Fig. 3 |. Tumours have lower TCA flux compared with healthy tissues.
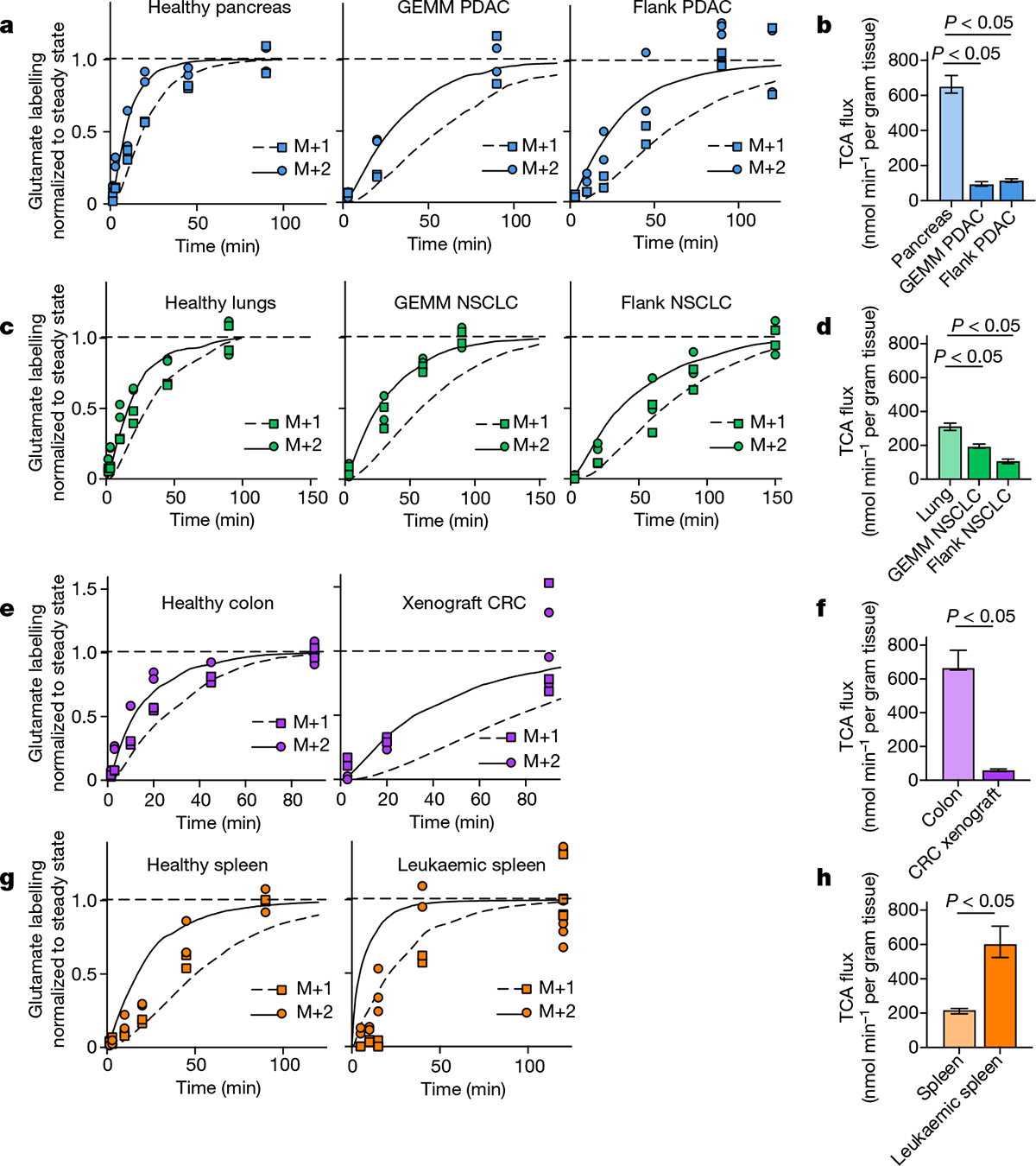
a, Glutamate M+2 and M+1 labellingusing a [U-13C]lactate primed infusion in healthy pancreas, in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Pdx1-cre;LSL-KrasG12D/+Trp53−/− (GEMM PDAC)) and in a flank-implanted model of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (implanted tumour fragments were Pdx1-cre;LSL-KrasG12D/+Trp53R172H/+ (flank PDAC)), normalized to steady-state labelling (labelling at the latest timepoint measured). b, TCA fluxes of pancreas and pancreatic tumour models. Primed infusion timepoints in n = 12 mice (pancreas), n = 6 (GEMM PDAC), n = 13 (flank PDAC); tissue metabolite concentrations in n = 4 mice per tissue or tumour. c,d, Glutamate labelling (c) and TCA fluxes (d) for healthy lung, a genetically engineered mouse model of non-small cell lung cancer (adenovirus-cre LSL-KrasG12D/+; Stk11−/−;Trp53−/− (GEMM NSCLC)) and a flank-implanted model of non-small cell lung cancer (implanted cell line derived from tumour that was adenovirus-cre LSL-KrasG12D/+;Trp53−/− (flank NSCLC)). Primed infusion timepoints in n = 12 mice (lung), n = 9 (GEMM NSCLC), n = 10 (flank NSCLC); tissue metabolite concentrations in n = 4 mice per tissue. e,f, Glutamate labelling (e) and TCA fluxes (f) for healthy colon and a xenograft of the human colorectal cancer cell line HCT116 (xenograft CRC). Primed infusion timepoints in n = 12 mice (colon) and n = 7 mice (xenograft CRC); tissue metabolite concentrations in n = 4 mice per tissue. g,h, Glutamate labelling (g) and TCA fluxes (h) for healthy spleen and spleen from mice with transplanted NOTCH1-constitutively-active mouse T acute lymphocytic leukaemia (leukaemic spleen). Primed infusion timepoints in n = 12 mice (healthy spleen) and n = 15 mice (leukaemic spleen); tissue metabolite concentrations in n = 3 mice (healthy spleen) and n = 4 mice (leukaemic spleen). All measured healthy tissues were from non-tumour-bearing mice. For b, d, f and h, data are best estimates of flux from computational fitting of experimental data ± s.d. For b, d, f and h, P values were calculated using two-tailed t-tests.
