Abstract
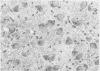
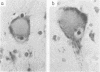
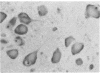
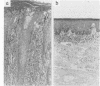
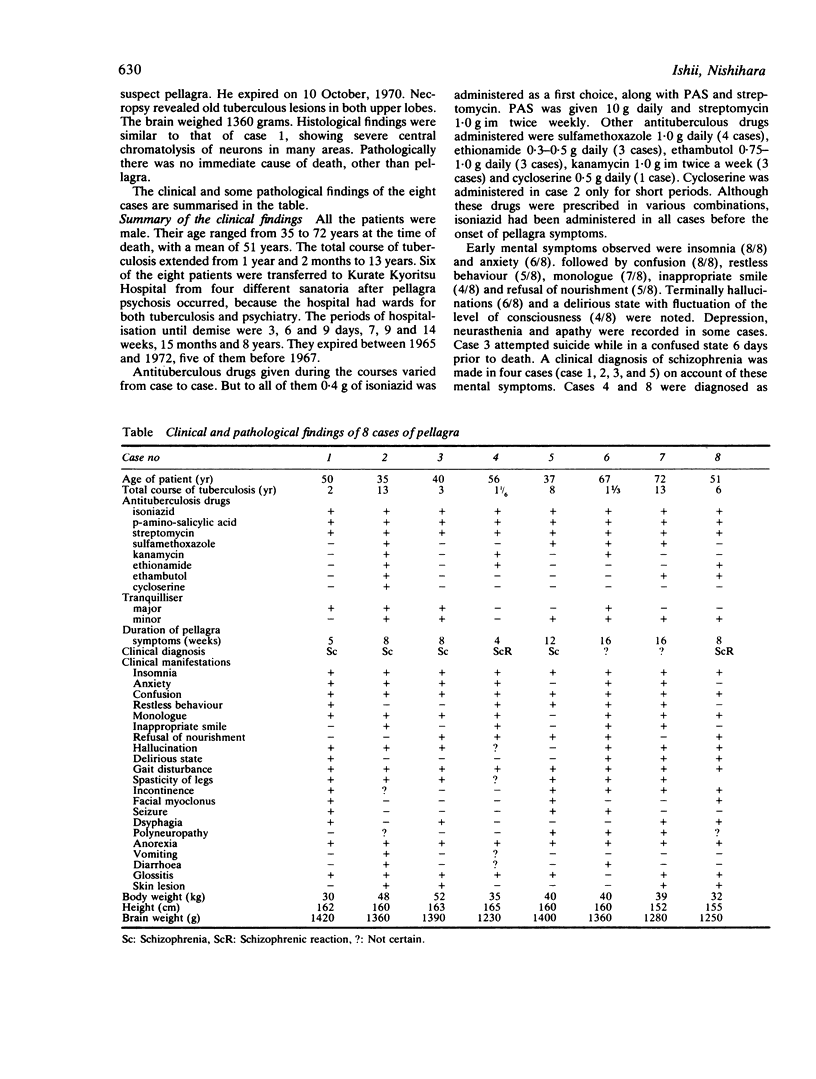
Eight cases of pellagra, diagnosed on the grounds of neuropathological findings and retrospective study of clinical data, were found among 106 necropsy cases of tuberculosis. Although these eight patients had shown various mental, neurological and gastrointestinal symptoms, as well as skin lesions, the diagnosis of pellagra had not been made clinically. In all the patients, pellagra symptoms appeared during isoniazid therapy. Death occurred 4 to 16 weeks later. Isoniazid inhibits the conversion of tryptophan to niacin and may induce pellagra, particularly in poorly nourished patients. Pellagra should be suspected whenever tuberculous patients under treatment with isoniazid develop mental, neurological or gastrointestinal symptoms, even in the absence of typical pellagra dermatitis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS B. G., DAVIES B. M. Neurological changes associated with P.A.S. and I.N.A.H. therapy. J Ment Sci. 1961 Sep;107:943–947. doi: 10.1192/bjp.107.450.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADAMS P., WHITE C. ISONIAZID-INDUCED ENCEPHALOPATHY. Lancet. 1965 Mar 27;1(7387):680–682. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIEHL J. P., VILTER R. W. Effects of isoniazid on pyridoxine metabolism. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Dec 25;156(17):1549–1552. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.02950170003002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E. The etiology of pellagra and its significance for modern medicine. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIWEL M., HARRISON R. J. Pellagra caused by isoniazid. Br Med J. 1956 Oct 13;2(4997):852–854. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4997.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARE E. H. Psychotic reactions due to anti-tuberculous drugs. Tubercle. 1958 Apr;39(2):90–95. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(58)80024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYNES W. S. Pellagra occurring in Africans under treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis. East Afr Med J. 1958 Apr;35(4):171–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER R. A. Confusional psychosis with residual organic cerebral impairment following isoniazid therapy. Lancet. 1952 Nov 15;2(6742):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)92203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Nishihara Y. Pellagra among chronic alcoholics: clinical and pathological study of 20 necropsy cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Mar;44(3):209–215. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. L. Psychosis due to isoniazid. Br Med J. 1957 Sep 28;2(5047):743–746. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5047.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES W. A., JONES G. P. Peripheral neuropathy due to isoniazid; report of two cases. Lancet. 1953 May 30;1(6770):1073–1074. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIGH D. Pellagra and the nutritional neuropathies: a neuropathological review. J Ment Sci. 1952 Jan;98(410):130–142. doi: 10.1192/bjp.98.410.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONNELL R. B., CHEETHAM H. D. Acute pellagra during isoniazid therapy. Lancet. 1952 Nov 15;2(6742):959–960. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)92202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. R., Pandey S. K., Rathi R. Psychiatric manifestation in pellagra. J Assoc Physicians India. 1972 Aug;20(8):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. R., Singh S. V., Jain I. L. Neurological manifestations in pellagra. J Assoc Physicians India. 1971 Jun;19(6):443–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar P. S. Pellagra in Gulgarga. J Indian Med Assoc. 1970 Jan 16;54(2):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]