Abstract
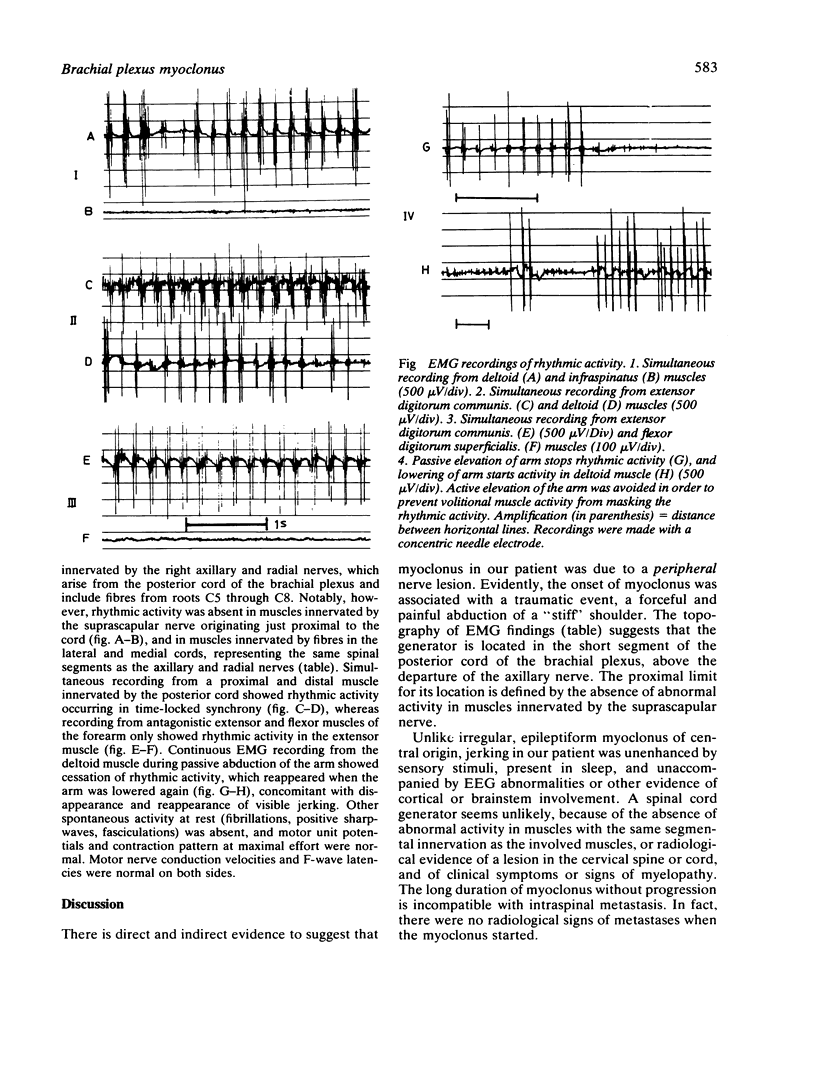
Rhythmic myoclonus in an arm began abruptly following an injury and persisted continuously for six years. Topographical EMG showed abnormal activity confined to muscles innervated by the axillary and radial nerves from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. Abduction of the arm above horizontal level stopped myoclonus and EMG discharges. EEG was normal. It is suggested that the myoclonus was caused by mechanical irritation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garcin R., Rondot P., Guiot G. Rhythmic myoclonus of the right arm as the presenting symptom of a cervical cord tumour. Brain. 1968 Mar;91(1):75–84. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn M. M., Cherington M. Spinal myoclonus. Neurology. 1977 Oct;27(10):942–946. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.10.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins A. P., Michael W. F. Spinal myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;37(10):1112–1115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.10.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Obeso J. A., Traub M. M., Rothwell J. C., Kranz H., La Cruz F. Muscle spasms associated with Sudeck's atrophy after injury. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jan 21;288(6412):173–176. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6412.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen V. K., Jannetta P. J. Pathophysiology of hemifacial spasm: III. Effects of facial nerve decompression. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):891–897. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen V. K. Pathophysiology of hemifacial spasm: I. Ephaptic transmission and ectopic excitation. Neurology. 1984 Apr;34(4):418–426. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILFVERSKIOLD B. P. Rhythmic myoclonus in three girls. Acta Neurol Scand. 1962;38:45–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said G., Bathien N. Myoclonies rythmées du quadriceps en relation avec un envahissement sarcomateux du nerf crural. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1977 Mar;133(3):191–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillane J. D., Nathan P. W., Kelly R. E., Marsden C. D. Painful legs and moving toes. Brain. 1971;94(3):541–556. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöhr M. Special types of spontaneous electrical activity in radiogenic nerve injuries. Muscle Nerve. 1982;5(9S):S78–S83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


