Abstract
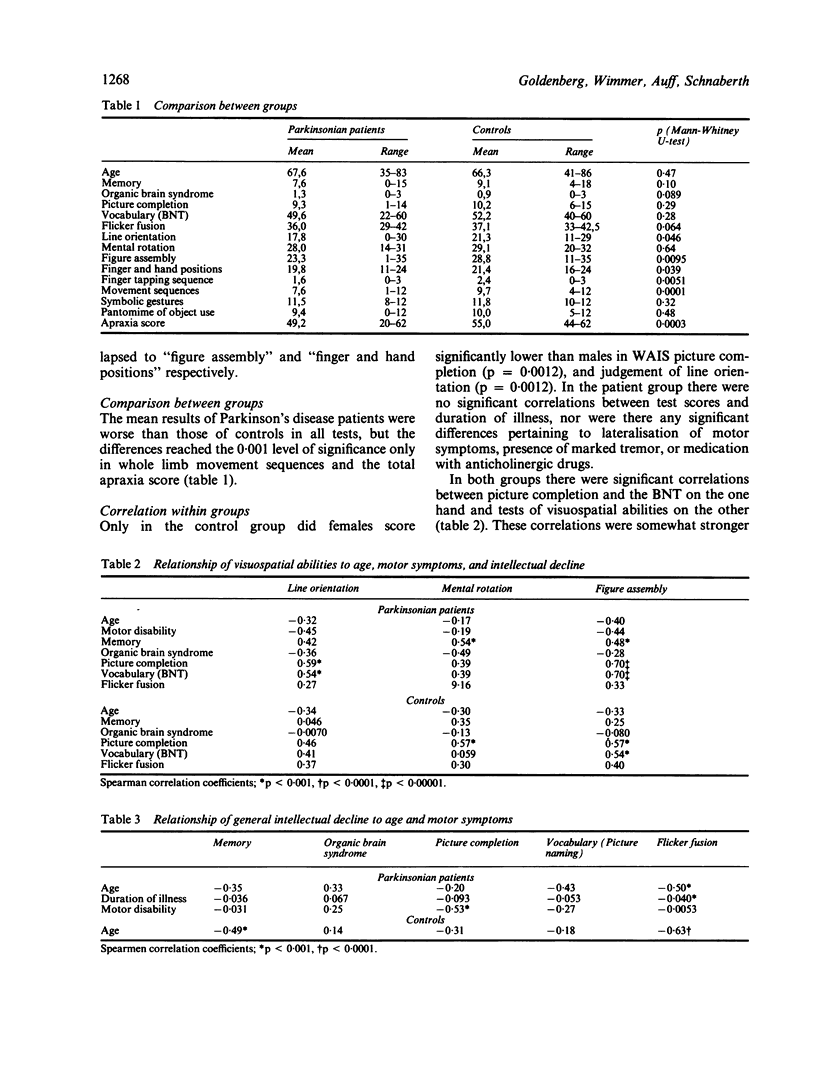
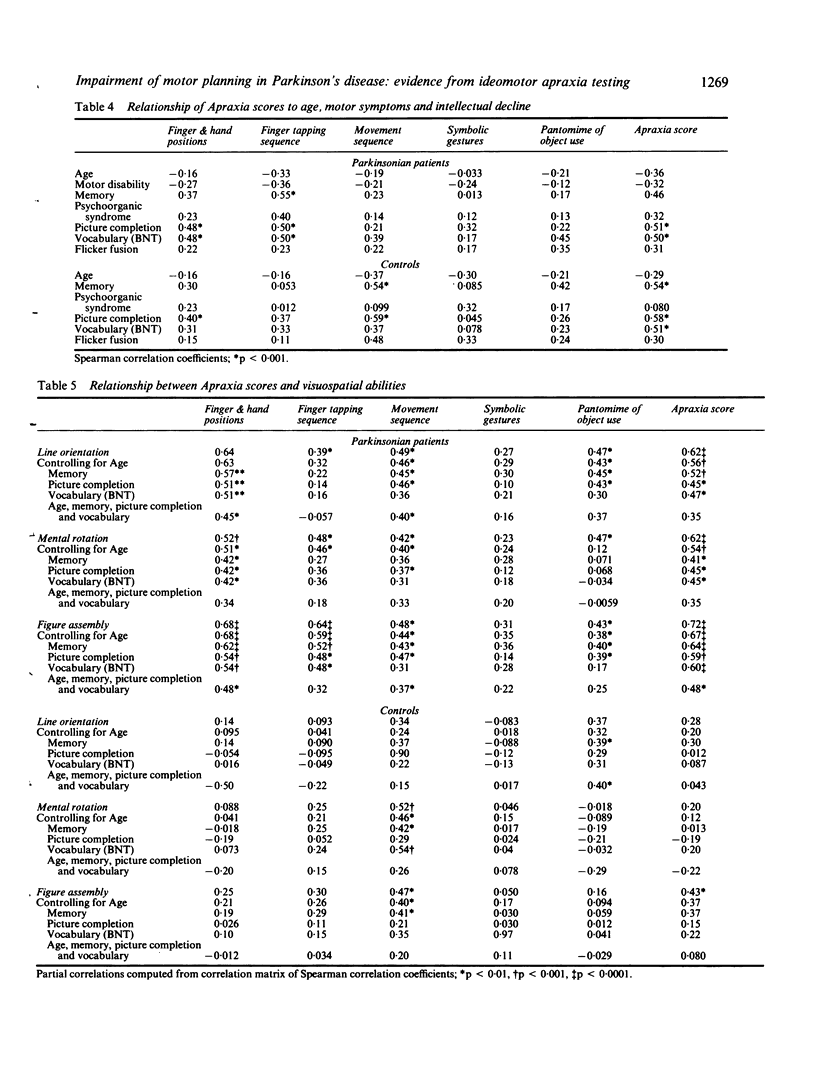
Compared with a group of age matched controls, patients with Parkinson's disease scored significantly lower in testing for ideomotor apraxia. Imitation of movement sequences was affected more severely than performance of single movements. The degree of impairment was not related to severity of motor disability, but correlated strongly with the results of tests that measured visuospatial and visuoperceptive abilities. It is suggested that defective encoding and central processing of visuospatial information impairs memory for movement which is necessary for correct imitation of movements. Enhanced vulnerability to interference between successively presented items may cause further deterioration of performance in the copying of movement sequences.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkmayer W., Neumayer E. Die moderne medikamentöse Behandlung des Parkinsonismus. Z Neurol. 1972;202(4):257–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller F., Passafiume D., Keefe N. C., Rogers K., Morrow L., Kim Y. Visuospatial impairment in Parkinson's disease. Role of perceptual and motor factors. Arch Neurol. 1984 May;41(5):485–490. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050170031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., van den Bercken J. H., Horstink M. W., van Spaendonck K. P., Berger H. J. Cognitive and motor shifting aptitude disorder in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 May;47(5):443–453. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.5.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn M. M., Yahr M. D. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967 May;17(5):427–442. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hore J., Meyer-Lohmann J., Brooks V. B. Basal ganglia cooling disables learned arm movements of monkeys in the absence of visual guidance. Science. 1977 Feb 11;195(4278):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.402029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kertesz A., Ferro J. M. Lesion size and location in ideomotor apraxia. Brain. 1984 Sep;107(Pt 3):921–933. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.3.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees A. J., Smith E. Cognitive deficits in the early stages of Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1983 Jun;106(Pt 2):257–270. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. Function of the basal ganglia as revealed by cognitive and motor disorders in Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):129–135. doi: 10.1017/s031716710004628x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y. Intellectual dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease. Adv Neurol. 1983;38:211–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer J. A., Pirozzolo F. J., Hansch E. C., Webster D. D. Relationship of motor symptoms to intellectual deficits in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1982 Feb;32(2):133–137. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR F., RIKLAN M., COOPER I. S., TEUBER H. L. JUDGMENT OF VISUAL AND POSTURAL VERTICAL BY PARKINSONIAN PATIENTS. Neurology. 1964 Apr;14:287–293. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poeck K. The two types of motor apraxia. Arch Ital Biol. 1982 May;120(1-3):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff G. Spatial thought, mental rotation and the right cerebral hemisphere. Neuropsychologia. 1979;17(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(79)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. H., Cermak S. A., Sax D. S. Motor planning in Parkinson patients. Neuropsychologia. 1983;21(5):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(83)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storandt M., Botwinick J., Danziger W. L., Berg L., Hughes C. P. Psychometric differentiation of mild senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch Neurol. 1984 May;41(5):497–499. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050170043013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe B. T., Hirst W. Amnesia following the rupture and repair of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Aug;46(8):704–709. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.8.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


