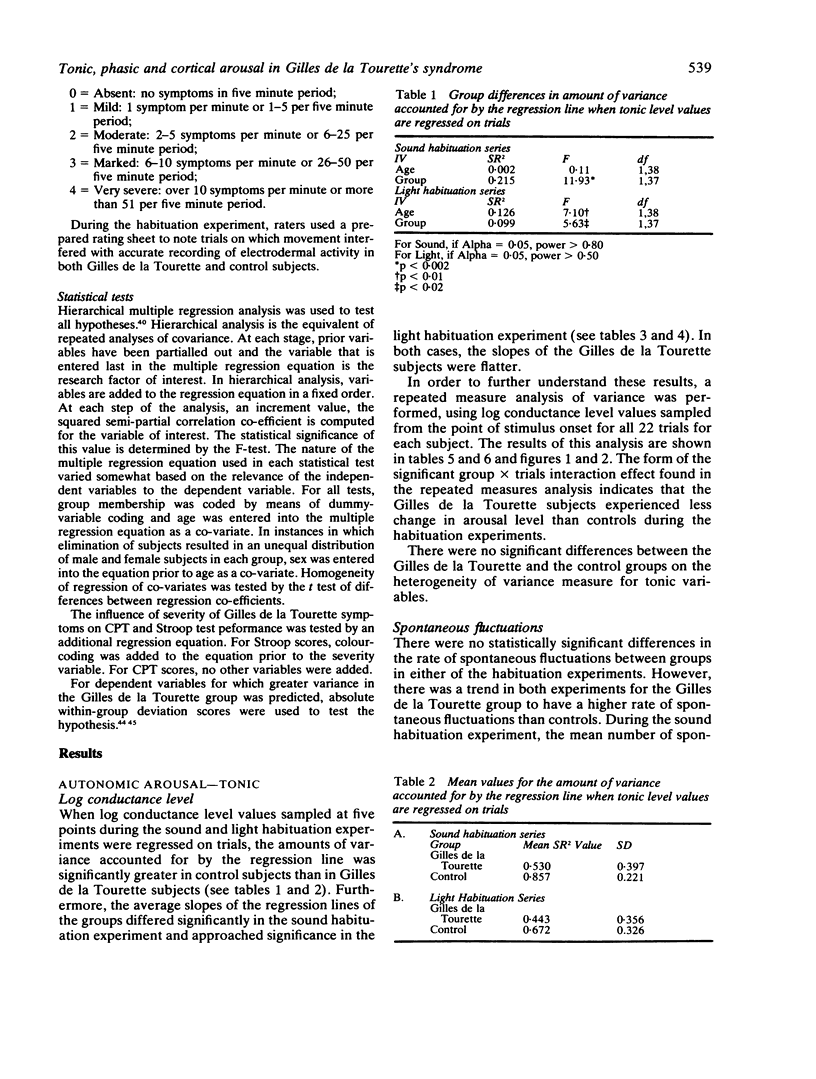
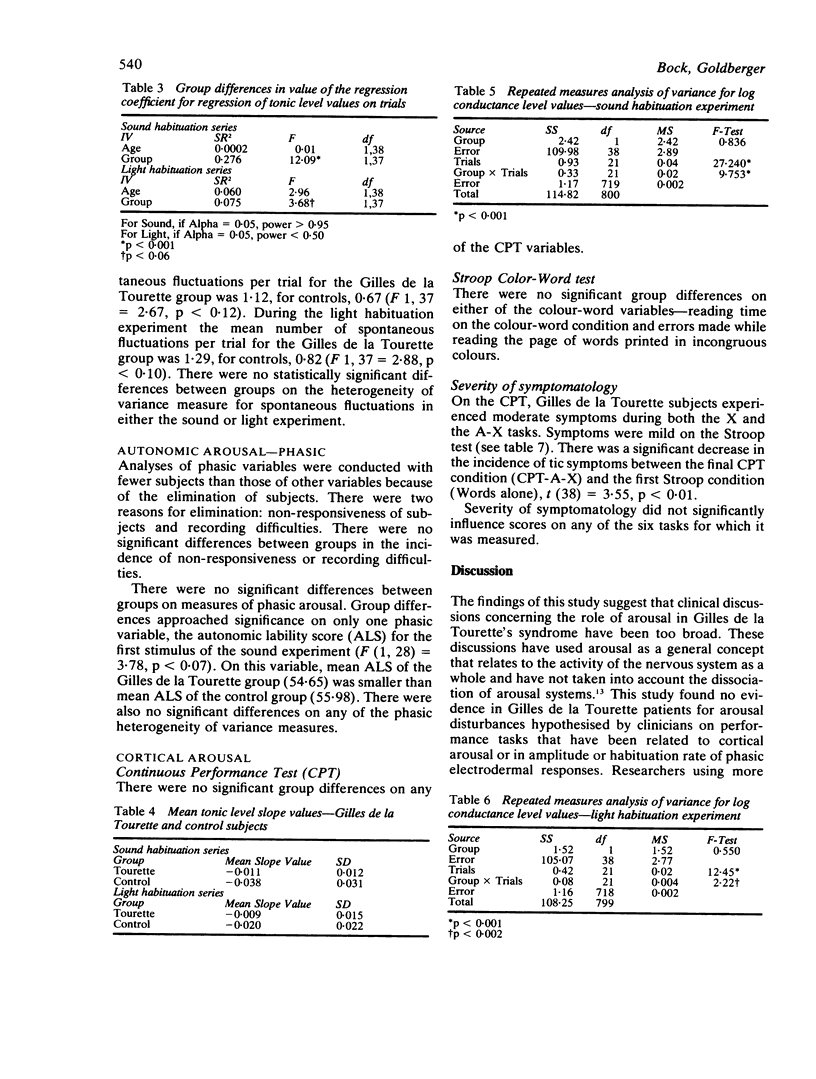
This study explored the hypothesis that Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome involves a disturbance in arousal modulation. The experimental group consisted of 20 unmedicated subjects with the Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome, and the control group of 20 subjects with chronic medical illnesses (haemophilia, von Willebrandt's disease and diabetes). There were differences between groups in the manner in which log conductance level changed over time during sound and light habituation experiments involving mild levels of stimulation with the Gilles de la Tourette group showing less change in arousal level over trials than the control group. No group differences were found in measures of phasic arousal, rate of spontaneous fluctuations and performance on two tasks that have been related to cortical arousal. It is suggested that the slower change in log conductance level in the Gilles de la Tourette group during the sound and light habituation experiments indicates that reticular activity is more persistent in these patients.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK L. H., BRANSOME E. D., Jr, MIRSKY A. F., ROSVOLD H. E., SARASON I. A continuous performance test of brain damage. J Consult Psychol. 1956 Oct;20(5):343–350. doi: 10.1037/h0043220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernal M. E., Miller W. H. Electrodermal and cardiac responses of schizophrenic children to sensory stimuli. Psychophysiology. 1970 Sep;7(2):155–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1970.tb02222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull R., Gale A. Does the law of initial value apply to the galvanic skin response? Biol Psychol. 1974;1(3):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0301-0511(74)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLAWAY E., 3rd The influence of amobarbital (amylobarbitone) and methamphetamine on the focus of attention. J Ment Sci. 1959 Apr;105(439):382–392. doi: 10.1192/bjp.105.439.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. F. Behaviour therapy of Gilles de la Tourette's syndome. Br J Psychiatry. 1966 Aug;112(489):771–778. doi: 10.1192/bjp.112.489.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. J., Shaywitz B. A., Young J. G., Carbonari C. M., Nathanson J. A., Lieberman D., Bowers M. B., Jr, Maas J. W. Central biogenic amine metabolism in children with the syndrome of chronic multiple tics of Gilles de la Tourette: norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1979 Spring;18(2):320–341. doi: 10.1016/s0002-7138(09)61046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley L. R., Adams R. G. Effect of noise on the Stroop Test. J Exp Psychol. 1974 Jan;102(1):62–66. doi: 10.1037/h0035695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN G. S. SEMANTIC POWER MEASURED THROUGH THE INTERFERENCE OF WORDS WITH COLOR-NAMING. Am J Psychol. 1964 Dec;77:576–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornetsky C., Orzack M. H. Physiological and behavioral correlates of attention dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. J Psychiatr Res. 1978;14(1-4):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(78)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADER M. H., WING L. HABITUATION OF THE PSYCHO-GALVANIC REFLEX IN PATIENTS WITH ANXIETY STATES AND IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Jun;27:210–218. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY E. Z., THALER V. H., RUFF G. E. New technique for recording skin resistance changes. Science. 1958 Jul 4;128(3314):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3314.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykken D. T., Venables P. H. Direct measurement of skin conductance: a proposal for standardization. Psychophysiology. 1971 Sep;8(5):656–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1971.tb00501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY A. F., KORNETSKY C. ON THE DISSIMILAR EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON THE DIGIT SYMBOL SUBSTITUTION AND CONTINOUS PERFORMANCE TESTS. A REVIEW AND PRELIMINARY INTEGRATION OF BEHAVIORAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL EVIDENCE. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Feb 12;5:161–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00413239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson W. B., Caine E. D., Goyer P., Ebert M., Gillin J. C. Sleep in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Biol Psychiatry. 1980 Apr;15(2):339–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldofsky H., Tullis C., Lamon R. Multiple tic syndrome (Giles de la Tourette's syndrome). J Nerv Ment Dis. 1974 Oct;159(4):282–292. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197410000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nee L. E., Caine E. D., Polinsky R. J., Eldridge R., Ebert M. H. Gilles de la Tourette syndrome: clinical and family study of 50 cases. Ann Neurol. 1980 Jan;7(1):41–49. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orzack M. H., Kornetsky C. Attention dysfunction in chronic schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1966 Mar;14(3):323–326. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1966.01730090099015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. G., Mefferd R. B., Jr, Houck R. L. The interaction of extraversion and neuroticism in orienting response habituation. Psychophysiology. 1971 May;8(3):312–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1971.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpin G., Powell G. E. Effects of massed practice and cue-controlled relaxation on tic frequency in Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Behav Res Ther. 1984;22(2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(84)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlberg G. W., Kornetsky C. Sustained attention in remitted schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;28(4):533–537. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1973.01750340065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn T. P., Rosenthal D., Lawlor W. G. Electrodermal and heart rate orienting reactions in chronic schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 1968 Aug;6(2):117–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(68)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


