Abstract
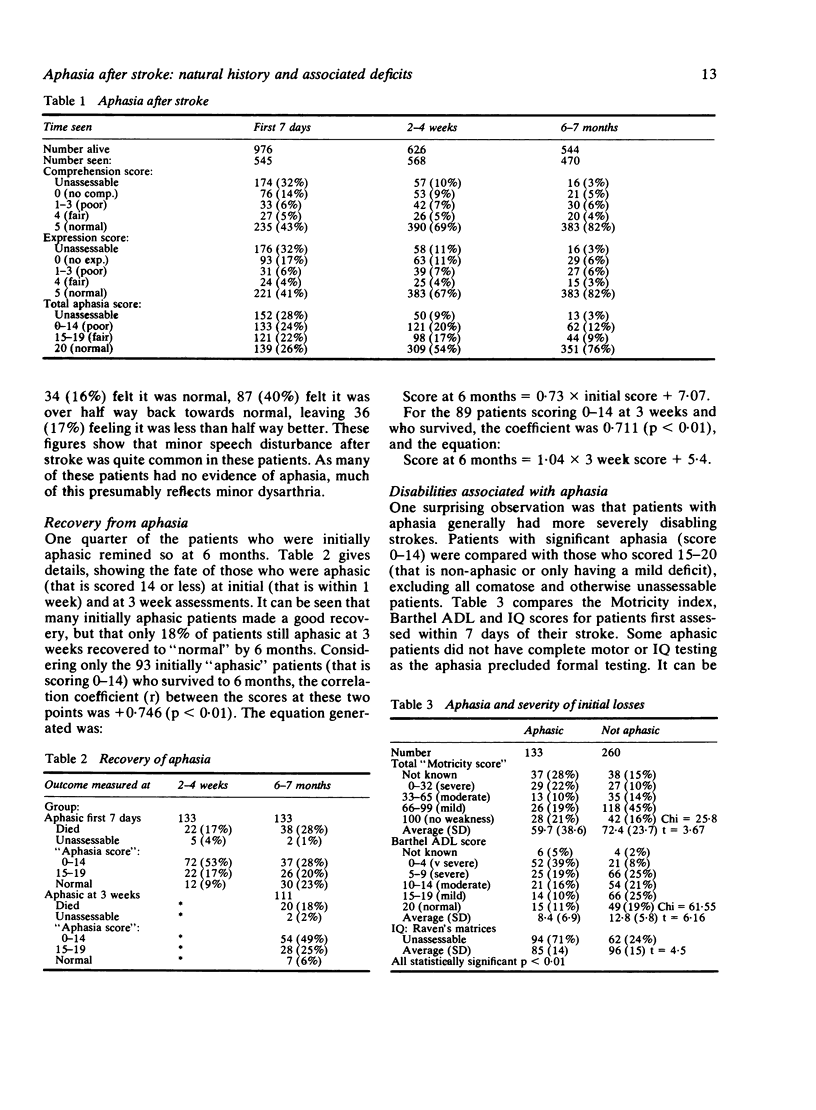
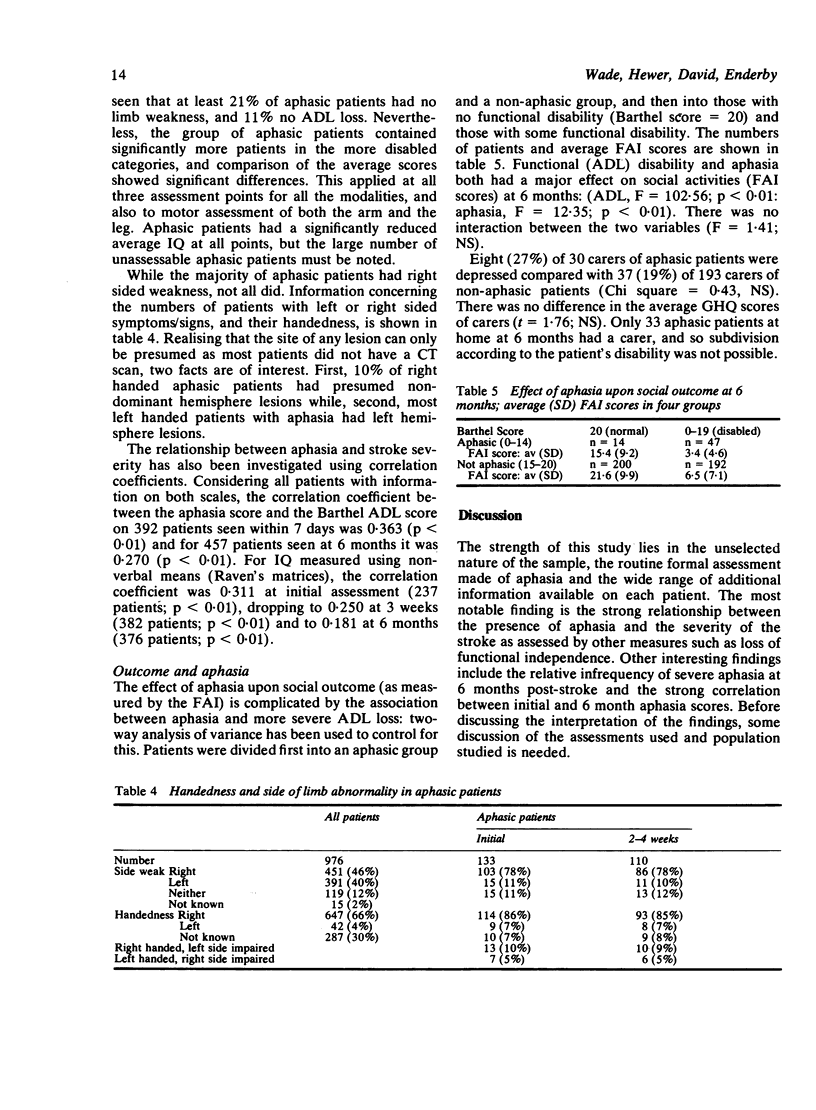
Data relating to 976 patients registered as suffering an acute stroke has been analysed to determine the natural history of speech disturbance: these patients came from a community survey of 215,000 people over a 28 month period. Of the 545 patients assessed within 7 days of stroke, 24% were aphasic and 28% unassessable. At 3 weeks, when over 90% of survivors were tested, 20% of those tested had aphasia. At 6 months only 12% of survivors had significant aphasia, but 44% of patients and 57% of carers thought speech was abnormal. Of those aphasic within 7 days, 40% remained so at 6 months; 60% of those aphasic at 3 weeks remained so. There was a high correlation between early and late aphasia scores. Aphasia was associated with more severe disability (degree of limb weakness, loss of function, loss of IQ), and with a less good recovery of social activities, but did not cause any measurable increase in stress upon carers. In a Health District of 250,000 people, about 60 patients each year may be referred for speech therapy after an acute stroke.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Harmsen P., Hatano S., Marquardsen J., Smirnov V. E., Strasser T. Cerebrovascular disease in the community: results of a WHO collaborative study. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(1):113–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst J. C., Andrews K., Morris P., Richards B. R., Laycock P. L. Why admit stroke patients to hospital? Age Ageing. 1978 May;7(2):100–108. doi: 10.1093/ageing/7.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst J. C., Andrews K., Richards B., Laycock P. J. How much physical therapy for patients with stroke? Br Med J. 1978 May 20;1(6123):1307–1310. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6123.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brust J. C., Shafer S. Q., Richter R. W., Bruun B. Aphasia in acute stroke. Stroke. 1976 Mar-Apr;7(2):167–174. doi: 10.1161/01.str.7.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeurisse G., Demol O., Robaye E. Motor evaluation in vascular hemiplegia. Eur Neurol. 1980;19(6):382–389. doi: 10.1159/000115178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. P., Hillier V. F. A scaled version of the General Health Questionnaire. Psychol Med. 1979 Feb;9(1):139–145. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700021644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger C. V., Dewis L. S., Peters N. C., Sherwood C. C., Barrett J. E. Stroke rehabilitation: analysis of repeated Barthel index measures. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1979 Jan;60(1):14–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresham G. E., Phillips T. F., Wolf P. A., McNamara P. M., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. Epidemiologic profile of long-term stroke disability: the Framingham study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1979 Nov;60(11):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman J. Measurement of early spontaneous recovery from aphasia with stroke. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jan;9(1):89–91. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson V. W. Speech fluency in crossed aphasia. Brain. 1983 Dec;106(Pt 4):837–857. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B., Schulte B. P., van Luijk J. H., Leyten A. C., Frenken C. W. Epidemiology of stroke in Tilburg, The Netherlands. The population-based stroke incidence register: 1. Introduction and preliminary results. Stroke. 1980 Mar-Apr;11(2):162–165. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook M., Skilbeck C. E. An activities index for use with stroke patients. Age Ageing. 1983 May;12(2):166–170. doi: 10.1093/ageing/12.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella G. J., Duffy F. D. Psychosocial readjustment in the spouses of aphasic patients. A comparative Survey of 79 subjects. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1979;11(3):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. C., Phillips D. S. Prognosis for improved verbal communication in aphasic stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1983 Dec;64(12):597–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith R. P., Ahmed S. N., Mehta S., Hamilton M. Assessment of the severity of primary depressive illness. Wakefield self-assessment depression inventory. Psychol Med. 1971 Feb;1(2):143–149. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700000064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



