Abstract
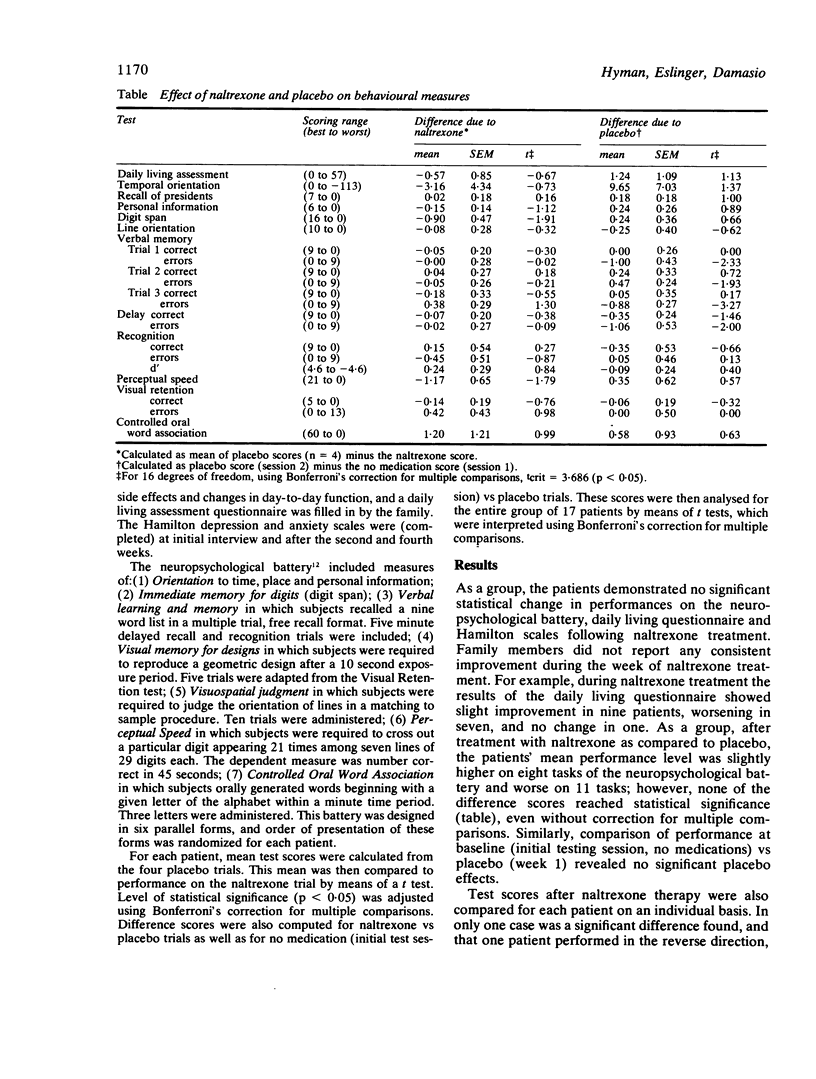
Some reports have suggested that naloxone, a short-acting opiate receptor blocker given intravenously, has a beneficial effect on the symptoms of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. We have performed a double-blind, crossover trial of naltrexone, an orally active, long acting opiate antagonist, in 17 Alzheimer-type dementia patients. None showed any improvement in assessments of day-to-day living skills or on a battery of neuropsychological tests. No side effects were noted. In the dosage used, naltrexone appears not to be useful in Alzheimer-type dementia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnsten A. F., Segal D. S., Neville H. J., Hillyard S. A., Janowsky D. S., Judd L. L., Bloom F. E. Naloxone augments electrophysiological signs of selective attention in man. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):725–727. doi: 10.1038/304725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley P., Feehally J., Doré P., Coupes B., Short C. D., Pumphrey R. S., Mallick N. P. Gm allotypes in membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 1;309(9):556–557. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309013090914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco M. A., Dias R. D., Izquierdo I. Naloxone reverses retrograde amnesia induced by electroconvulsive shock. Behav Neural Biol. 1982 Apr;34(4):352–357. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(82)91738-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. M., Cohen M. R., Weingartner H., Pickar D., Murphy D. L. High-dose naloxone affects task performance in normal subjects. Psychiatry Res. 1983 Feb;8(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(83)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Katzman R., Terry R. D. Reduced somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex from cases of Alzheimer disease and Alzheimer senile dementa. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):279–280. doi: 10.1038/288279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Maloney A. J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1403–1403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91936-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M. Naloxone enhancement of memory processes: effects of other opiate antagonists. Behav Neural Biol. 1982 Aug;35(4):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(82)91020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Rossor M. N., Reynolds G. P., Hills R., Roth M., Mountjoy C. Q., Foote S. L., Morrison J. H., Bloom F. E. Loss of pigmented dopamine-beta-hydroxylase positive cells from locus coeruleus in senile dementia of Alzheimer's type. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 19;39(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang K. C., Messing R. B., McGaugh J. L. Naloxone attenuates amnesia caused by amygdaloid stimulation: the involvement of a central opioid system. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 18;271(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panella J. J., Jr, Blass J. P. Lack of clinical benefit from naloxone in a dementia day hospital. Ann Neurol. 1984 Mar;15(3):308–308. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisberg B., Ferris S. H., Anand R., Mir P., Geibel V., De Leon M. J., Roberts E. Effects of naloxone in senile dementia: a double-blind trial. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):721–722. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1983 Nov;14(5):497–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thal L. J., Fuld P. A., Masur D. M., Sharpless N. S. Oral physostigmine and lecithin improve memory in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol. 1983 May;13(5):491–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


