Abstract
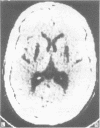
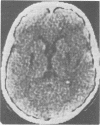
A unique disorder is described in seven members of two families in whom dystonia was variably associated with subacute visual loss or asymptomatic optic atrophy, and striking bilateral symmetrical lucencies on CT scan, especially involving the putamen. It is possible that this is a variant of Leigh's disease. However, there were considerable differences between these patients and those with pathologically proven Leigh's disease. This condition must be excluded in all patients thought to have idiopathic dystonia, subacute visual failure similar to Leber's optic neuropathy, or a combination of these disorders.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aquilonius S. M., Askmark H., Enoksson P., Lundberg P. O., Moström U. Computerised tomography in severe methanol intoxication. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 30;2(6142):929–930. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6142.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARGETON-FARKAS E., COCHARD A. M., BRISSAUD H. E., ROBAIN O., LEBALLE J. C. ENC'EPHALOPATHIE INFANTILE FAMILIALE AVEC N'ECROSE BILAT'ERLE ET SYM'ETRIQUE DES CORPS STRI'ES. J Neurol Sci. 1964 Sep-Oct;1(5):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(64)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton K., Farrell K., Li D., Calne D. B. Lesions of the putamen and dystonia: CT and magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):962–965. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN E., MELCHIOR J., PLUM P. Combined lesions of basal ganglia, medulla oblongata, and spinal cord in a 10 year old boy. Acta Paediatr. 1956 Jul;45(4):396–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1956.tb06890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton B. E., Dobbs R. H., Patrick A. D. Leigh's subacute necrotizing encephalopathy: clinical and biochemical study, with special reference to therapy with lipoate. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Oct;42(225):467–478. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.225.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David R. B., Gomez M. R., Okazaki H. Necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh). Dev Med Child Neurol. 1970 Aug;12(4):436–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1970.tb01937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan A. D., Ockenden B. G., Crome L. Necrotizing encephalomyelopathy of Leigh. Neuropathological findings in 8 cases. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Feb;45(239):39–48. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.239.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVivo D. C., Haymond M. W., Obert K. A., Nelson J. S., Pagliara A. S. Defective activation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh disease). Ann Neurol. 1979 Dec;6(6):483–494. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooling E. C., Schoene W. C., Richardson E. P., Jr Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jan;30(1):70–83. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490310072012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans O. B. Pyruvate decarboxylase deficiency in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. Arch Neurol. 1981 Aug;38(8):515–519. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510080077012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIN R., GRUNER J., GODLEWSKI S. Spongiose disséminée de l'encéphale evoluant cliniquement par poussées chez un enfant malgache; ses rapports éventuels avec l'encéphalopathie subaiguë de Wernicke. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1956 Oct;95(4):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Katz D., Rapin I., Purpura D. P., Suzuki K. Chronic GM1 gangliosidosis presenting as dystonia: I. Clinical and pathological features. Ann Neurol. 1981 May;9(5):465–475. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutières F., Aicardi J. Acute neurological dysfunction associated with destructive lesions of the basal ganglia in children. Ann Neurol. 1982 Oct;12(4):328–332. doi: 10.1002/ana.410120403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Gardner-Medwin D. CT scan appearances in Leigh's disease (subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy). Neuroradiology. 1978;16:48–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00395200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommes F. A., Polman H. A., Reerink J. D. Leigh's encephalomyelopathy: an inborn error of gluconeogenesis. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Aug;43(230):423–426. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.230.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. O., Albert D. M. Ocular manifestations of subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh's disease). Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Sep;74(3):386–393. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90896-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo H., Lundberg P. O., Olsson Y. Familial subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy of the adult form (adult Leigh syndrome). Ann Neurol. 1979 Sep;6(3):200–206. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Stein R. W., Tanner C. M., Goetz C. G. A pure parkinsonian syndrome following acute carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1982 May;39(5):302–304. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510170044012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIGH D. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy in an infant. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1951 Aug;14(3):216–221. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.14.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplane D., Baulac M., Widlöcher D., Dubois B. Pure psychic akinesia with bilateral lesions of basal ganglia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Apr;47(4):377–385. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.4.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Akimoto H., Enomoto T. Injuries of basal ganglia following head trauma in children. Childs Brain. 1980;7(3):113–123. doi: 10.1159/000119936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark R. E., Kaloni P. N., Tang R. C., Gillis P. P. Cellulose: refutation of a folded-chain structure. Science. 1969 Apr 4;164(3875):72–73. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3875.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux P. Un nouveau type de mucopolysaccharidose avec athétose et élimination urinaire de kératan-sulfate. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 Apr 14;2(15):975–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo F., Cummins J. W., Anderson R. E. Neurological sequelae of massive hydrogen sulfide inhalation. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jul;36(7):451–452. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500430081019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D., Wolfe L. S., Andermann E., Andermann F. Juvenile progressive dystonia: a new phenotype of GM2 gangliosidosis. Ann Neurol. 1984 Apr;15(4):348–352. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn D. B., Hertzanu Y., Chaitowitz B., Cartwright J. D. Cranial CT in the haemolytic uraemic syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;47(8):876–878. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.8.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Matsuoka T., Mizushima S. Familial holotopistic striatal necrosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;13(3):240–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00690644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville B. G., Lake B. D., Stephens R., Sanders M. D. A neurovisceral storage disease with vertical supranuclear ophthalmoplegia, and its relationship to Niemann-Pick disease. A report of nine patients. Brain. 1973;96(1):97–120. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen E., Sogg R. L., Rosenthal A. R., Friberg T. R., Dorfman L. J. The early phase in Leber hereditary optic atrophy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977 Jun;95(6):969–978. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1977.04450060055002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis S. G., Phillips P. C., DiMauro S., De Vivo D. C., Rowland L. P. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):481–488. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson H. de C., Alvord E. C., Jr Necrotizing encephalopathy with predilection for the brainstem. Subacute infantile and chronic juvenile familial forms. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1964;89:104–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus J. H., Cooper J. R., Murphy J. V., Rabe E. F., Lonsdale D., Dunn H. G. Thiamine derivatives in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. A preliminary report. Pediatrics. 1973 Apr;51(4):716–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus J. H. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh's disease): a consideration of clinical features and etiology. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1972 Feb;14(1):87–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb02563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondot P., de Recondo J., Davous P., Fredy D., Roux F. X. Rigidité extra-pyramidale avec dystonie, atrophie optique et atteinte bilatérale du putamen chez un adolescent. Forme juvénile de la maladie de Leigh. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1982;138(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. N., Schotland D. L., Lovelace R. E., Rowland L. P. Progressive ophthalmoplegia. Report of cases. Arch Neurol. 1968 Oct;19(4):362–376. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480040028002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing H. S., Hopkins L. C., Wallace D. C., Epstein C. M., Weidenheim K. Maternally inherited mitochondrial myopathy and myoclonic epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):228–237. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge J. C., Haas J. E., Monnat R., Milstein J. M. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a component of subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. J Pediatr. 1982 Nov;101(5):706–710. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W. J., Hutchison H. T., Berg B. O. Computerized tomography in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh disease). Ann Neurol. 1981 Sep;10(3):268–271. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorbi S., Blass J. P. Abnormal activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in Leigh disease fibroblasts. Neurology. 1982 May;32(5):555–558. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.5.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLWILL F. J., PAINE R. S. Progressive demyelinating leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 1958 Apr;8(4):285–295. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.4.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashon D., Jane J. A. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy of infancy and childhood. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jan;20(1):28–37. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]