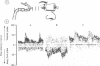Abstract
Pulsed wave 2 MHz Doppler with acoustical focusing was used to obtain blood flow velocity recordings through the intact cranium in 11 patients with occlusive disease of major intracranial arteries. Increased blood flow velocities were recorded from stenoses of the carotid siphon and of the middle cerebral, anterior cerebral and basilar arteries. A clear, inverse relationship existed between angiographical residual lumen diameter and flow velocity. The Kendall rank correlation coefficient (Tau) was -0.89 (p = 0.0001). Transcranial Doppler is a useful means for evaluating patients with this disorder.
Full text
PDF
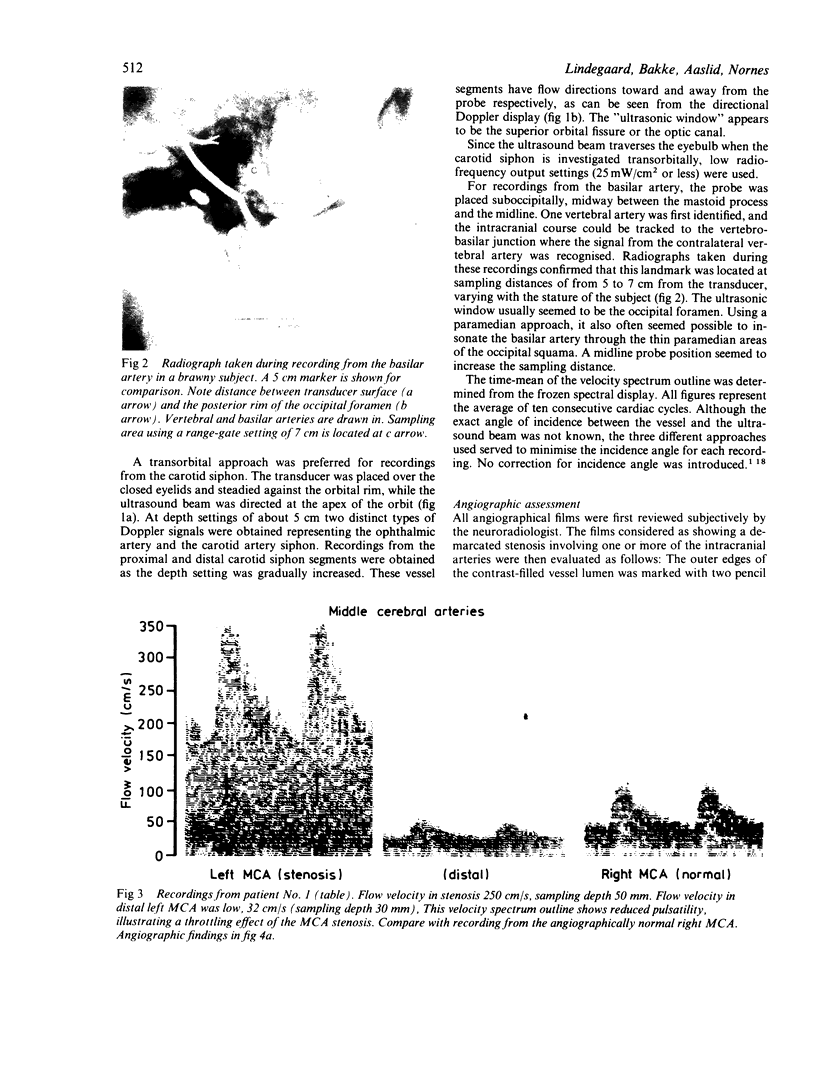
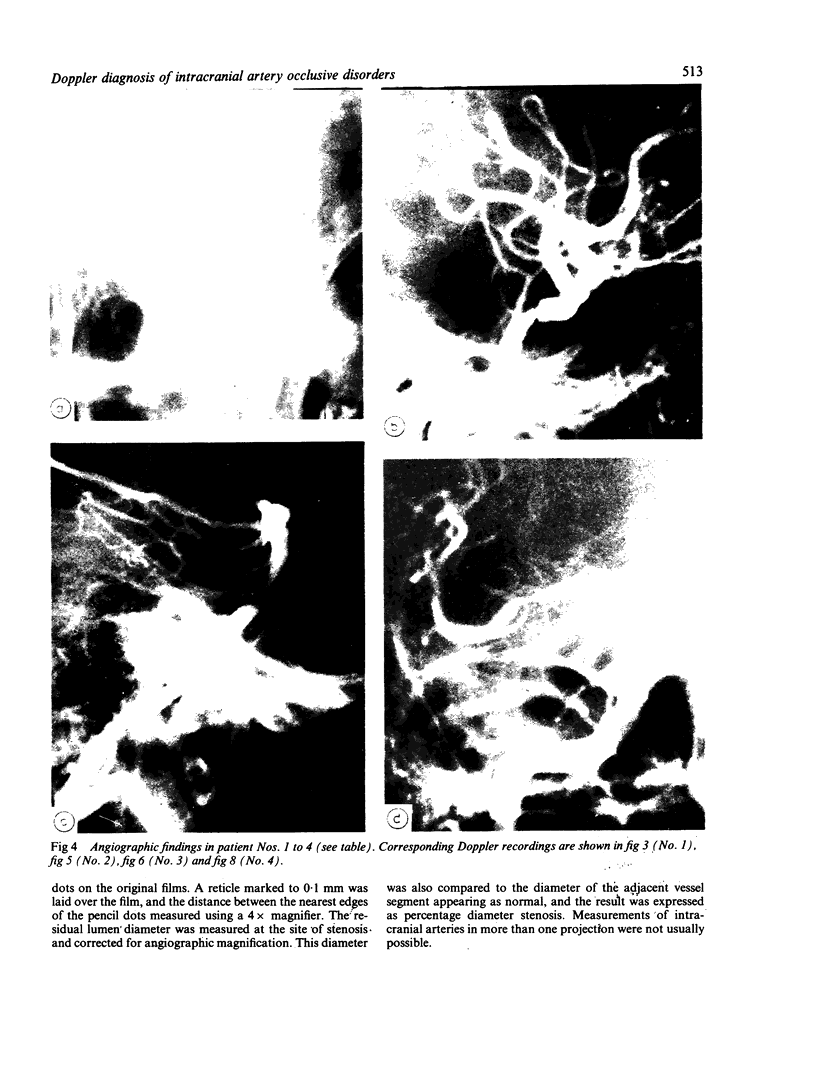
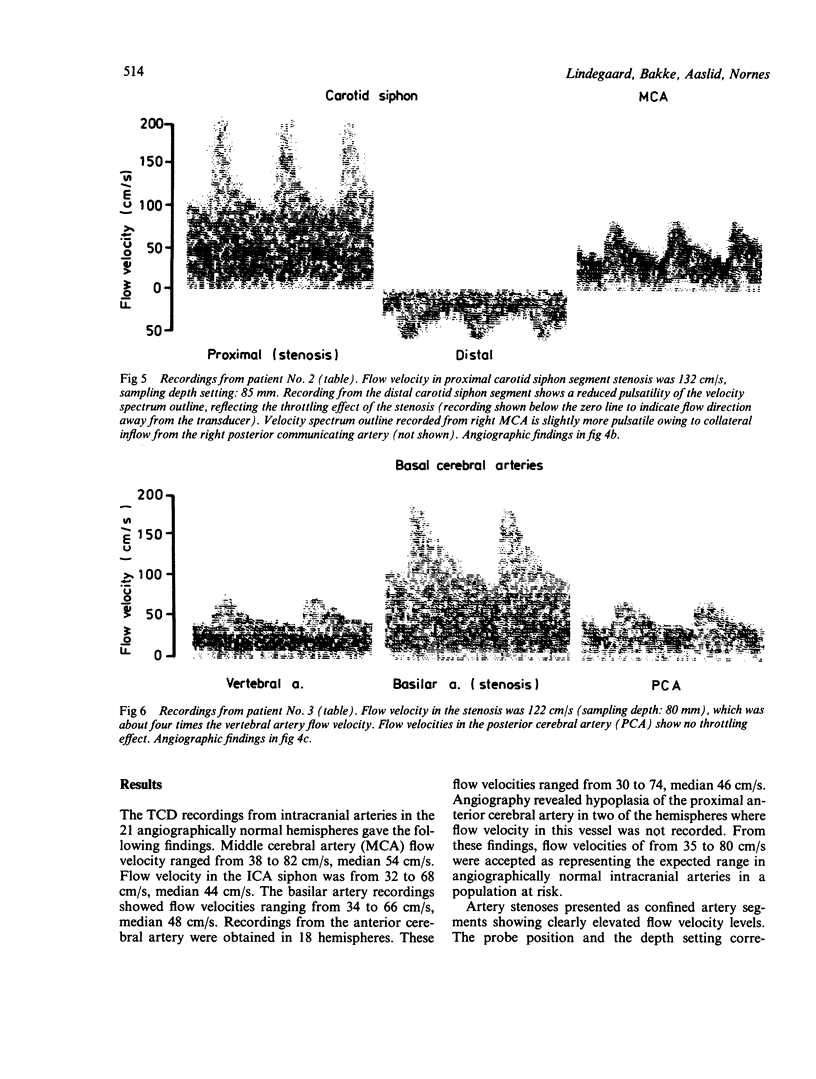
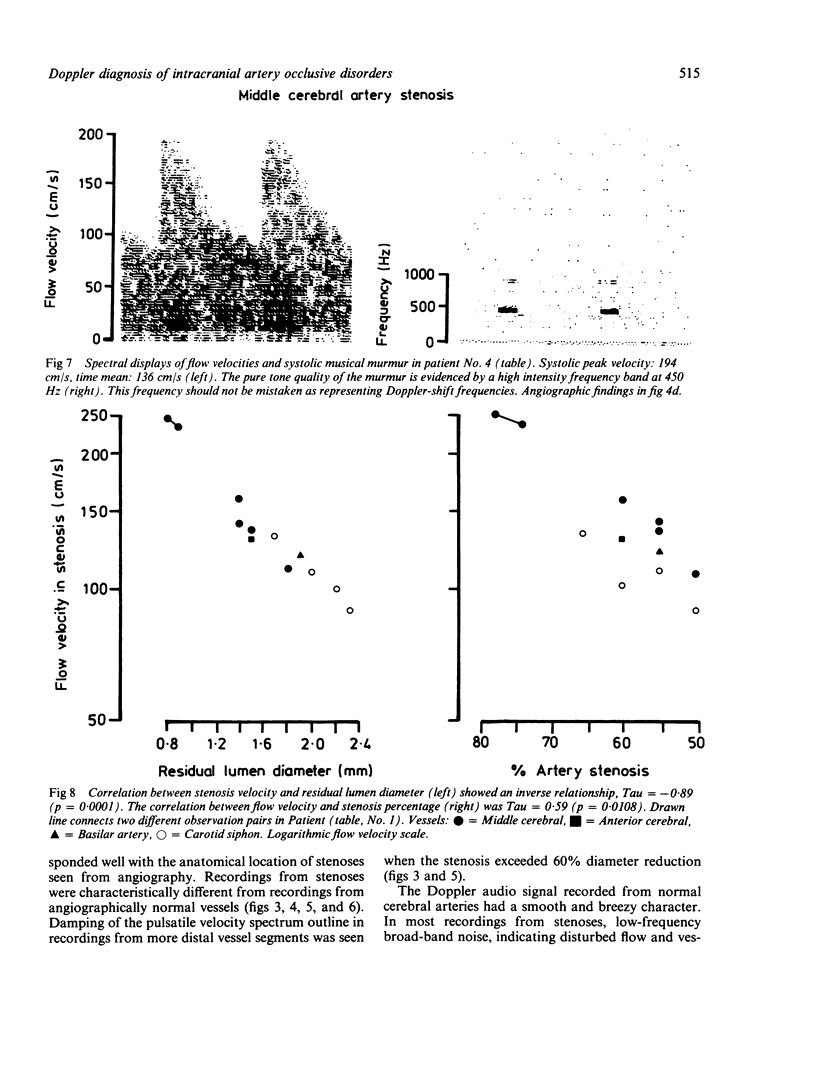



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaslid R., Huber P., Nornes H. Evaluation of cerebrovascular spasm with transcranial Doppler ultrasound. J Neurosurg. 1984 Jan;60(1):37–41. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.1.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaslid R., Markwalder T. M., Nornes H. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1982 Dec;57(6):769–774. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.57.6.0769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaslid R., Nornes H. Musical murmurs in human cerebral arteries after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1984 Jan;60(1):32–36. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.1.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Fischer G. G. Impact of digital subtraction angiography on carotid evaluation. Stroke. 1985 Jan-Feb;16(1):23–28. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berguer R., Hwang N. H. Critical arterial stenosis: a theoretical and experimental solution. Ann Surg. 1974 Jul;180(1):39–50. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197407000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear W. M., Jr, Connar R. G. Carotid endarterectomy without angiography. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1982 Nov-Dec;23(6):477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corston R. N., Kendall B. E., Marshall J. Prognosis in middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke. 1984 Mar-Apr;15(2):237–241. doi: 10.1161/01.str.15.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crew J. R., Dean M., Johnson J. M., Knighton D., Bashour T. T., Ellertson D., Hanna E. S. Carotid surgery without angiography. Am J Surg. 1984 Aug;148(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. L. Indications for surgical intervention in middle cerebral artery obstruction. J Neurosurg. 1984 Feb;60(2):296–304. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.2.0296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. L. Cerebral arterial revascularization: the value of repeated angiography in selection of patients for operation. Neurosurgery. 1978 May-Jun;2(3):205–209. doi: 10.1227/00006123-197805000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan A. J., Little J. R., Dohn D. F. Arterial occlusion following anastomosis of the superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery. Stroke. 1980 Jan-Feb;11(1):91–95. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen T. O., Greitz T. Normal size of the internal carotid, middle cerebral and anterior cerebral arteries. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1970 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1177/028418517001000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumerlock M. K., Ono H., Neuwelt E. A. Can a patent extracranial-intracranial bypass provoke the conversion of an intracranial arterial stenosis to a symptomatic occlusion? Neurosurgery. 1983 Apr;12(4):391–400. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198304000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton R. C., Mohr J. P., Ackerman R. H., Adair L. B., Fisher C. M. Symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis. Ann Neurol. 1979 Feb;5(2):152–157. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holen J., Aaslid R., Landmark K., Simonsen S. Determination of pressure gradient in mitral stenosis with a non-invasive ultrasound Doppler technique. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(6):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye A. H., Little J. R., Bryerton B., Modic M. Intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients for carotid endarterectomy. J Neurosurg. 1983 Nov;59(5):835–838. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.59.5.0835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindegaard K. F., Bakke S. J., Grip A., Nornes H. Pulsed Doppler techniques for measuring instantaneous maximum and mean flow velocities in carotid arteries. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1984 Jul-Aug;10(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(84)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindegaard K. F., Bakke S. J., Grolimund P., Aaslid R., Huber P., Nornes H. Assessment of intracranial hemodynamics in carotid artery disease by transcranial Doppler ultrasound. J Neurosurg. 1985 Dec;63(6):890–898. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.63.6.0890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massimo C., Orazio A., Felice F. Bypass surgery in patients with intracranial stenotic lesions. Postoperative morbidity and angiographic findings. J Neurosurg. 1985 Apr;62(4):532–538. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.4.0532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi H., Sawada T., Kuriyama Y., Kinugawa H., Kaneko T., Takamiya M. Effect of chronic middle cerebral artery stenosis on the local cerebral hemodynamics. Stroke. 1985 Mar-Apr;16(2):214–219. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reneman R. S., Spencer M. P. Local Doppler audio spectra in normal and stenosed carotid arteries in man. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1979;5(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(79)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D., Lindegaard K. F., Nakstad P., Nyberg-Hansen R., Oygarden K. G. Detection of carotid occlusive disease by pulsed Doppler spectral analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Dec;47(12):1307–1313. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.12.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. P., Reid J. M. Quantitation of carotid stenosis with continuous-wave (C-W) Doppler ultrasound. Stroke. 1979 May-Jun;10(3):326–330. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundt T. M., Jr, Siekert R. G., Piepgras D. G., Sharbrough F. W., Houser O. W. Bypass surgery for vascular disease of the carotid system. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Nov;51(11):677–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]