Abstract
Rett syndrome is a rare, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder. Trofinetide is a synthetic analog of glycine–proline–glutamate, the N-terminal tripeptide of the insulin-like growth factor 1 protein, and has demonstrated clinical benefit in phase 2 studies in Rett syndrome. In this phase 3 study (https://clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT04181723), females with Rett syndrome received twice-daily oral trofinetide (n = 93) or placebo (n = 94) for 12 weeks. For the coprimary efficacy endpoints, least squares mean (LSM) change from baseline to week 12 in the Rett Syndrome Behaviour Questionnaire for trofinetide versus placebo was −4.9 versus −1.7 (P = 0.0175; Cohen’s d effect size, 0.37), and LSM Clinical Global Impression–Improvement at week 12 was 3.5 versus 3.8 (P = 0.0030; effect size, 0.47). For the key secondary efficacy endpoint, LSM change from baseline to week 12 in the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant–Toddler Checklist Social Composite score was −0.1 versus −1.1 (P = 0.0064; effect size, 0.43). Common treatment-emergent adverse events included diarrhea (80.6% for trofinetide versus 19.1% for placebo), which was mostly mild to moderate in severity. Significant improvement for trofinetide compared with placebo was observed for the coprimary efficacy endpoints, suggesting that trofinetide provides benefit in treating the core symptoms of Rett syndrome.
Subject terms: Neurodevelopmental disorders, Medical research
Results from the LAVENDER phase 3 study demonstrate that trofinetide, a synthetic analog of glycine–proline–glutamate, provides significant therapeutic benefits in the core symptoms of Rett syndrome
Main
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a rare, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by loss of verbal communication with limited nonverbal skills, loss of fine and gross motor function (including purposeful hand use), behavioral issues, seizures, hand stereotypies and gastrointestinal problems1,2. Almost all cases of RTT are caused by de novo loss-of-function mutations in the X-linked gene MECP2 encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2), a DNA-binding protein with a role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression3 and deficiency of which results in abnormal neuronal maturation and plasticity4–6.
RTT primarily affects females (1 in 10,000–15,000 live female births)7, but some males are affected8. Individuals with the syndrome undergo apparently normal development for the first 6 months of life, with failure to reach developmental milestones between 6 and 18 months9,10. A period of regression follows at 12–30 months with gait dysfunction, loss of acquired hand skills and spoken language and the onset of repetitive hand stereotypies1,10,11. From approximately 5 years of age through adulthood, no continued skill regression has been observed, with the exception of some loss of ambulation in the teen years1,10. Other common symptoms include awake breathing disruptions, autonomic abnormalities, scoliosis and interest in social interaction (intense eye communication)1,10,11. Seizures have a lifetime prevalence in RTT of around 90%, with a highly variable course of occurrence and remission, with age of seizure onset ranging from <4 years to middle age12. Gastrointestinal dysfunction, including substantial constipation, gastroesophageal reflux disease and chewing and swallowing difficulties are observed in most individuals with RTT2,13.
Trofinetide ((2S)-2-{[(2S)-1-(2-aminoacetyl)-2-methylpyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino}pentanedioic acid) is a synthetic analog of glycine–proline–glutamate (GPE), a naturally occurring tripeptide in the brain that is enzymatically cleaved from insulin-like growth factor 1 (refs. 14,15). In the Mecp2-deficient mouse model of RTT, GPE partially reversed RTT-like symptoms, improved survival and enhanced synaptic morphology and function16. Trofinetide was designed to improve the poor pharmacokinetic profile of GPE17. In a phase 2 study in pediatric and adolescent females with RTT18, treatment with trofinetide (200 mg per kg twice daily (BID)) for 6 weeks was generally well tolerated and provided nominally statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05) improvements in caregiver- and clinician-assessed efficacy measures, including on the Rett Syndrome Behaviour Questionnaire (RSBQ)19 and the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement (CGI-I) scale20, compared with placebo. Clinical benefit was also observed in a previous phase 2 study in adolescent and adult females with RTT21.
The main objective of this phase 3 study was to investigate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of trofinetide in a larger, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in RTT.
Results
Demographic and baseline characteristics
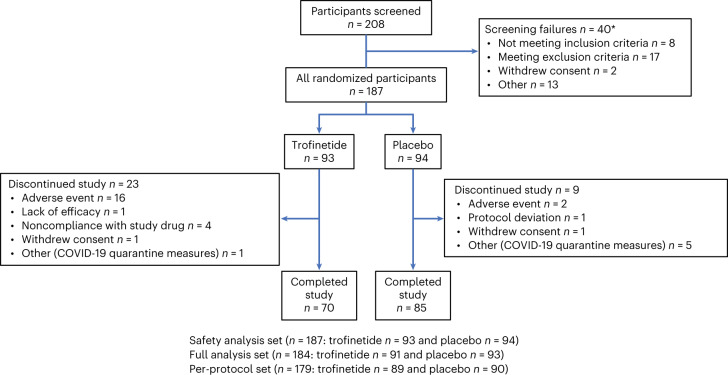
Enrollment occurred between 29 October 2019 and 28 October 2021, with 208 participants screened and 187 participants randomized to trofinetide (n = 93) or placebo (n = 94); 155 participants (82.9%) completed the study (trofinetide, n = 70 (75.3%); placebo, n = 85 (90.4%)) (Fig. 1). Treatment groups were well balanced for demographic and baseline characteristics (Table 1). In the respective trofinetide and placebo groups, 40.9% and 41.5% of participants were administered study medication via gastrostomy tube.
Fig. 1. Participant disposition.
Note that the three participants missing from the full analysis set (n = 184), who were included in the randomized analysis set (n = 187), had a baseline assessment but no post-baseline efficacy assessments. *208 unique participants were screened, but some were rescreened, for a total of 227 screenings. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019.
Table 1.
Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics, RTT history and history of symptoms related to RTT*
| Randomized analysis set | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 94) | Trofinetide (n = 93) | Total (n = 187) | |
| Mean (s.d.) age, years | 10.9 (4.57) | 11.0 (4.69) | 10.9 (4.62) |
| Age categories, n (%) | |||
| 5–10 years | 52 (55.3) | 49 (52.7) | 101 (54.0) |
| 11–15 years | 24 (25.5) | 25 (26.9) | 49 (26.2) |
| 16–20 years | 18 (19.1) | 19 (20.4) | 37 (19.8) |
| 5–11 years | 55 (58.5) | 53 (57.0) | 108 (57.8) |
| 12–16 years | 24 (25.5) | 23 (24.7) | 47 (25.1) |
| 17–20 years | 15 (16.0) | 17 (18.3) | 32 (17.1) |
| Primary race, n (%) | |||
| White | 90 (95.7) | 82 (88.2) | 172 (92.0) |
| Black or African American | 1 (1.1) | 1 (1.1) | 2 (1.1) |
| Asian | 1 (1.1) | 5 (5.4) | 6 (3.2) |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 0 | 1 (1.1) | 1 (0.5) |
| Other | 2 (2.1) | 4 (4.3) | 6 (3.2) |
| Mean (s.d.) baseline RSBQ total scorea | 44.4 (12.13) | 43.8 (11.42) | 44.1 (11.76) |
| Baseline RSBQ severity, n (%) | |||
| <35 | 25 (26.6) | 23 (24.7) | 48 (25.7) |
| ≥35 | 69 (73.4) | 70 (75.3) | 139 (74.3) |
| Mean (s.d.) baseline CGI-S scale scoreb | 4.9 (0.76) | 4.9 (0.77) | 4.9 (0.76) |
| Baseline CGI-S scale category | |||
| 1 = normal to 3 = mildly ill | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 = moderately ill | 33 (35.1) | 32 (34.4) | 65 (34.8) |
| 5 = markedly ill | 42 (44.7) | 38 (40.9) | 80 (42.8) |
| 6 = severely ill | 18 (19.1) | 23 (24.7) | 41 (21.9) |
| 7 = among the most extremely ill patients | 1 (1.1) | 0 | 1 (0.5) |
| Mean (s.d.) RTT-CSS scorec at screening | 24.2 (6.68) | 24.1 (6.40) | 24.1 (6.53) |
| Mean (s.d.) baseline CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite scored | 8.9 (3.23) | 8.7 (3.32) | 8.8 (3.27) |
| Safety analysis set | |||
| MECP2 gene mutation severity category, n (%) | |||
| Mild | 37 (39.4) | 30 (32.3) | 67 (35.8) |
| Moderate | 8 (8.5) | 13 (14.0) | 21 (11.2) |
| Severe | 46 (48.9) | 46 (49.5) | 92 (49.2) |
| Unknown | 3 (3.2) | 4 (4.3) | 7 (3.7) |
| RTT-related medical history, n (%) | |||
| Constipation | 74 (78.7) | 70 (75.3) | 144 (77.0) |
| Seizure | 47 (50.0) | 40 (43.0) | 87 (46.5) |
| Epilepsy | 16 (17.0) | 20 (21.5) | 36 (19.3) |
| Focal dyscognitive seizures | 1 (1.1) | 2 (2.2) | 3 (1.6) |
| Partial seizures | 1 (1.1) | 2 (2.2) | 3 (1.6) |
| Status epilepticus | 2 (2.1) | 1 (1.1) | 3 (1.6) |
| Gastrostomy | 34 (36.2) | 37 (39.8) | 71 (38.0) |
*No significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) were detected between the study groups. P values for continuous variables are based on a t-test. P values for categorical variables with large cell counts are based on the χ2 test of association. P values for categorical variables with any small cell counts are based on Fisher’s exact test.
aRSBQ consists of 45 items, rated as 0 = ‘not true’, 1 = ‘somewhat or sometimes true’ or 2 = ‘very true’, that can be grouped into eight symptom domain subscales graded on a scale of 0–90 (maximum severity)19; the score for item 31 (‘uses eye gaze to convey feelings, needs and wishes’) was reversed in the calculations of total score and subscores for all analyses.
bThe CGI-S scale score uses a Likert scale (1 = normal to 7 = among the most extremely ill patients)20.
cRTT-CSS is based on 13 items on a Likert scale of either 0–4 or 0–5 with a maximum total score of 58 (a higher score indicates more severe clinical status)20.
dCSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score consists of 13 caregiver-rated items, each scored 0 = ‘not yet’, 1 = ‘sometimes’ or 2 = ‘often’, and ranges from 0 to 26 (an increasing score indicates better social communication development). CGI-S, Clinical Global Impression–Severity; CSS, Clinical Severity Scale.
Primary efficacy outcomes
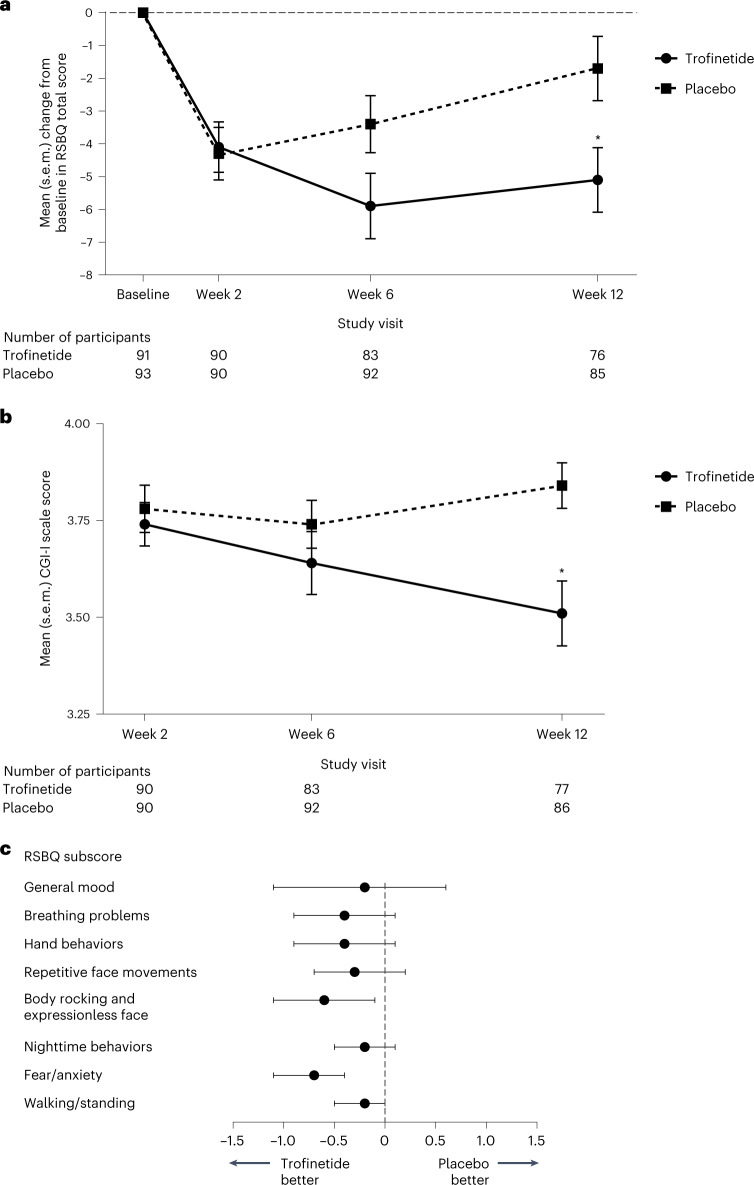
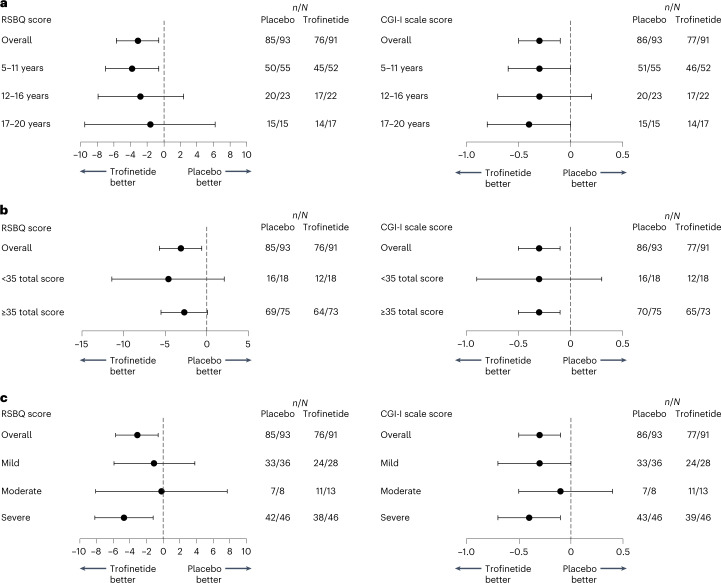
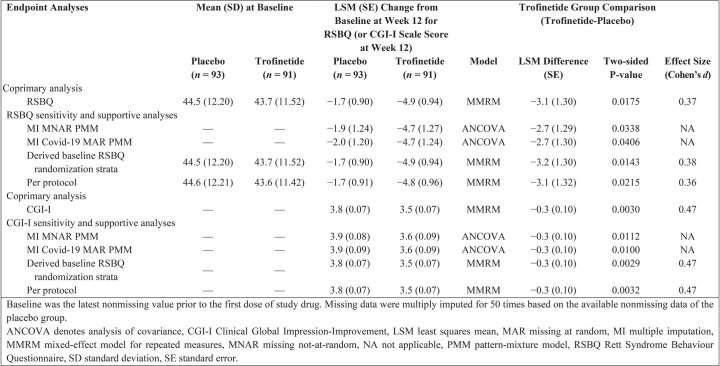
The mean (s.e.m.) change from baseline to week 12 in the RSBQ total score was −5.1 (0.99) and −1.7 (0.98) in the trofinetide and placebo groups, respectively. Based on the mixed-effect model for repeated measure (MMRM) analysis, the LSM (s.e.m.) change from baseline to week 12 in the RSBQ total score was statistically significantly greater with trofinetide (−4.9 (0.94)) than with placebo (−1.7 (0.90)), with an LSM (s.e.m.) treatment difference of −3.1 (1.30) (95% confidence interval (CI), −5.7 to −0.6; P = 0.0175; Cohen’s d effect size, 0.37) (Fig. 2a). At week 12 in the trofinetide and placebo groups, respectively, the mean (s.e.m.) CGI-I scores were 3.5 (0.08) and 3.8 (0.06). MMRM analysis showed a statistically significant improvement with trofinetide compared with placebo at week 12, with an LSM (s.e.m.) treatment difference of −0.3 (0.10) (95% CI, −0.5 to −0.1; P = 0.0030; Cohen’s d effect size, 0.47) (Fig. 2b). Changes from baseline for all RSBQ domain subscores were directionally in favor of trofinetide (Fig. 2c). For the coprimary endpoints, the subgroup analyses showed a similar benefit with trofinetide over placebo irrespective of age, baseline RSBQ severity and category of MECP2 mutation severity (Fig. 3a–c); the results for the sensitivity analyses and per-protocol analysis were consistent with those of the primary analyses (Extended Data Table 1).
Fig. 2. RSBQ total scores, CGI-I scale scores and RSBQ subscores.
a, Mean (s.e.m.) change from baseline in RSBQ total score at each study visit in the full analysis set. b, Mean (s.e.m.) CGI-I scale score at each study visit in the full analysis set. c, LSM treatment differences with 95% CIs for the change in RSBQ subscores from baseline to week 12. In a,b, data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m.; asterisks at week 12 denote significance based on the LSM treatment difference from the MMRM analysis in which adjustments were made for multiple comparisons (two-sided P = 0.0175 and Cohen’s d effect size = 0.37 for the RSBQ change from baseline to week 12 and two-sided P = 0.0030 and Cohen’s d effect size = 0.47 for the CGI-I scale score at week 12). In c, data are presented as LSM treatment difference, and whiskers represent the lower and upper limits of the 95% CI; CI widths have not been adjusted for multiplicity. Sample size for each RSBQ subscore analysis: trofinetide (n = 76) and placebo (n = 85).
Fig. 3. Subgroup analyses of the coprimary efficacy endpoints.
a–c, LSM treatment differences with 95% CIs for the coprimary efficacy endpoints by age (a), baseline RSBQ severity (b) and category of mutation severity (c) based on the MMRM analysis in the full analysis set. In a–c, data are presented as LSM treatment difference, and whiskers represent the lower and upper limits of the 95% CI; CI widths have not been adjusted for multiplicity.
Extended Data Table 1.
Primary Analysis, Sensitivity Analysis (Actual Derived Baseline Values for Randomization Strata, MI for MNAR PMM, MI for Covid-19 MAR PMM) and Supportive Analyses (Per Protocol) of the Coprimary Endpoints
Key secondary efficacy outcome
The mean (s.e.m.) change from baseline to week 12 in the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant–Toddler Checklist (CSBS-DP-IT) Social Composite score was −0.1 (0.28) and −1.1 (0.28) in the trofinetide and placebo groups, respectively. MMRM analysis showed a statistically significant difference between trofinetide and placebo, with an LSM (s.e.m.) treatment difference of 1.0 (0.37) (95% CI, 0.3 to 1.7; P = 0.0064; Cohen’s d effect size, 0.43).
Secondary efficacy outcomes
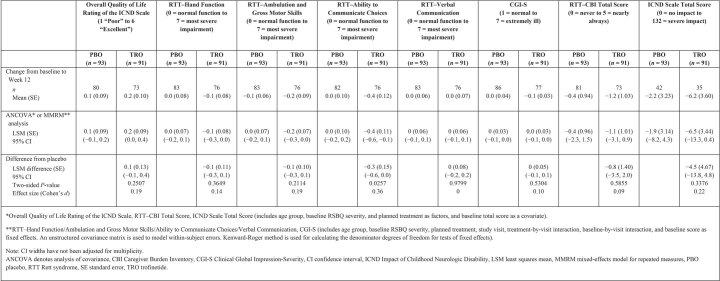
Results for the other secondary endpoints are shown in Extended Data Table 2.
Extended Data Table 2.
Change From Baseline to Week 12 in the Other Secondary Endpoints (Full Analysis Set)
Safety analysis
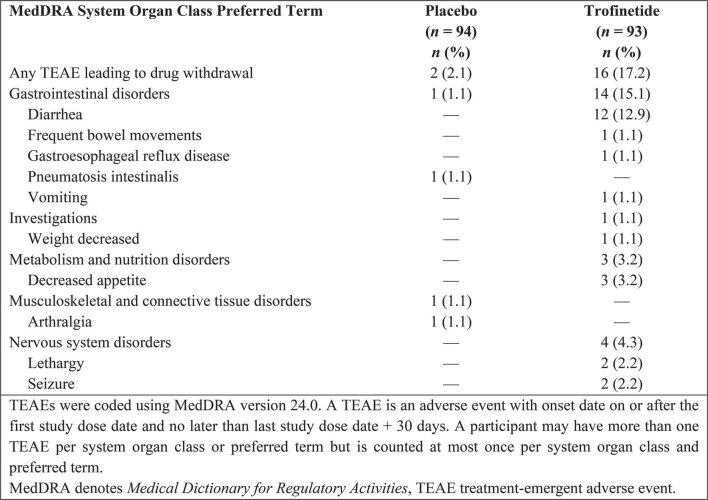
In the respective trofinetide and placebo groups, at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) was reported for 86 (92.5%) and 51 (54.3%) participants. No deaths were reported. Serious TEAEs were reported for three participants (3.2%) in each of the treatment groups (Table 2).
Table 2.
Summary of TEAEs, the most common TEAEs (≥5% in any group) and by severity in the trofinetide and placebo groups (safety analysis set)
| TEAEs and preferred term, n (%) | Placebo (n = 94) | Trofinetide (n = 93) | P value* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any TEAE | 51 (54.3) | 86 (92.5) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Serious TEAEa | 3 (3.2) | 3 (3.2) | 0.9894 | ||||
| TEAE leading to drug withdrawal | 2 (2.1) | 16 (17.2) | 0.0005 | ||||
| Fatal TEAE | – | – | – | ||||
| TEAEs reported in ≥5% of participants in any group | |||||||
| Diarrhea | 18 (19.1) | 75 (80.6) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Vomiting | 9 (9.6) | 25 (26.9) | 0.0022 | ||||
| Seizure | 5 (5.3) | 8 (8.6) | 0.3775 | ||||
| Pyrexia | 4 (4.3) | 8 (8.6) | 0.2252 | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 2 (2.1) | 5 (5.4) | 0.2419 | ||||
| Irritability | – | 6 (6.5) | – | ||||
| TEAEs reported in ≥5% of participants in any group by severity | |||||||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| Diarrhea | 15 (16.0) | 3 (3.2) | – | 39 (41.9) | 34 (36.6) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Vomiting | 8 (8.5) | 1 (1.1) | – | 18 (19.4) | 6 (6.5) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Seizure | 3 (3.2) | 2 (2.1) | – | 3 (3.2) | 5 (5.4) | – | |
| Pyrexia | 2 (2.1) | 2 (2.1) | – | 7 (7.5) | 1 (1.1) | – | |
| Decreased appetite | 1 (1.1) | 1 (1.1) | – | 2 (2.2) | 3 (3.2) | – | |
| Irritability | – | – | – | 3 (3.2) | 2 (2.2) | 1 (1.1) | |
*Two-sided P values were based on a post hoc analysis using the χ2 test of association. P values ≤ 0.05 denote nominal statistical significance.
A TEAE is an adverse event with onset date on or after the first study dose date and no later than the last study dose date +30 days. TEAEs were coded using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities version 24.0. A participant may have more than one TEAE per preferred term, but a participant is counted at most once per preferred term. Adverse event severity was graded as mild (easily tolerated, minimal discomfort), moderate (interferes with everyday activities) or severe (incapacitating and/or preventing normal everyday activities).
aSerious TEAEs were bacteremia, urinary tract infection and bronchiolitis (n = 1), COVID-19 pneumonia (n = 1) and seizure (n = 1) in the participants treated with trofinetide; and respiratory distress (n = 1), constipation (n = 1) and pneumatosis intestinalis (n = 1) in the participants treated with placebo.
The most common TEAEs in the trofinetide and placebo groups were diarrhea (80.6% and 19.1%, respectively) and vomiting (26.9% and 9.6%, respectively); of the TEAEs in the trofinetide group, 97.3% and 96.0% of diarrhea and vomiting TEAEs, respectively, were mild to moderate in severity (Table 2). Eighteen participants withdrew due to a TEAE (trofinetide, n = 16 (17.2%); placebo, n = 2 (2.1%)), with diarrhea being the primary TEAE leading to discontinuation (trofinetide, n = 12 (12.9%)) (Extended Data Table 3).
Extended Data Table 3.
Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events Leading to Drug Withdrawal (Safety Analysis Set)
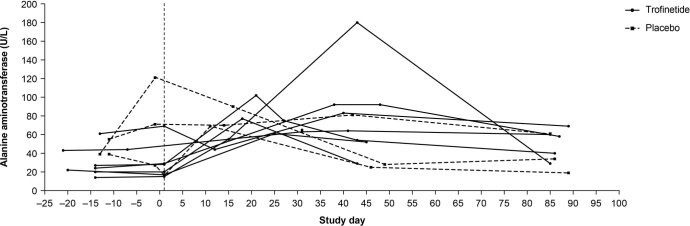
Changes in laboratory tests, electrocardiograms and vital signs were generally small and similar in the treatment groups; none were considered clinically meaningful. Small, transient changes in alanine aminotransferase values were reported in seven of 92 (7.6%) and three of 93 (3.2%) participants in the trofinetide and placebo groups, respectively (Extended Data Fig. 1). These changes were not associated with notable changes in other liver function tests, and no instances met Hy’s law criteria22. The most frequently used concomitant medications in the trofinetide and placebo groups were antiseizure medication (64.5% and 72.3%, respectively) and drugs for constipation (60.2% and 70.2%); antipropulsives (that is, loperamide) were used more frequently in the trofinetide group (50.5% versus 3.2%), consistent with the treatment of diarrhea.
Extended Data Fig. 1. Alanine Aminotransferase Values.
Figure footnote: The dashed vertical line at day 1 indicates when study treatment was initiated.
Post hoc efficacy analyses
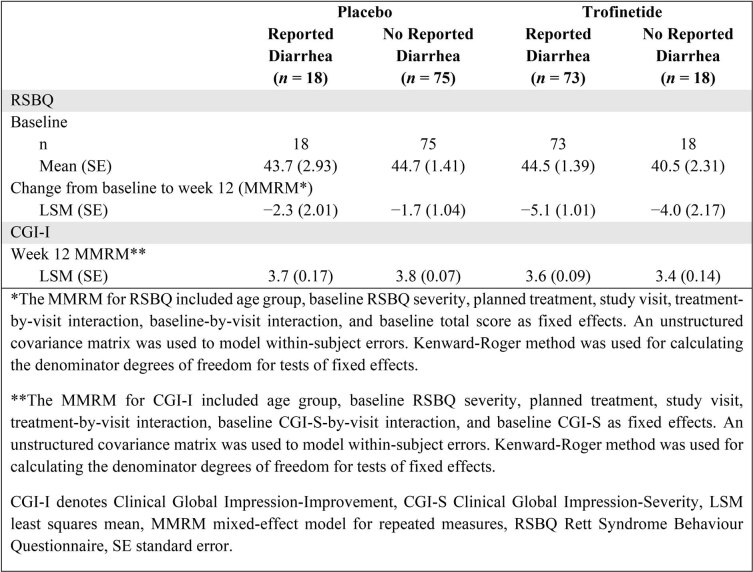
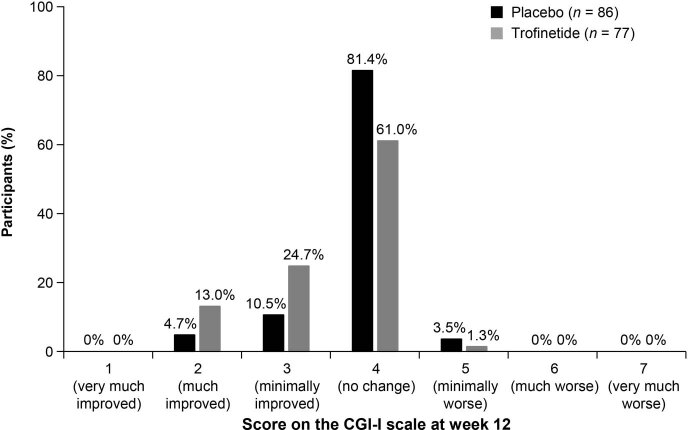
The results for the coprimary endpoints were comparable irrespective of diarrhea TEAE status (Extended Data Table 4). CGI-I responder rates (defined as CGI-I score ≤3 at week 12) were greater in the trofinetide group than in the placebo group (37.7% versus 15.2%; Extended Data Fig. 2).
Extended Data Table 4.
RSBQ Total Score Change From Baseline at Week 12 and CGI-I Scale Score at Week 12 in Participants With and Without Diarrhea (Full Analysis Set)
Extended Data Fig. 2. Score on the CGI-I Scale at Week 12.
Figure footnote: CGI-I denotes Clinical Global Impression-Improvement.
Discussion
In this phase 3 study in a large cohort of girls and women 5–20 years of age with RTT, trofinetide demonstrated a statistically significant improvement over placebo for both the coprimary and key secondary efficacy endpoints. Treatment with trofinetide improved key symptoms of the syndrome from the perspective of both the caregiver (RSBQ) and clinician (CGI-I). All RSBQ subscores were directionally in favor of trofinetide, suggesting broad improvement across key symptoms of the syndrome.
Cohen’s d effect sizes for the coprimary and key secondary endpoints fell in the 0.4–0.5 range (0.37 for the RSBQ, 0.47 for the CGI-I scale and 0.43 for the CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score), suggesting that the findings of treatment benefit with trofinetide are consistent and, given that Cohen’s d effect sizes within this range are considered medium23, clinically meaningful.
The efficacy endpoints are complementary and reflect functionally important dimensions of RTT, including the ability to communicate. The RSBQ shows correlations with functioning, is validated across a range of ages (2–47 years) in RTT24–26 and is the most widely used instrument in RTT studies. As a clinician rating, the CGI-I scale provides clinical meaningfulness to the caregiver-rated coprimary endpoint and has been widely used in clinical trials of RTT and other neurodevelopmental disorders18,21,27–31. In this study, CGI-I scale ratings were assessed using RTT-specific anchors across major symptom areas that were developed to improve trial outcomes20, and an effort was made to standardize the CGI-I scale rating by independently rating case vignettes to fidelity as compared with a gold-standard rating32. Communication is one of the most important concerns for caregivers in RTT33, and the items comprising the CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score are the most commonly used communication modalities by individuals with RTT.
Mild or moderate diarrhea was frequently associated with trofinetide and was responsible for the majority of discontinuations due to TEAEs; however, diarrhea was self-limited and resolved soon after withdrawal of trofinetide. The implementation of a diarrhea-management plan partway through the study, which involved the adjustment or discontinuation of laxative medications commonly taken for RTT-associated constipation, the initiation of fiber supplements and antidiarrheal medication and dose reduction or interruption of trofinetide, if necessary, appeared to mitigate this risk, as 75% of participants receiving trofinetide completed the study. Furthermore, analyses indicate that the risk of functional unblinding due to an imbalance of TEAEs of diarrhea did not bias the efficacy data in favor of trofinetide. Given that most participants were using concomitant antiseizure medication, many of which cause changes in liver enzymes34, the minimal effect on liver enzymes in this study does not preclude the use of trofinetide with these drugs.
The exclusion of individuals without a documented disease-causing MECP2 mutation, males and individuals <5 and >20 years of age are limitations of the study and were based on considerations of study design to reduce variability in the population sample. Males with RTT were not enrolled due to the rarity of cases and variable phenotype in these individuals8. Although the study enrolled females exclusively, based on the underlying pathophysiology of RTT and the biological effects of trofinetide, the results should be applicable to the fewer males with RTT as well. Adults >20 years of age were not included due to the challenge of controlling for wide discrepancies in services available to individuals in the United States after they are no longer eligible for services through the educational system. However, similar efficacy is anticipated in older individuals, given the benefit observed in the phase 2 study that included individuals 15–44 years of age21 and the age subgroup analysis results in this study. The primary reason for maintaining an age cutoff of ≥5 years was in consideration of the variable early developmental regression in this age range. An ongoing study (https://clinicaltrials.gov identifier NCT04988867) is investigating the safety and pharmacokinetics of trofinetide in individuals with RTT as young as 2 years of age35. Of the 187 participants in the LAVENDER study, 154 elected to roll over to the open-label LILAC extension study (NCT04279314) and may be eligible to enter the follow-up LILAC-2 extension study (NCT04776746); both will inform on the long-term safety of trofinetide.
In conclusion, statistically significant differences were demonstrated between trofinetide and placebo for efficacy endpoints relevant to RTT, suggesting that trofinetide is potentially capable of modifying core symptoms consistent with the underlying pathophysiology of the syndrome. Furthermore, this study demonstrated an acceptable safety profile for trofinetide. When we evaluate the benefit versus risk associated with trofinetide, it is important to consider the medium effect size that was demonstrated for the efficacy endpoints, which can be interpreted as clinically meaningful, particularly as this is a rare disease with a high burden for patients and families. When we consider the risk element, it is important to note that diarrhea and vomiting were issues of tolerability, not safety. Almost all TEAEs of diarrhea and vomiting were mild or moderate in severity and can be managed with appropriate interventions. Given that numerous phase 2 and 3 studies in neurodevelopmental disorders including RTT have failed to meet efficacy endpoints36,37, these findings represent the first time treatment of a neurodevelopmental disorder has been shown to be beneficial in a large, controlled study and provides hope for a meaningful therapeutic development to treat RTT.
Methods
Study design
The study design and methods have been published previously32. In this randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study conducted at 21 sites in the United States, participants were stratified by age (5–10, 11–15 and 16–20 years) and baseline RSBQ severity (<35 and ≥35 total score) and randomized 1:1 to trofinetide or placebo using an interactive response technology system via a pre-generated permuted-block randomization schedule. The sponsor, participants, caregivers and clinicians were blinded to treatment assignment via restriction to treatment codes and the identical appearance of the study drug and placebo.
A single dose level of trofinetide was tested using weight-based dosing to achieve the target exposure identified based on the results of the previous phase 2 study18. Trofinetide was given at 30 ml (6 g), 40 ml (8 g), 50 ml (10 g) or 60 ml (12 g) BID orally or by gastrostomy tube for participants weighing 12–20, >20–35, >35–50 and >50 kg, respectively (equivalent to a range of 200–500 mg per kg BID).
The study included a screening period of ≤3 weeks, a 12-week double-blind treatment period and a 30-day safety follow-up for participants who did not continue into the open-label extension study (https://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT04279314). The study was conducted in compliance with guidelines from the International Council for Harmonisation (Good Clinical Practice), the Declaration of Helsinki and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. The protocol was approved by central (WCG IRB) and local institutional review boards. Before screening, informed consent was obtained from the parent or guardian on behalf of the participant.
Study population
Girls and women 5–20 years of age with RTT, a score of 10–36 on the RTT Clinical Severity Scale20 and a CGI-S score20 of ≥4 (moderate) were included. Eligible participants were at least 6 months after regression at screening (that is, no loss or degradation in ambulation, hand function, speech or nonverbal communicative or social skills within 6 months of screening) and had a stable pattern of seizures or no seizures, within 8 weeks of screening. Key exclusion criteria were current clinically significant cardiovascular, endocrine, renal, hepatic, respiratory or gastrointestinal disease or major surgery planned during the study; treatment with insulin, IGF-1 or growth hormone within 12 weeks of baseline; known history or symptoms of long QT syndrome; and QTcF interval >450 ms, history of risk factor for torsades de pointes or clinically meaningful QT prolongation deemed to increase risk. Full inclusion and exclusion criteria are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Intervention
Trofinetide (200 mg ml−1 solution) or matching placebo was administered orally or by gastrostomy tube BID (doses at least 8 h apart).
Assessments
Coprimary and key secondary efficacy assessments using the RSBQ, the CGI-I scale and the CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score were completed at baseline (except the CGI-I scale) and at each visit (weeks 2, 6 and 12 (or end of treatment)). The RSBQ is a caregiver-completed scale assessing key symptoms of RTT19 and includes 45 items (rated as 0 = ‘not true’, 1 = ‘somewhat or sometimes true’ or 2 = ‘very true’) that can be grouped into eight symptom domain subscales. The score for item 31 (‘uses eye gaze to convey feelings, needs and wishes’) was reversed in the calculations of total score and subscores for all analyses. The CGI-I scale is a clinician rating of global clinical change using a seven-point scale with RTT-specific anchors20. The CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score is derived from the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile, originally developed to assess communication and social interaction skills in young children38, and can be used for older children with developmental delay39,40. The CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score consists of 13 caregiver-rated items, each scored 0 = ‘not yet’, 1 = ‘sometimes’ or 2 = ‘often’. Safety assessments included TEAEs, clinical laboratory assessments, vital signs and electrocardiograms. A full description of the schedule of study procedures is described in Supplementary Table 2.
Efficacy endpoints
Coprimary endpoints were the change from baseline to week 12 in RSBQ total score and the CGI-I scale score at week 12. The key secondary endpoint was the change from baseline to week 12 in the CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score. A prespecified subgroup analysis examined treatment effects by age, baseline RSBQ severity and MECP2 mutation severity as categorized according to the RTT Natural History Study41.
Post hoc efficacy analyses
Two additional efficacy analyses were conducted post hoc: CGI-I scale responders (scores ≤3) at week 12 and coprimary endpoints assessed in the presence or absence of the most commonly reported TEAE of diarrhea.
Statistical analysis
A sample size of 184 participants (92 per group) was planned to provide 90% power for both coprimary endpoints combined with a two-sided significance level of 0.05. Efficacy was assessed in the full analysis set (received at least one dose and had a baseline value and at least one post-baseline value for the RSBQ or the CGI-I score); the safety analysis set consisted of participants who received at least one dose.
Coprimary and key secondary efficacy endpoints were analyzed using the MMRM method assuming data missing at random. The MMRM included randomization strata of age group and baseline RSBQ severity score, baseline RSBQ (for RSBQ analysis), baseline CGI-S (for CGI-I scale analysis) and baseline CSBS-DP-IT Social Composite score (for the key secondary endpoint), treatment, visit, treatment-by-visit interaction and baseline-by-visit interaction as fixed effects and participant as a random effect; an unstructured covariance matrix modeled within-participant errors. The Kenward–Roger method was used for calculating denominator degrees of freedom for tests of fixed effects. Each coprimary endpoint was considered positive if P ≤ 0.05, and both must be positive for the study to be positive. If both coprimary endpoints were positive, the key secondary endpoint was also considered positive if P ≤ 0.05 and was statistically controlled for type 1 error at 5% through a hierarchical sequential gatekeeper procedure. Effect size was determined with Cohen’s d23. Sensitivity analyses of the coprimary endpoints included multiple imputations based on pattern-mixture models assuming missing not at random using the analysis of covariance method, the use of actual derived baseline values for randomization strata (MMRM) and visits impacted by COVID-19 (analysis of covariance); a supportive analysis (MMRM) used the per-protocol analysis set. Possible intercurrent events included treatment discontinuation not due to COVID-19, treatment discontinuation due to COVID-19, COVID-19 events leading to intermediate missing data, non-COVID-19 events leading to intermediate missing data and remote assessments (regardless of COVID-19 or not). Observations on the coprimary efficacy endpoints were used regardless of the occurrence of intercurrent events. Alternative approaches to handling intercurrent events are addressed in sensitivity analyses. The following sensitivity analyses of the coprimary efficacy endpoints were planned and conducted to account for intercurrent events of treatment discontinuations and missing assessments. For the pattern-mixture models assuming missing not at random, the sensitivity analysis was implemented for the full analysis set using multiple imputations based on the distribution of placebo group responses over time. The underlying assumption is that missing data due to early withdrawal of participants evolves in the same way as the data for placebo-treated participants who remain in the study. For missing data due to COVID-19, this sensitivity analysis operates under the assumption that missing data after withdrawal due to COVID-19 are missing at random, while missing data after withdrawal not due to COVID-19 are not missing at random and are assumed to evolve in the same manner as for placebo-treated participants who remain in the study. Statistical analyses were performed using version 9.4 of SAS. The statistical analysis plan and protocol are available at Protocol Exchange.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Online content
Any methods, additional references, Nature Portfolio reporting summaries, source data, extended data, supplementary information, acknowledgements, peer review information; details of author contributions and competing interests; and statements of data and code availability are available at 10.1038/s41591-023-02398-1.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
Final version of the statistical analysis plan.
Final version of the study protocol.
Source data
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Acknowledgements
We thank the trial participants, their families and our fellow investigators involved in this trial: B. Suter (Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, Texas, US), C. Buhrfiend, P. Heydemann (Rush University Children’s Hospital, Chicago, Illinois, US), S. Standridge, E. Broomall, K. Peariso (Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Division of Neurology and University of Cincinnati, College of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Cincinnati, OH, US), C. Fu, S. Peters (Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, US), R. Haas, N. Guido-Estrada (University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, California, US), S. Kessler, S. Massey (Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, US), A. Ananth (University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, US), R. Ryther, J. Weisenberg (Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri, US), D. Lieberman, R. Witt, D. Friedman (Boston Children’s Hospital Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, US), A. Stratton (Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, Colorado, US), V. Narayanan, N. Belnap (Translational Genomics Research Institute, Phoenix, Arizona, US), R.J. Hagerman, B. Restrepo, M. Jones* (UC Davis MIND Institute, Sacramento, California, US; *investigator passed away before participating in the trial), S.A. Skinner (Greenwood Genetic Center, Greenwood, South Carolina, US), T. Feyma, A. Beisang (Gillette Children’s Specialty Healthcare, Saint Paul, Minnesota, US), A. Djukic (Montefiore Medical Center, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, New York, US), Y. Shiloh-Malawsky, D. Cejas, Z. Fan (the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, US), R. Saneto (Seattle Children’s, Seattle, Washington, US), J. Ranells, A. Sanchez-Valle, C. Griffith, K. Morgan (University of South Florida Children’s Medical Services, Tampa, Florida, US), C. Smith-Hicks, M. Jain (Kennedy Krieger Institute, Clinical Trials Unit, Baltimore, Maryland, US), S. Parikh, G. Hsich (Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, US), A.L. Talboy, R. Sanchez (Emory Genetics Clinical Trial Center, Atlanta, Georgia, US). We also thank K. Raudibaugh, K. O’Rourke-Kosko, C. Murphy and R. Nunez of Acadia Pharmaceuticals. The study was funded by Acadia Pharmaceuticals. The study sponsor (Acadia Pharmaceuticals) contributed to the study design, the writing of the report and the decision to submit the article for publication. Medical writing support was provided by S. Murray, MSc, CMPP, of Evidence Scientific Solutions and funded by Acadia Pharmaceuticals.
Extended data
Author contributions
The sponsor, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, and J.L.N., A.K.P., T.A.B., E.M.B.-K. and D.G.G. conceived and designed the study; all authors conducted the study and collected data, performed the formal analysis, participated in data interpretation, critically revised the manuscript content for important intellectual content, approved the final version and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Medicine thanks Kyle Fink and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Jerome Staal, in collaboration with the Nature Medicine team
Data availability
This clinical trial was sponsored by Acadia Pharmaceuticals. Acadia supports data sharing consistent with the Principles for Responsible Clinical Trial Data Sharing and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors’ recommendations. Acadia shares data from completed clinical trials through public registries (https://clinicaltrials.gov), presentation at scientific congresses and through open access in peer-reviewed journals. Clinical study results from this study were submitted to https://clinicaltrials.gov in April 2023. Additional, related information necessary to appraise the quality and robustness of the findings (study protocol, statistical analysis plan) is available in the Supplementary Information. The authors will provide access to individual-deidentified participant-level data that underlie the data presented in this paper, including data dictionaries, the study protocol and other relevant information, to any researcher who provides a methodologically sound proposal for academic purposes to interpret, verify and extend research in the article beginning 6 months and ending 5 years after article publication. Requests for the ‘minimum dataset’ should go through Acadia Medical Information and will be reviewed by the sponsor (Acadia) to verify whether the request is subject to any intellectual property or confidentiality obligations. For additional information, please contact Acadia Medical Information at medicalinformation@acadia-pharm.com. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
J.L.N. has received research funding from the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, the National Institutes of Health and Rett Syndrome Research Trust; and personal consultancy fees from Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Analysis Group, AveXis, GW Pharmaceuticals, Hoffmann-La Roche, Myrtelle, Neurogene, Newron Pharmaceuticals, Signant Health and Taysha Gene Therapies and for the preparation of CME activities for Medscape and PeerView Institute; serves on the scientific advisory board of Alcyone Lifesciences; is a scientific cofounder of LizarBio Therapeutics; and was a member of a data safety monitoring board for clinical trials conducted by Ovid Therapeutics. A.K.P. is coeditor of Translational Science of Rare Diseases, received research funding from the National Institutes of Health and is a consultant for Acadia Pharmaceuticals, AveXis, GW Pharmaceuticals and Anavex Life Science as well as an adviser to the International Rett Syndrome Foundation. T.A.B. received research funding from the GRIN2B Foundation, the International Foundation for CDKL5 Research, the Loulou Foundation, the National Institutes of Health and the Simons Foundation; has consultancies for Alcyone, AveXis, GRIN Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Neurogene, Ovid Therapeutics and Takeda Pharmaceutical; has clinical trials with Acadia Pharmaceuticals, GW Pharmaceuticals, Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Ovid Therapeutics and Rett Syndrome Research Trust; all remuneration has been made to his department. E.M.B.-K. has received funding from Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Alcobra Pharmaceuticals, AMO Pharma, Asuragen, AveXis, Biogen, BioMarin, Cydan Development, EryDel, Fulcrum Therapeutics, GeneTx, GW Pharmaceuticals, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Jaguar Health, Lumos Pharma, Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, Neurogene, Neurotrope, Novartis, Orphazyme, Ovid Therapeutics, Retrophin, Roche, Seaside Therapeutics, Taysha Gene Therapies, Tetra Bio-Pharma, Ultragenyx, Yamo Pharmaceuticals, Zynerba Pharmaceuticals and Vtesse–Sucampo–Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals to consult on trial design or run clinical or laboratory validation trials in genetic neurodevelopmental or neurodegenerative disorders, all of which is directed to Rush University Medical Center in support of rare disease programs; E.M.B.-K. receives no personal funds, and Rush University Medical Center has no relevant financial interest in any of the commercial entities listed. D.G.G. has received personal compensation and research support from Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Neuren Pharmaceuticals and Newron Pharmaceuticals. E.D.M. has received research support from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Eagles Autism Foundation, Penn Orphan Disease Center, the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, Rett Syndrome Research Trust, the International CDKL5 Research Foundation and the Loulou Foundation. He has been a site principal investigator for trials from Stoke Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, Zogenix, Acadia Pharmaceuticals and Marinus Pharmaceuticals. He has received personal compensation for consulting from Stoke Therapeutics and Acadia Pharmaceuticals. J.M.Y., K.M.B., S.S. and T.L. are employees of and stockholders in Acadia Pharmaceuticals. S.S. is also a board director and stockholder of Neurogene.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41591-023-02398-1.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41591-023-02398-1.
References
- 1.Neul, J. L. et al. Rett syndrome: revised diagnostic criteria and nomenclature. Ann. Neurol.68, 944–950 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Motil, K. J. et al. Gastrointestinal and nutritional problems occur frequently throughout life in girls and women with Rett syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr.55, 292–298 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Amir, R. E. et al. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet.23, 185–188 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Baj, G., Patrizio, A., Montalbano, A., Sciancalepore, M. & Tongiorgi, E. Developmental and maintenance defects in Rett syndrome neurons identified by a new mouse staging system in vitro. Front. Cell. Neurosci.8, 18 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bedogni, F. et al. Defects during Mecp2 null embryonic cortex development precede the onset of overt neurological symptoms. Cereb.Cortex26, 2517–2529 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Belichenko, P. V. et al. Widespread changes in dendritic and axonal morphology in Mecp2-mutant mouse models of Rett syndrome: evidence for disruption of neuronal networks. J. Comp. Neurol.514, 240–258 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hagberg, B. Rett’s syndrome: prevalence and impact on progressive severe mental retardation in girls. Acta Paediatr. Scand.74, 405–408 (1985). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Neul, J. L. et al. The array of clinical phenotypes of males with mutations in methyl-CpG binding protein 2. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet.180, 55–67 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Neul, J. L. et al. Developmental delay in Rett syndrome: data from the Natural History Study. J. Neurodev. Disord.6, 20 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hagberg, B. Clinical manifestations and stages of Rett syndrome. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev.8, 61–65 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Percy, A. K. et al. Rett syndrome diagnostic criteria: lessons from the Natural History Study. Ann. Neurol.68, 951–955 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tarquinio, D. C. et al. Longitudinal course of epilepsy in Rett syndrome and related disorders. Brain140, 306–318 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baikie, G. et al. Gastrointestinal dysmotility in Rett syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr.58, 237–244 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bickerdike, M. J. et al. NNZ-2566: a Gly–Pro–Glu analogue with neuroprotective efficacy in a rat model of acute focal stroke. J. Neurol. Sci.278, 85–90 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Collins, B. E. & Neul, J. L. Trofinetide. Glycine–proline–glutamate (GPE) analogue, treatment of Rett syndrome, treatment of fragile X syndrome. Drugs Future46, 29–42 (2021). [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tropea, D. et al. Partial reversal of Rett syndrome-like symptoms in MeCP2 mutant mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA106, 2029–2034 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Batchelor, D. C. et al. Pharmacokinetics of glycine–proline–glutamate, the N-terminal tripeptide of insulin-like growth factor-1, in rats. Anal. Biochem.323, 156–163 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Glaze, D. G. et al. Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of trofinetide in pediatric Rett syndrome. Neurology92, e1912–e1925 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mount, R. H., Charman, T., Hastings, R. P., Reilly, S. & Cass, H. The Rett Syndrome Behaviour Questionnaire (RSBQ): refining the behavioural phenotype of Rett syndrome. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry43, 1099–1110 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Neul, J. L. et al. Improving treatment trial outcomes for Rett syndrome: the development of Rett-specific anchors for the Clinical Global Impression Scale. J. Child Neurol.30, 1743–1748 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Glaze, D. G. et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study of trofinetide in the treatment of Rett syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol.76, 37–46 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Temple, R. Hy’s law: predicting serious hepatotoxicity. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf.15, 241–243 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988).
- 24.Barnes, K. V. et al. Anxiety-like behavior in Rett syndrome: characteristics and assessment by anxiety scales. J. Neurodev. Disord.7, 30 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cianfaglione, R. et al. A national survey of Rett syndrome: behavioural characteristics. J. Neurodev. Disord.7, 11 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Robertson, L. et al. The association between behavior and genotype in Rett syndrome using the Australian Rett Syndrome Database. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet.141B, 177–183 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Berk, M. et al. The validity of the CGI severity and improvement scales as measures of clinical effectiveness suitable for routine clinical use. J. Eval. Clin. Pract.14, 979–983 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Busner, J., Targum, S. D. & Miller, D. S. The Clinical Global Impressions scale: errors in understanding and use. Compr. Psychiatry50, 257–262 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kaufmann, W. E., Stallworth, J. L., Everman, D. B. & Skinner, S. A. Neurobiologically-based treatments in Rett syndrome: opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin.OrphanDrugs4, 1043–1055 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Berry-Kravis, E. et al. Outcome measures for clinical trials in fragile X syndrome. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr.34, 508–522 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Budimirovic, D. B. et al. Updated report on tools to measure outcomes of clinical trials in fragile X syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord.9, 14 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Neul, J. L. et al. Design and outcome measures of LAVENDER, a phase 3 study of trofinetide for Rett syndrome. Contemp. Clin. Trials114, 106704 (2022). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Neul, J. L., Benke, T. A., Marsh, E. D. et al. Top caregiver concerns in Rett syndrome and related disorders: data from the US Natural History Study. Preprint at Research Square10.21203/rs.3.rs-2566253/v1 (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Ahmed, S. N. & Siddiqi, Z. A. Antiepileptic drugs and liver disease. Seizure15, 156–164 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ryther, R. et al. Design and outcome measures of an open label study of trofinetide for the treatment of girls 2 to 5 years of age with Rett syndrome. Poster presented at ASCEND/IRSF Rett Syndrome National Summit Nashville, TN, 27–30 April 2022.
- 36.Berry-Kravis, E. M. et al. Drug development for neurodevelopmental disorders: lessons learned from fragile X syndrome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.17, 280–299 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gomathi, M., Padmapriya, S. & Balachandar, V. Drug studies on Rett syndrome: from bench to bedside. J. Autism Dev. Disord.50, 2740–2764 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wetherby, A. M., Allen, L., Cleary, J., Kublin, K. & Goldstein, H. Validity and reliability of the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile with very young children. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res.45, 1202–1218 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Urbanowicz, A., Downs, J., Girdler, S., Ciccone, N. & Leonard, H. An exploration of the use of eye gaze and gestures in females with Rett syndrome. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res.59, 1373–1383 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Anagnostou, E. et al. Measuring social communication behaviors as a treatment endpoint in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Autism19, 622–636 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stallworth, J. L. et al. Hand stereotypies: lessons from the Rett Syndrome Natural History Study. Neurology92, e2594–e2603 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
Final version of the statistical analysis plan.
Final version of the study protocol.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Clinical study report.
Data Availability Statement
This clinical trial was sponsored by Acadia Pharmaceuticals. Acadia supports data sharing consistent with the Principles for Responsible Clinical Trial Data Sharing and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors’ recommendations. Acadia shares data from completed clinical trials through public registries (https://clinicaltrials.gov), presentation at scientific congresses and through open access in peer-reviewed journals. Clinical study results from this study were submitted to https://clinicaltrials.gov in April 2023. Additional, related information necessary to appraise the quality and robustness of the findings (study protocol, statistical analysis plan) is available in the Supplementary Information. The authors will provide access to individual-deidentified participant-level data that underlie the data presented in this paper, including data dictionaries, the study protocol and other relevant information, to any researcher who provides a methodologically sound proposal for academic purposes to interpret, verify and extend research in the article beginning 6 months and ending 5 years after article publication. Requests for the ‘minimum dataset’ should go through Acadia Medical Information and will be reviewed by the sponsor (Acadia) to verify whether the request is subject to any intellectual property or confidentiality obligations. For additional information, please contact Acadia Medical Information at medicalinformation@acadia-pharm.com. Source data are provided with this paper.