Abstract
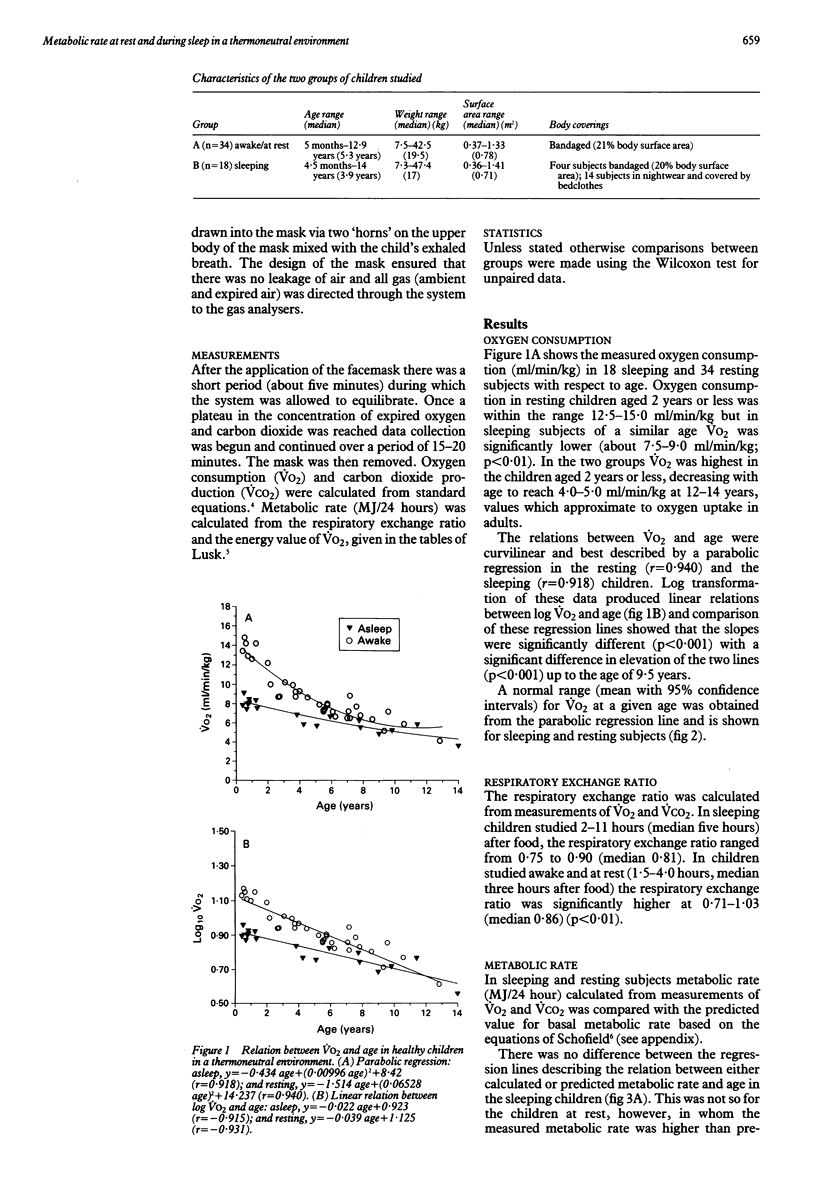
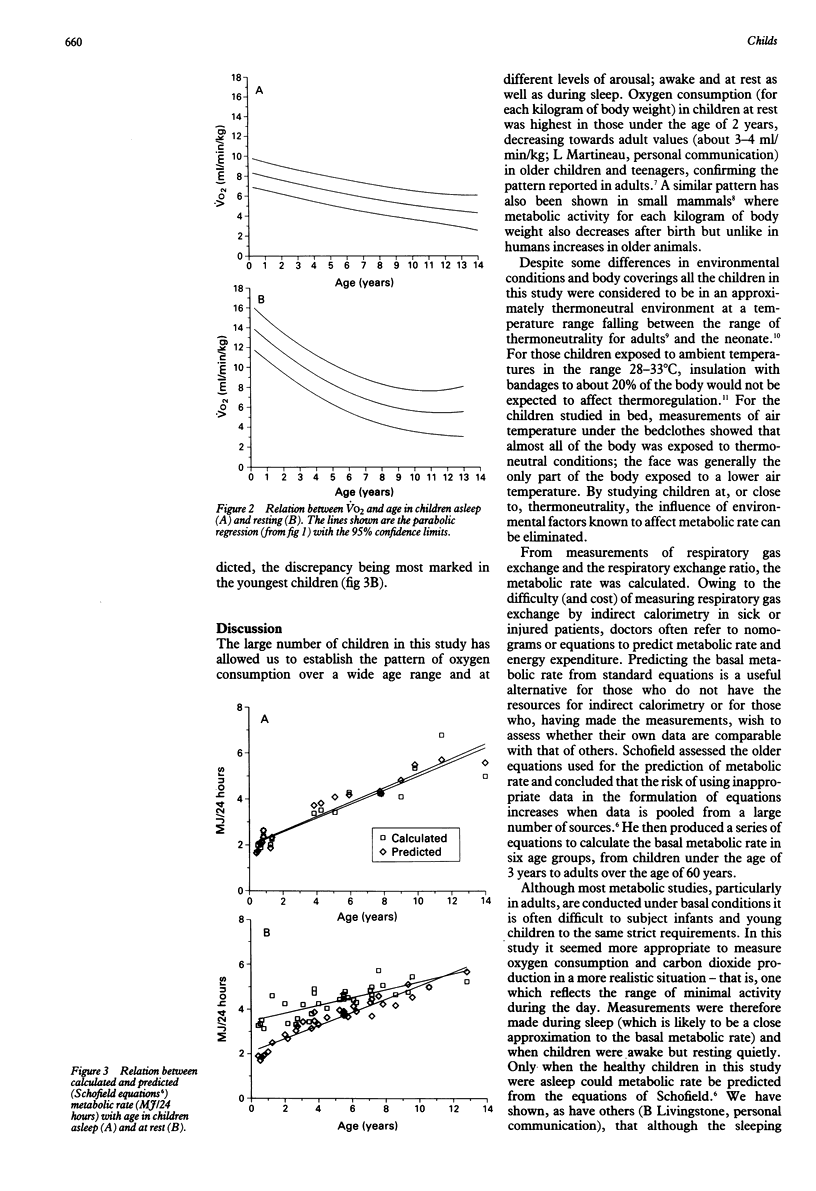
This study characterised the pattern of oxygen consumption (VO2) in healthy infants and children asleep and awake (at rest) in a thermoneutral environment. Measurement of respiratory gas exchange (VO2 and VCO2) was made using an open circuit flow through system of indirect calorimetry with a specially designed facemask for the collection of exhaled breath. Fifty two healthy subjects aged 4.5 months to 12.8 years were studied for 15-20 minutes; 18 during sleep and 34 at rest (awake). There was a curvilinear relation between VO2 and age in the two groups and children aged 2 years or less had the highest values. The value of VO2 was significantly higher in the awake subjects (12.5-15.0 ml/min/kg compared with 7.5-9.0 ml/min/kg in sleeping children). Comparison of the regression lines after log transformation of these data showed a significant difference in VO2 of resting and sleeping subjects up to the age of 9.5 years.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Childs C., Stoner H. B., Little R. A., Davenport P. J. A comparison of some thermoregulatory responses in healthy children and in children with burn injury. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Oct;77(4):425–430. doi: 10.1042/cs0770425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey E. Thermal neutrality. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness K., Childs C. Development of an indirect calorimeter for use in infants and young children. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1991 Nov;12(4):343–351. doi: 10.1088/0143-0815/12/4/004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgatroyd P. R., Davies H. L., Prentice A. M. Intra-individual variability and measurement noise in estimates of energy expenditure by whole body indirect calorimetry. Br J Nutr. 1987 Nov;58(3):347–356. doi: 10.1079/bjn19870104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


