Abstract
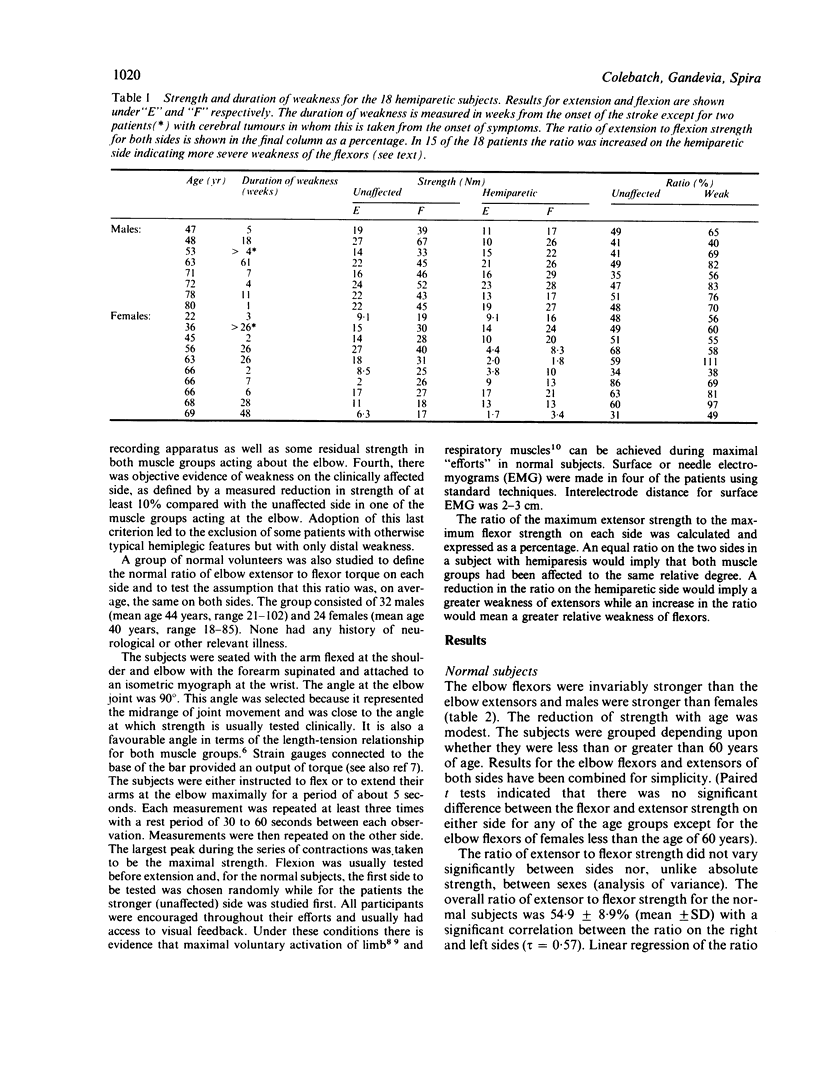
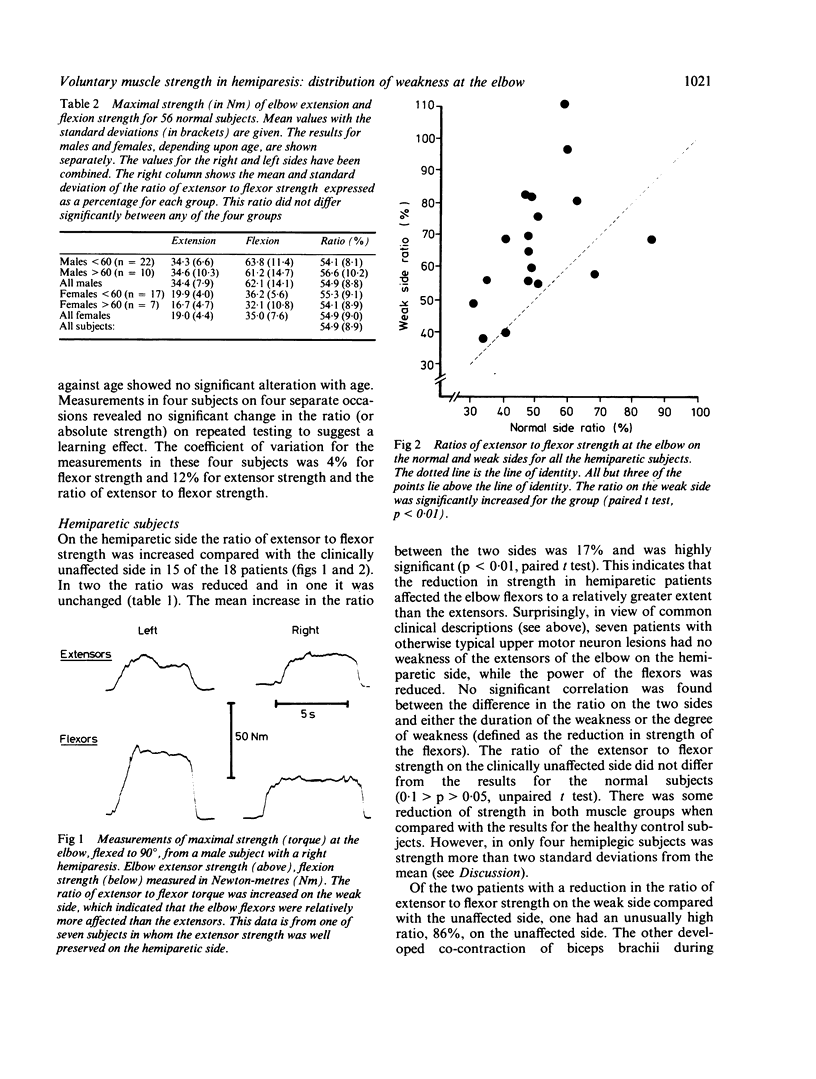
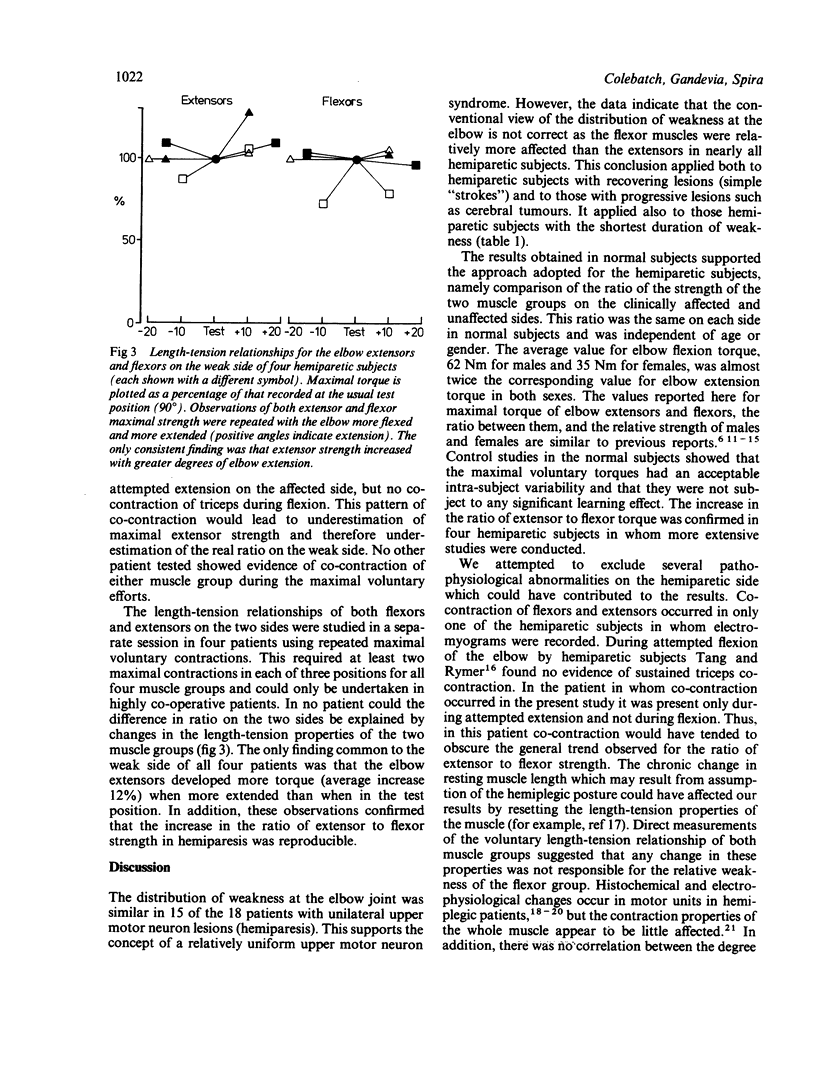
Maximal voluntary strength (torque) of the flexors and extensors of the elbow was measured in 56 normal subjects and 18 hemiparetic subjects. In normal subjects the ratio of extension to flexion strength averaged 55% and did not differ significantly between sides or sexes. The ratio of maximal extensor to flexor strength on the clinically unaffected side of hemiparetic subjects was the same as that for the normal subjects but it was significantly increased on the affected side. This increase indicates that the elbow flexors were relatively more weakened than the extensors on the hemiparetic side, a conclusion contrary to conventional clinical teaching. The increase in the ratio was not the result of co-contraction of either muscle group. A possible physiological basis for the observed distribution of weakness is suggested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELKINS E. C., LEDEN U. M., WAKIM K. G. Objective recording of the strength of normal muscles. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1951 Oct;32(10):639–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L. Selective changes in the sizes of red and white muscle fibres in upper motor lesions and Parkinsonism. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Dec;11(6):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McKenzie D. K. Activation of the human diaphragm during maximal static efforts. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:45–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McKenzie D. K., Neering I. R. Endurance properties of respiratory and limb muscles. Respir Physiol. 1983 Jul;53(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldspink G., Tabary C., Tabary J. C., Tardieu C., Tardieu G. Effect of denervation on the adaptation of sarcomere number and muscle extensibility to the functional length of the muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):733–742. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail H. M., Ranatunga K. W. Isometric contractions of normal and spastic human skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1981 May-Jun;4(3):214–218. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasser R. J., Cheney P. D. Characteristics of corticomotoneuronal postspike facilitation and reciprocal suppression of EMG activity in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):959–978. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard E., Houston M., Suzuki Y., Jørgensen K., Saltin B. Morphology of the brachial biceps muscle and elbow flexion in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Feb;117(2):287–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. THE PYRAMIDAL PROJECTION TO MOTONEURONES OF SOME MUSCLE GROUPS OF THE BABOON'S FORELIMB. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:222–245. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROVINS K. A., SALTER N. Maximum torque exerted about the elbow joint. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jan;7(4):393–398. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.7.4.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Karpovich P. V. Isotonic and isometric forces of forearm flexors and extensors. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jul;21(4):1435–1437. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.4.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWITCHELL T. E. The restoration of motor function following hemiplegia in man. Brain. 1951 Dec;74(4):443–480. doi: 10.1093/brain/74.4.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A., Rymer W. Z. Abnormal force--EMG relations in paretic limbs of hemiparetic human subjects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Aug;44(8):690–698. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.8.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. L., Mayer R. F. Physiological alterations of motor units in hemiplegia. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Jun;54(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


