Abstract
Finger tremor was measured in six normal subjects during intravenous infusions of adrenaline (10 ngkg-1min-1 and 50 ngkg-1min-1) resulting in venous plasma adrenaline concentrations within the physiological range (0.77 +/- 0.08 and 2.28 +/- 0.18 nmoll-1). Tremor amplitude significantly increased after 15 and 25 minutes infusion at the higher dose of adrenaline. The lower dose of adrenaline increased tremor in three of the six subjects.
Full text
PDF
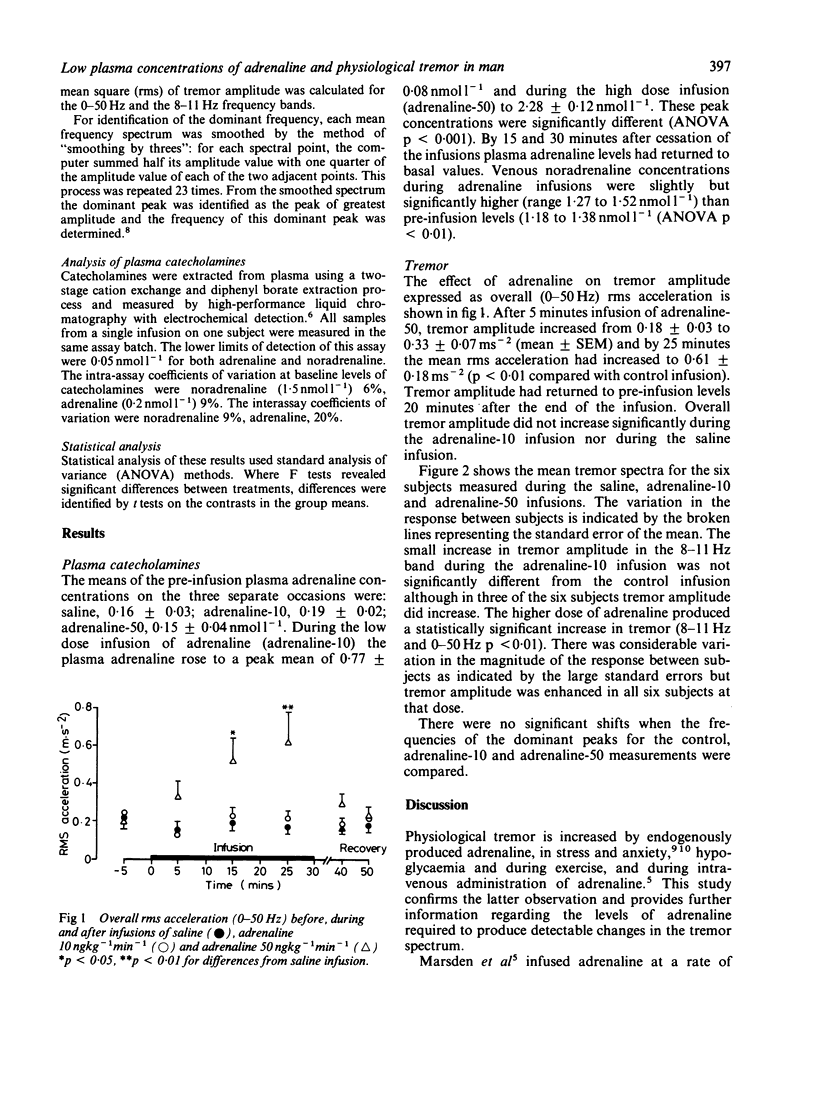
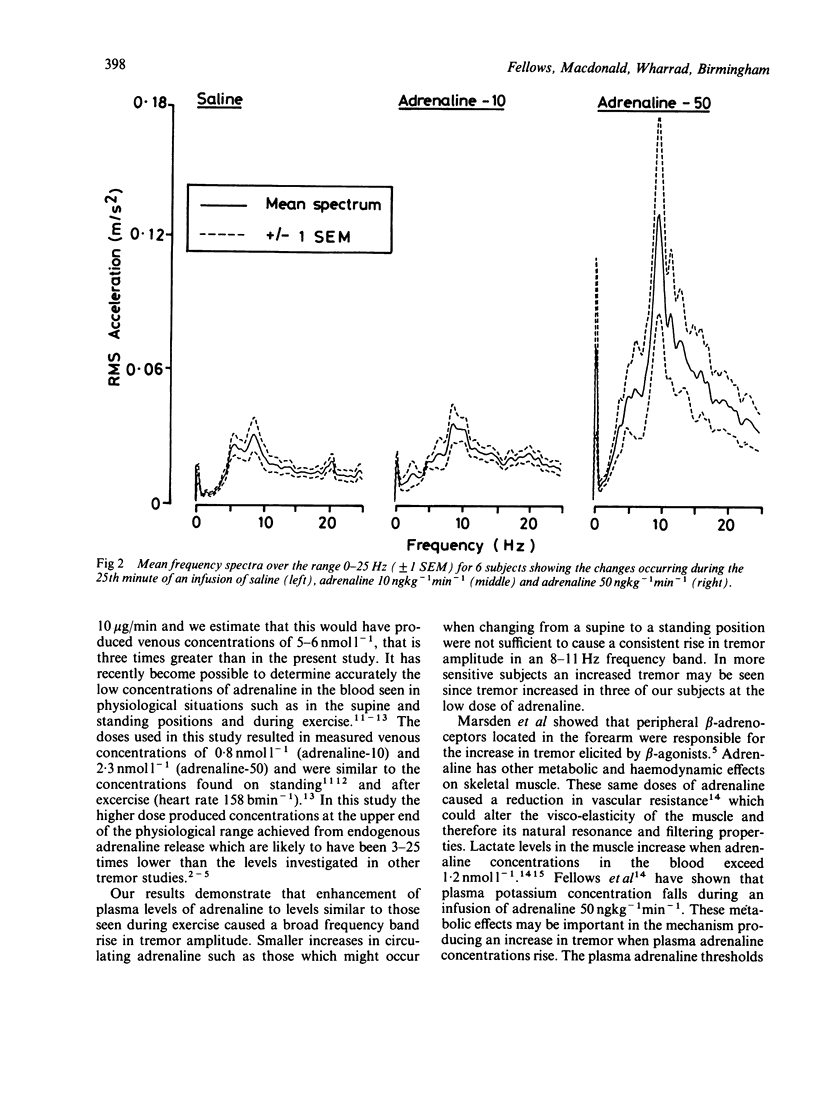

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARCROFT H., PETERSON E., SCHWAB R. S. Action of adrenaline and noradrenaline on the tremor in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1952 Mar-Apr;2(2):154–160. doi: 10.1212/wnl.2.5-6.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONSTAS C. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and isoprenaline on parkinsonian tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 May;25:116–121. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Isotope-derivative measurements of plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine in man. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1071–1082. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows I. W., Bennett T., MacDonald I. A. The effect of adrenaline upon cardiovascular and metabolic functions in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Aug;69(2):215–222. doi: 10.1042/cs0690215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Lake D. M. An improved technique for extracting catecholamines from body fluids. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 May;13(3-4):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Foley T. H., Owen D. A., McAllister R. G. Peripheral beta-adrenergic receptors concerned with tremor. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Schnieden H. Effect of adrenaline, noradrenaline, atropine, and nicotine on some types of human tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Jun;29(3):214–218. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. A., Marsden C. D. Effect of adrenergic beta-blockade on parkinsonian tremor. Lancet. 1965 Dec 18;2(7425):1259–1262. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrer P. J., Lader M. H. Tremor in acute and chronic anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;31(4):506–509. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760160056012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. B., Dalton N. A comparison of the bronchodilator and vasopressor effects of exercise levels of adrenaline in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 May;64(5):475–479. doi: 10.1042/cs0640475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. B., O'Brien M., Dalton N., Turner C. T. Sympathetic activity in benign familial tremor. Lancet. 1984 Feb 25;1(8374):461–462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91804-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


