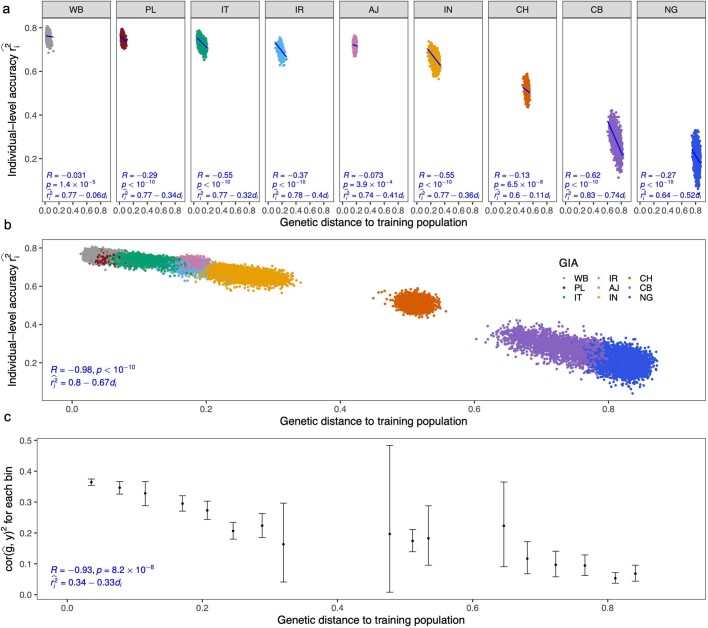
Extended Data Fig. 5. The individual-level accuracy for height PGS decreases across the genetic ancestry continuum in UKBB.
(a) Individual PGS accuracy decreases within subcontinental GIA clusters. Each dot represents a testing individual from UKBB. For each dot, the x-axis represents its distance from the training population on the genetic continuum; the y-axis represents its PGS accuracy. The color represents the GIA cluster. (b) Individual PGS accuracy decreases across the entire UKBB. (c) The population PGS accuracy decreases with the average GD in each bin. All UKBB individuals are divided into 20 equal-interval GD bins. The x-axis is the average GD within the bin; the y-axis is the squared correlation between PGS and phenotype for individuals in the bin. The dot and error bar show mean and 95% confidence interval from 1000 bootstrap samples. R and p refer to the correlation between GD and PGS accuracy and its significance from two-sided Pearson correlation tests without adjustment for multiple hypothesis testing. Any p-value below is shown as .