ABSTRACT
The opportunistic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses the LasR-I quorum-sensing system to increase resistance to the aminoglycoside antibiotic tobramycin. Paradoxically, lasR-null mutants are commonly isolated from chronic human infections treated with tobramycin, suggesting there may be a mechanism that permits the emergence of lasR-null mutants under tobramycin selection. We hypothesized that some other genetic mutations that emerge in these isolates might modulate the effects of lasR-null mutations on antibiotic resistance. To test this hypothesis, we inactivated lasR in several highly tobramycin-resistant isolates from long-term evolution experiments. In some of these isolates, inactivating lasR further increased resistance, compared with decreasing resistance of the wild-type ancestor. These strain-dependent effects were due to a G61A nucleotide polymorphism in the fusA1 gene encoding amino acid substitution A21T in the translation elongation factor EF-G1A. The EF-G1A mutational effects required the MexXY efflux pump and the MexXY regulator ArmZ. The fusA1 mutation also modulated ΔlasR mutant resistance to two other antibiotics, ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime. Our results identify a gene mutation that can reverse the direction of the antibiotic selection of lasR mutants, a phenomenon known as sign epistasis, and provide a possible explanation for the emergence of lasR-null mutants in clinical isolates.
IMPORTANCE One of the most common mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates is in the quorum sensing lasR gene. In laboratory strains, lasR disruption decreases resistance to the clinical antibiotic tobramycin. To understand how lasR mutations emerge in tobramycin-treated patients, we mutated lasR in highly tobramycin-resistant laboratory strains and determined the effects on resistance. Disrupting lasR enhanced the resistance of some strains. These strains had a single amino acid substitution in the translation factor EF-G1A. The EF-G1A mutation reversed the selective effects of tobramycin on lasR mutants. These results illustrate how adaptive mutations can lead to the emergence of new traits in a population and are relevant to understanding how genetic diversity contributes to the progression of disease during chronic infections.
KEYWORDS: LasR, antibiotic resistance, evolution, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, quorum sensing, tobramycin
INTRODUCTION
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic multidrug-resistant pathogen that regulates about 10% of its genes using quorum sensing, a type of bacterial communication that is activated in a population density-dependent manner (1–4). One type of quorum sensing involves a LuxR-family signal receptor and a LuxI-family signal synthase (2, 5, 6). In P. aeruginosa, there are two complete LuxR-I-type quorum-sensing systems; the LasR-I system, which produces and responds to the signal N-3-oxododecanoyl-homoserine lactone (3OC12-HSL) (2–4, 7), and the RhlR-I system, which produces and responds to the signal N-butanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL) (8). In laboratory strains, the LasR-I system regulates the expression of the rhlR and rhlI genes, resulting in a hierarchy in quorum sensing, wherein LasR is the master regulator (5, 7, 9). The LasR-I system is essential for pathogenesis in several acute infection animal models (10–12).
We, and others, have shown that the LasR-I system increases P. aeruginosa resistance to tobramycin, a clinically relevant antibiotic that is commonly used to treat acute and chronic P. aeruginosa infections (13–17). Quorum-sensing systems in other bacteria can also increase antibiotic resistance (18), suggesting that the control of antibiotic resistance by quorum sensing might provide some advantages that are conserved across several bacterial species and environments. The P. aeruginosa LasR-I system increases tobramycin resistance in planktonic cultures (17) and also in biofilm conditions (13–16). Tobramycin can also suppress the proliferation of lasR mutants that emerge de novo during the propagation of populations in certain conditions in the laboratory (17). These results suggest tobramycin treatment could have a strong selective pressure on quorum sensing in a clinical setting.
Clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa are remarkably genetically diverse in part due to adaptations to the cystic fibrosis lung environment (19–21). One of the most commonly observed adaptations in clinical infections is a lasR mutation, resulting in the loss of quorum-sensing function (21–25). Although LasR contributes to pathogenesis in acute infection models with laboratory strains (26–28), the emergence of LasR mutants in a clinical setting correlates with worse outcomes in infection (22, 29–32). It is counterintuitive that lasR-null mutations emerge in infections of patients treated with tobramycin when these mutations increase sensitivity to tobramycin in laboratory strains. There are several potential explanations for this puzzling finding. Certain nutritional conditions can select for lasR mutants (23, 33–35), which could possibly overcome tobramycin effects. Alternatively, some conditions have been shown to alter the physiology of lasR mutants to make them more tobramycin resistant (36, 37). Whether the conditions of the infection environment contribute to the selection of lasR mutations in infections of tobramycin-treated patients remains unknown.
Here, we sought to explore another possibility for lasR mutant emergence in infections of tobramycin-treated patients: the possibility that the effects of tobramycin on lasR-null mutants might be dependent on genetic background. In particular, we hypothesized that the tobramycin susceptibility of ΔlasR mutants might be modified by epistatic gene interactions (38). We identify one such mutation, a point mutation in the gene encoding the translation accessory factor EF-G1A (fusA1). We show that fusA1 G61A (EF-G1AA21T) facilitates the emergence of ΔlasR mutations in populations under tobramycin selection. Our results show that antibiotic susceptibility of lasR mutants can be genotype dependent and support the idea that genetic interactions could contribute to the emergence of lasR-null mutations in a clinical setting.
RESULTS
ΔlasR has strain-dependent effects on tobramycin resistance.
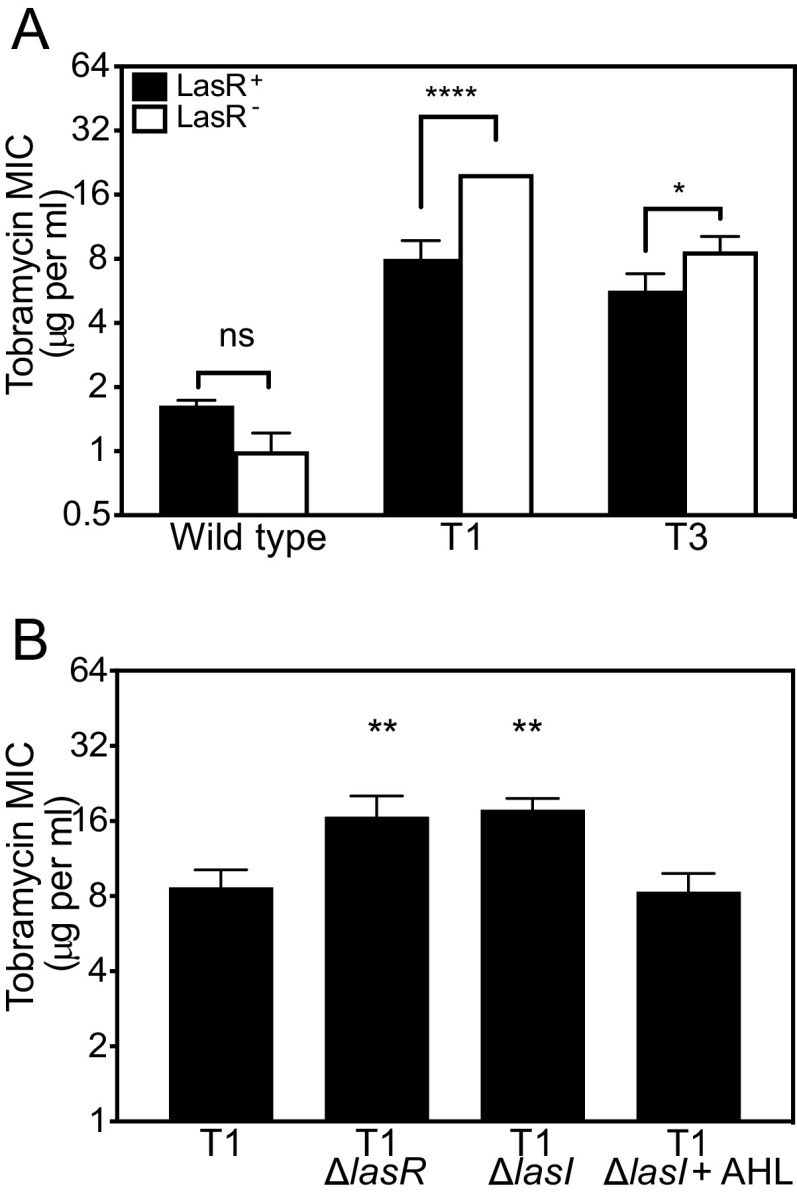
We previously characterized six tobramycin-resistant genetic isolates of P. aeruginosa PA14 with mutations in unique genes (e.g., fusA1 and ptsP, see Table S1 in the supplemental material) (17). We used these isolates to test the hypothesis that antibiotic adaptations could alter the effect of ΔlasR mutations on antibiotic resistance. We used allelic exchange to delete lasR from each of the six isolates from our prior study (termed T1 to T6). We compared the MIC of the ΔlasR isolates with their parent (Fig. 1A). Similar to our prior results (17), deleting lasR caused a small decrease in tobramycin resistance of PA14, although in this study the difference was not significant due to comparisons with a wider range of MICs in our statistical analyses. Deleting lasR in the T1 isolate increased tobramycin resistance ~2-fold (Fig. 1A). Deleting lasR in T3 had a smaller but similar effect (Fig. 1A). In pairwise comparisons with the PA14 wild-type strain, the effects of ΔlasR on the tobramycin MIC were significantly different in T1 and T3 (P < 0.05, Fig. 1A). We did not observe significantly different effects of deleting lasR on the MIC for any of the other four isolates (Fig. S1).
FIG 1.
Tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants is strain dependent. (A) The MIC of tobramycin was determined for each strain carrying intact lasR (LasR+, black bars) or ΔlasR (LasR−, white bars). The significance of the effect of strain (wild type, T1, or T3) and lasR allele (LasR+ or LasR−) and the interaction of the two on MIC was determined by two-way ANOVA by performing pairwise comparisons of each LasR+/− strain pair with that of PA14. The interaction was significant for T1 (F1,8 = 156.8 and P < 0.0001) and T3 (F1,8 = 10.67 and P < 0.05). Pairwise comparisons of LasR+ and LasR− of each strain were determined using Sidak’s post hoc test with P-values adjusted for multiple comparisons; *, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. (B) Tobramycin MIC of T1 and T1-mutated strains. Where indicated, AHL (3OC12-HSL) was added before inoculating culture tubes at the 10-μM final concentration. Statistical analysis was done by one-way ANOVA and Dunett’s multiple comparisons with T1; **, P < 0.01. For panels A and B, results are the average of three independent experiments and the vertical bars indicate standard deviation.
To further confirm the effects of the LasR-I system on tobramycin resistance in the T1 isolate, we deleted the lasI signal synthase gene (Fig. 1B). Because LasI synthesizes the LasR signal, we anticipated that deleting lasI would cause changes in tobramycin MIC similar to that of a lasR deletion. Consistent with this expectation, deleting lasI significantly increased tobramycin resistance in T1, and adding synthetic 3OC12-HSL to the ΔlasI mutant culture restored resistance levels to that of T1 (Fig. 1B). These results offer further support that the effects of disrupting the LasR-I circuit on tobramycin resistance are strain dependent.
fusA1 (G61A) modulates the effects of ΔlasR on tobramycin resistance.
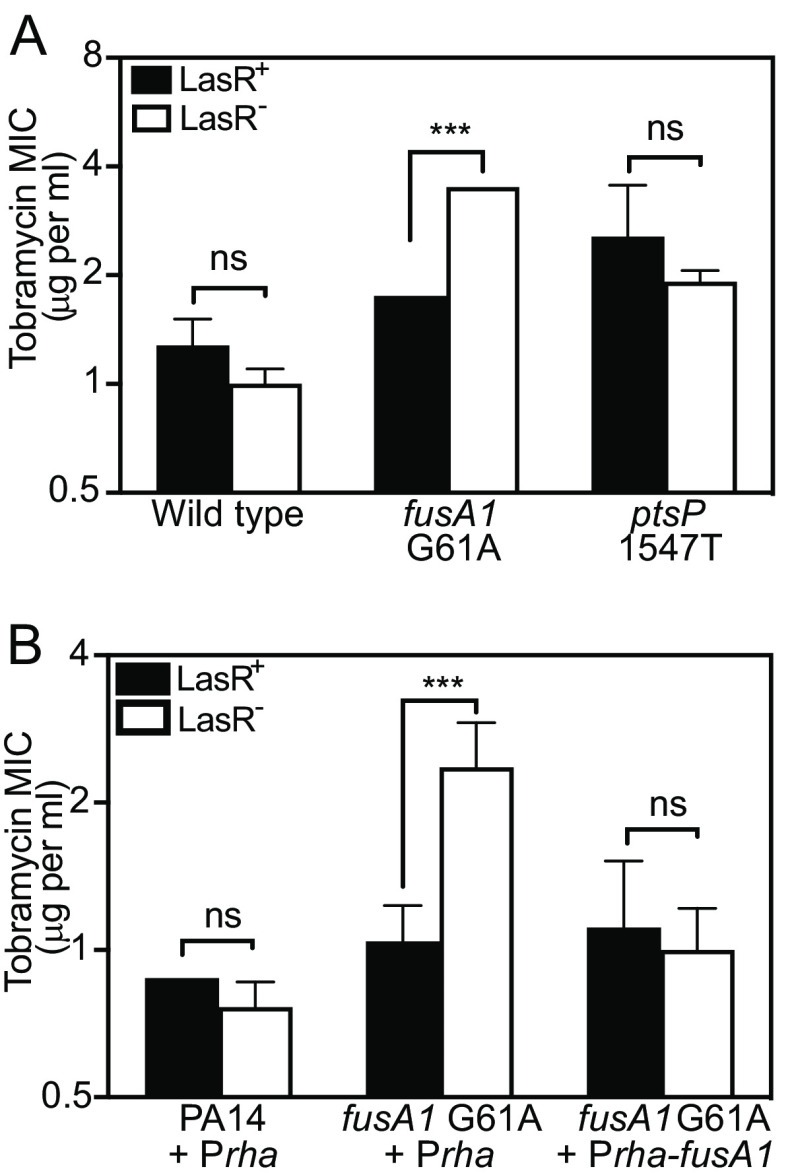
We hypothesized that one or more genetic mutations in T1 and T3 altered the susceptibility of ΔlasR mutants to tobramycin. In our prior study, we determined that the T1 and T3 isolates have only two common mutations, fusA1 G61A (EF-G1AA21T) and ptsP 1547T (a frameshift mutation that is predicted to result in an inactivated protein) (Table S1) (17). We individually introduced each of these mutations to PA14 and PA14 ΔlasR using allelic exchange and compared the MIC of the mutated strains to that of the PA14 parent strains (Fig. 2A). Introducing the fusA1 G61A mutation on its own did not change the MIC of PA14. However, deleting lasR in PA14 fusA1 G61A increased the MIC of the fusA1 G61A mutant ~2-fold, which was a significantly different effect from deleting lasR in PA14 (P < 0.0001). In contrast, deleting lasR in the ptsP 1547T mutant was not significantly different from that of PA14 (P = 0.9865). These results suggested that the fusA1 G61A mutation is responsible for increasing the tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants.
FIG 2.
Effects of fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR on tobramycin resistance. The MIC of tobramycin was determined for each strain carrying intact lasR (LasR+, black bars) or ΔlasR (LasR−, white bars). The significance of the effect of strain (indicated along the x axis) and lasR allele (LasR+ or LasR−) and the interaction of the two on MIC was determined by 2-way ANOVA by performing pairwise comparisons of each LasR+/− strain pair with that of PA14 (A) or PA14 Prha (B). Pair-wise comparisons of LasR+ and LasR− of each strain were determined using Sidak’s post hoc test with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons; ***, P < 0.001; ns = not significant. (A) There was a statistically significant interaction between the effects of strain and lasR for fusA1 G61A (F1,8 = 156.8, P < 0.0001) but not for ptsP 1547T (F1,8 = 0.3642, P = 0.5629). An additional Sidak’s post hoc test comparing PA14 and fusA1 G61A of the LasR+ strains revealed no significance (P > 0.4). (B) Strains had either the empty CTX-1 Prha or the CTX-1 Prha-fusA1 cassette inserted into the neutral attB site in the genome. Rhamnose was added to all cultures at 0.1% final concentration. There was a statistically significant interaction between the effects of strain and lasR for fusA1 G61A Prha (F1,8 = 17.41, P < 0.005) but not for fusA1 G61A + Prha-fusA1 (F1,8 = 1.7 × 10−7, P = 0.997). For panels A and B, results are the average of three independent experiments and the vertical bars indicate standard deviation.
Next, we asked if ectopic expression of the wild-type fusA1 could restore the MIC to that of wild type. To do so, we fused the wild-type fusA1 gene to a rhamnose-inducible promoter (Prha) and introduced this cassette to the neutral attB site in the genome of T1 and the PA14 fusA1 G61A mutant (Fig. 2B and Fig. S2). In wild-type fusA1-expressing strains, the effects of deleting lasR on the tobramycin MIC were indistinguishable from that of the parent (T1 or PA14 fusA1 G61A carrying Prha-fusA1 compared with ΔlasR of each strain). The results show that the defects caused by the G61A mutation can be restored by expression of the wild-type fusA1 and that this mutation is recessive. These results also validate the conclusion that the fusA1 G61A mutation causes the observed effects on lasR-dependent tobramycin resistance.
Strain-dependent effects of tobramycin on the proliferation of ΔlasR mutants in cocultures.
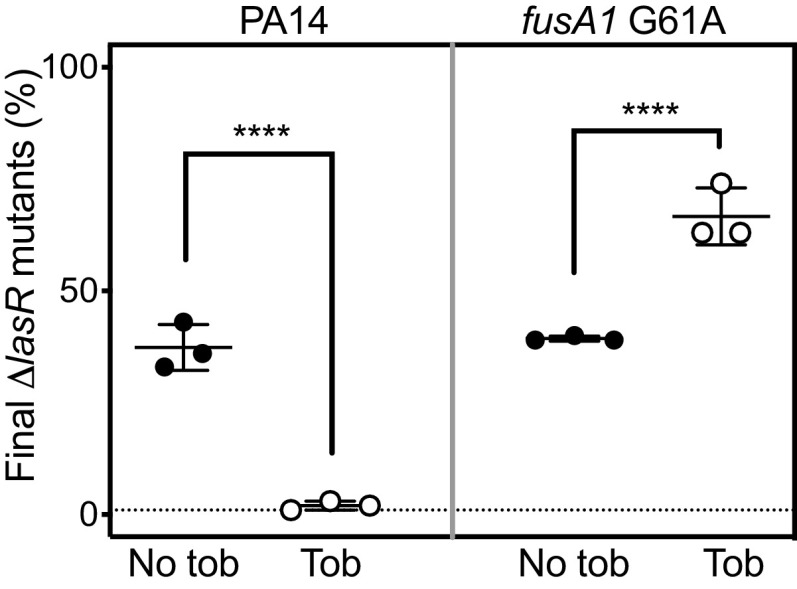
We sought to assess the selective effects of tobramycin on ΔlasR mutants in different strain backgrounds using coculture competition experiments. When PA14 is coinoculated with PA14 ΔlasR, the ΔlasR mutant rapidly proliferates to a higher frequency because it has a fitness advantage over PA14; however, ΔlasR mutants are suppressed in identical cocultures grown with subinhibitory tobramycin (17). We hypothesized that tobramycin would enhance rather than suppress the proliferation of ΔlasR mutants in strains carrying the fusA1 G61A mutation. To test this hypothesis, we inoculated cocultures with either PA14 or PA14 fusA1 G61A and a 1% initial population of each respective ΔlasR mutant and grew the cocultures with or without tobramycin. Cocultures were transferred daily to fresh medium, and the proportion of ΔlasR mutants in the final population was assessed after two daily transfers. The results (Fig. 3) showed that tobramycin had significantly different effects on ΔlasR mutant proliferation in each of the two strain backgrounds (P < 0.0001). At the end of the PA14 experiment, the ΔlasR mutants were ~30% of the population in cocultures grown with no tobramycin but reached only ~0.5% of the tobramycin-treated population (Fig. 3, left), consistent with prior results (17). In cocultures with strains carrying fusA1 G61A, the ΔlasR mutants similarly reached ~30% of the population in the absence of tobramycin but further increased to ~60% of the population in the presence of tobramycin (Fig. 3, right). These results show that tobramycin selection of ΔlasR mutations is reversed in the fusA1 G61A mutant compared with the wild-type parent and support the idea that fusA1 mutations could permit the emergence of lasR mutations in the population.
FIG 3.
Tobramycin effects on ΔlasR proliferation in cocultures. Cocultures of wild-type PA14 and PA14 ΔlasR (left) or of fusA1 G61A and fusA1 G61A ΔlasR (right) were grown with no tobramycin (No tob, closed circles) or with tobramycin (Tob, open circles) at the highest concentration that permits growth (0.3 μg/mL for PA14 or 2 μg/mL for fusA1 G61A). In both cases, the ΔlasR mutant was started at 1% of the total coculture population. After being combined, cocultures were inoculated into casein medium and subsequently transferred to fresh medium daily for 2 days. Final population densities ranged from 1 to 5 × 109 cells per mL. Each data point represents a single experiment and vertical lines represent standard deviation. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA was used to determine the significance of the effect of the tobramycin and the lasR allele and interaction between the two on the relative fitness of the ΔlasR mutant, and the interaction was significant (P < 0.0001 and F1,8 = 41.26). Pair-wise comparisons of LasR+ and LasR− for each condition (+/− tob) were performed using Sidak’s post hoc analysis with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons; ****, P < 0.0001.
Effects of other fusA1 mutations on tobramycin MIC of ΔlasR mutants.
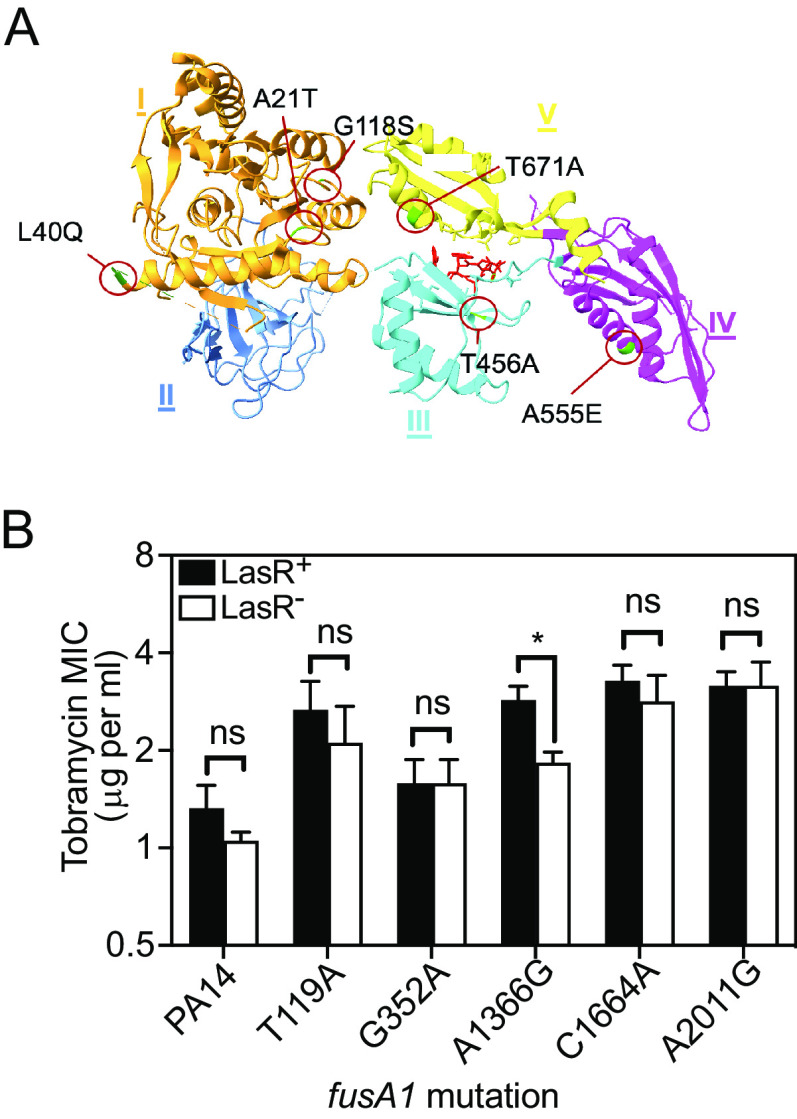
The fusA1 gene encodes elongation factor G1A (EF-G1A), a GTPase protein that hydrolyzes GTP to drive the elongation and recycling steps of protein synthesis (39, 40). EF-G1A is an essential component in translation, and fusA1-null mutations are not viable (39–41). Nevertheless, fusA1 has been reported to be among the most frequently mutated genes in clinical isolates (42–45), and in at least some cases, fusA1 mutations increase tobramycin resistance (41, 42, 46). EF-G1A has 5 domains (labeled I to V in Fig. 4A). The EF-G1AA21T substitution is within a motif in domain 1 called the Walker-A P-loop, which is responsible for binding phosphoryl groups and catalyzing phosphoryl transfer of NTPs (47).
FIG 4.
Other fusA1 mutations and their effects on tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants. (A) Ribbon diagram of the fusA1-encoded protein elongation factor-G (EF-G1A) (PDB ID: 4FN5). The protein was crystallized bound to argyrin, which is shown in red. Each one of the amino acid substitutions is indicated with green coloration in the ribbon diagram and a red circle and was identified using the UCSF ChimeraX (82) (B) The MIC of tobramycin was determined for each strain carrying the wild-type fusA1 allele (PA14) or PA14 with the indicated amino acid substitution in the encoded EF-G1A. Each strain had either an intact lasR (LasR+, black bars) or ΔlasR (LasR−, white bars). Results are the average of three independent experiments and the vertical bars indicate standard deviation. The significance of the effect of the fusA1 allele and the lasR allele and the interaction of the two on MIC was determined by 2-way ANOVA by performing pairwise comparisons of each LasR+/− strain pair with that of PA14. Only A1366G showed a significant interaction (P < 0.05, F1,8 = 10.25). Pairwise comparisons of LasR+ and LasR− of each strain were determined using Sidak’s post hoc test with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons. *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant.
To determine the prevalence of the fusA1 G61A mutation in natural isolates, we surveyed 4,312 sequenced strains in the Pseudomonas Genome Database (48). Only four strains were identified with any substitution in amino acid 21, all of them an A to T substitution at amino acid 21 caused by a G61A nucleotide polymorphism (Table S2). Interestingly, none of these four EF-G1AA21T strains were lasR-mutated. However, the environmental constraints particular to these strains are unknown, making the interpretation of this finding difficult. Our results indicate fusA1 G61A mutations do occur naturally but are relatively rare.
fusA1 is a hot spot for single-nucleotide mutations in clinical isolates in P. aeruginosa (41, 42, 45, 49, 50). To test whether other fusA1 mutations can enhance or alter the tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants, we introduced five fusA1 mutations to the genome of PA14 or PA14 ΔlasR by allelic exchange and determined the tobramycin MIC of each strain (Fig. 4). In all but one of the fusA1-mutated strains (A1366G, corresponding with an amino acid substitution T456A), the effect of LasR on antibiotic resistance was not significantly altered compared with that of PA14. In the fusA1 A1366G strain, ΔlasR decreased tobramycin resistance, which is the opposite of the effect observed with the G61A mutation. There were no effects of deleting lasR for the other fusA1 mutations tested (T119A, G352A, C1664A, and A2011G, corresponding with amino acid substitutions L40Q, G118S, A555E, and T671A). These results show that not all fusA1 mutations modulate the tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants in the same way.
fusA1 G61A modulates ΔlasR resistance to other antibiotics.
We next asked whether the fusA1 G61A mutation can also alter the susceptibility of ΔlasR mutants to antibiotics other than tobramycin. We tested the antibiotics ciprofloxacin (DNA gyrase inhibitor), ceftazidime (cell wall biosynthesis inhibitor), piperacillin (cell wall biosynthesis inhibitor), and tetracycline (protein synthesis inhibitor) against PA14 and our fusA1 and lasR single and double mutant strains (Table 1). We observed significant strain-dependent effects of the ΔlasR mutation on the MIC values for two of these antibiotics: ciprofloxacin (P < 0.01) and ceftazidime (P < 0.0001). With ciprofloxacin, ΔlasR increased the resistance of the fusA1 G61A mutant, but this mutation caused no changes in the PA14 MIC. With ceftazidime, we observed different effects: the ΔlasR mutation and fusA1 G61A mutations decreased PA14 resistance to the same degree as single mutations and in combination. These results show that fusA1 G61A mutations modulate the susceptibility of ΔlasR mutants to several different classes of antibiotics and demonstrate the broad interaction effect of these genes.
TABLE 1.
Antibiotic susceptibility of lasR and fusA1 G61A mutant strains
| Antibiotic susceptibilitya,b |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Cipro | Imi | Tet | Pip | Ceft |
| PA14 | 0.09 (0.01) | 0.7 (0.1) | 5 (2) | 50 | 49 (2) |
| PA14 ΔlasR | 0.08 (0.01) | 0.8 (0.1) | 5 (2) | 50 | 11 (5)**** |
| fusA1 G61A | 0.06 | 0.8 (0.1) | 6 (2) | 50 | 13 |
| fusA1 G61A ΔlasR | 0.12 (0.03)**c | 0.8 (0.2) | 4 (2) | 50 | 10 (2) |
Antibiotic susceptibility was determined by MIC as described in Materials and Methods. Cipro, ciprofloxacin; Imi, imipenem; Tet, tetracycline; Pip, piperacillin; Ceft, ceftazidime. The values represent the average of three independent MIC experiments with the standard deviation in parentheses. Standard deviation was zero where not indicated.
The significance of the effects of fusA1 (wild-type fusA1 in PA14 or G61A) and lasR allele (intact lasR or ΔlasR) and the interaction of the two on MIC was determined by two-way ANOVA. The interaction was significant for ciprofloxacin (P < 0.01 and F1,8 = 13.98) and for ceftazidime (P < 0.0001 and F1,8 = 91.16). There was no significance of interaction (P > 0.05) for imipenem, tetracycline, and piperacillin.
Superscripted asterisks indicate the significance of comparing LasR+ and LasR− of each strain (PA14 or fusA1 G61A) using Sidak’s post hoc analysis with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons of all strains. There was no significance (P > 0.05) unless indicated. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.
fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR increase tobramycin resistance by activating the MexXY efflux pump.
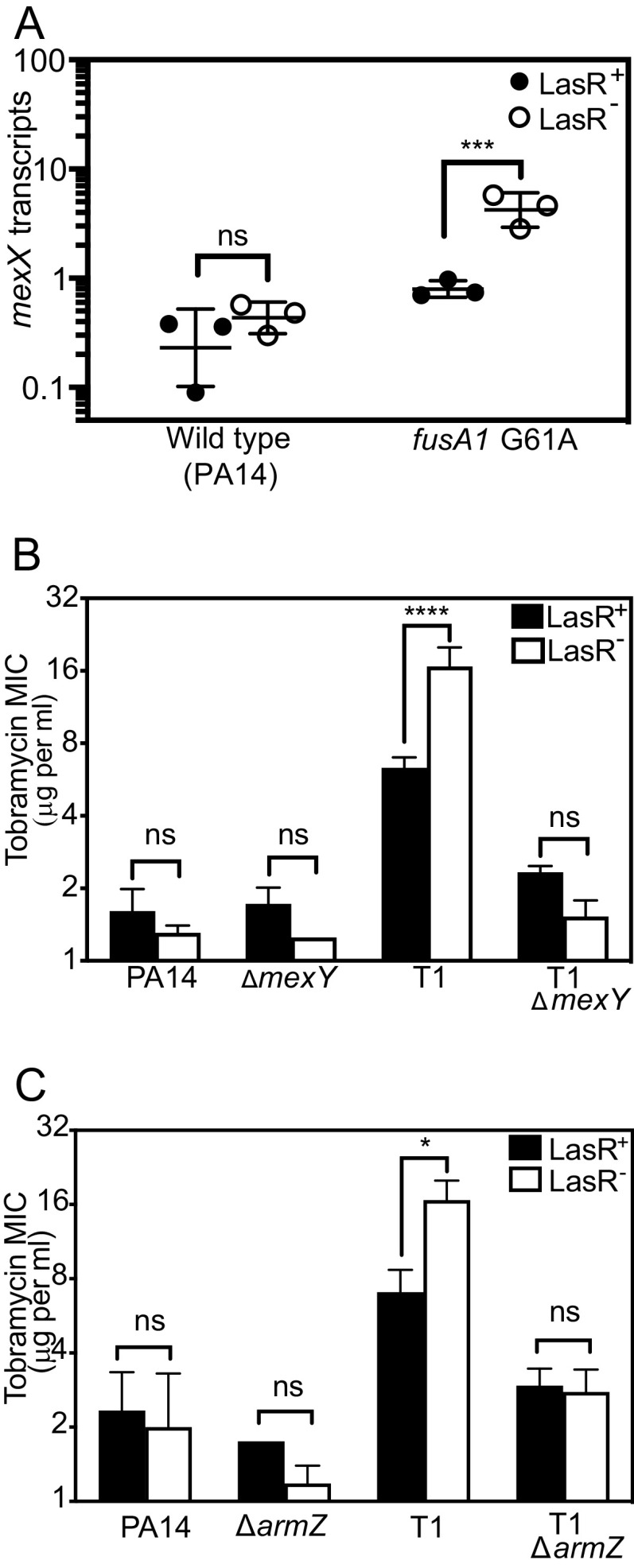
Some other P. aeruginosa fusA1 mutations can enhance aminoglycoside resistance through the multidrug efflux pump MexXY (41, 51). Thus, we hypothesized that MexXY is important for increasing the tobramycin resistance of fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR double mutants. As an initial test of this hypothesis, we measured the expression of the mexX gene, which is immediately upstream of and in the same operon as mexY (Fig. 5A). We quantified mexX transcripts in logarithmically growing cells of PA14 fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR single and double mutants. Consistent with our hypothesis, mexX transcripts were the highest in fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR double mutants. We also deleted the mexY gene that is essential for pump activity. Our attempts to delete mexY in fusA1 G61A were unsuccessful; however, we were able to delete this gene in T1 and T1 ΔlasR and also PA14 and PA14 ΔlasR. Deleting ΔmexY in T1 abolished the LasR-dependent changes in MIC observed in this strain (Fig. 5B), supporting that MexY is important for fusA1 G61A to increase the tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants.
FIG 5.
Role of MexXY on tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR and fusA1 G61A mutants. (A) mexX transcript levels were determined by droplet digital PCR and normalized to the housekeeping control gene proC. Strains were wild-type PA14 or PA14 with the fusA1 G61A substitution. Each strain had either an intact lasR (LasR+, filled circles) or ΔlasR (LasR−, open circles). Each point represents in independent experiment; horizontal lines represent the geometric mean, and the vertical lines represent the geometric standard deviation. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA showed a significant interaction between the effects of strain and lasR allele on mexX transcripts (P < 0.005, F1,8 = 15.67). An additional Sidak’s post hoc test comparing PA14 and fusA1 G61A of the LasR+ strains revealed no significance (P > 0.6). (B and C) The MIC of tobramycin was determined for each strain carrying intact lasR (LasR+, black bars) or ΔlasR (LasR−, white bars). Results are the average of three independent experiments and the vertical bars show standard deviation. In pairwise comparisons with the LasR+/− PA14 strains, there was a significant interaction between the effects of strain and lasR allele for T1 (P < 0.01 and F(1,8) = 29.01 for panel B and P < 0.005 and F(1,8) = 17.99 for panel C) but not for the other strains. In panels A to C, pairwise comparisons of LasR+ and LasR− of each strain were determined using Sidak’s post hoc test with P-values adjusted for multiple comparisons. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
One mechanism of MexXY induction is through the ArmZ regulator (52, 53), which is activated by a mechanism of transcription attenuation in response to perturbations that cause the ribosome to stall (53–55). ArmZ derepresses the MexXY regulator MexZ; thus, activation of ArmZ ultimately leads to increased MexXY activity (52, 53, 56). To test the hypothesis that ArmZ is required for MexXY activation in fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR double mutants, we deleted armZ in T1 and the T1 ΔlasR mutants and determined the MIC of these strains. Similar to the result of deleting mexY, we found that deleting armZ abolished LasR-dependent changes in MIC observed in T1 (Fig. 5C). Together, the results support that MexXY and the ArmZ regulator are both required for fusA1 G61A to increase the tobramycin resistance of ΔlasR mutants.
fusA1 mutations are associated with slower translation rates (41, 51, 57). Thus, we hypothesized that the fusA1 G61A mutation might cause ribosome stalling effects that are enhanced by the ΔlasR mutation, to subsequently activate ArmZ. To test this hypothesis, we measured the doubling times of our fusA1 G61A and ΔlasR mutant strains during logarithmic growth in minimal media, as growth rates can indirectly indicate the effects of fusA1 mutations on the translation rate (41, 58). We found that fusA1 G61A alone had no significant effect on growth; however, the growth of this mutant was slowed when combined with ΔlasR (Table 2). Although there are other possible explanations for why growth effects might be observed in these mutants, for example, pleiotropic effects of the fusA1 mutation on gene regulation (51), these results support the idea that the ΔlasR and fusA1 G61A mutants increase mexXY expression by increasing ribosome stalling.
TABLE 2.
Growth rates in MOPS minimal medium
| Strain/isolate | Doubling time (min)ab | Strain | lasR | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA14 | 62.5 (2.0) | |||
| PA14 ΔlasR | 61.4 (2.9) | |||
| fusA1 G61A | 66.3 (2.9) | P < 0.0005 | P < 0.01 | P < 0.005 |
| fusA1 G61A ΔlasR | 78.2 (2.2)***c | F = 49.91 | F = 13.81 | F = 19.73 |
| T1 | 67.7 (4.0) | P < 0.0005 | P < 0.02 | P < 0.005 |
| T1 ΔlasR | 79.7 (2.5)*** | F = 47.61 | F = 10.41 | F = 14.81 |
| T3 | 74.9 (3.4) | P < 0.0001 | ns | P < 0.04 |
| T3 ΔlasR | 83.0 (3.5)* | F = 96.27 | F = 4.084 | F = 6.930 |
The values represent the average doubling time during logarithmic growth determined from three independent experiments, with the standard deviation indicated in parentheses. Standard deviation was zero where not indicated.
The significance of the effects of strain (PA14, fusA1 G61A, T1, or T3) and lasR allele (intact lasR or ΔlasR) and the interaction of the two on MIC was determined by two-way ANOVA by performing pairwise comparisons of each LasR+/− strain pair with that of PA14. The interaction was significant in all cases. For fusA1 G61A, P < 0.005 and F = 19.73; for T1, P < 0.005 and F = 14.81; for T3, P < 0.04 and F = 6.930.
Asterisks indicate the significance of comparing LasR+ and LasR− of each strain using Sidak’s post hoc analysis with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons of all strains. There was no significance (P > 0.05) unless indicated. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we demonstrate that lasR-null mutations have strain-dependent effects on antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa. These effects are caused by mutations in the translation accessory fusA1 gene (G61A), a commonly mutated gene in clinical isolates. These results add to the growing body of work showing that adaptive mutations can modulate quorum sensing (17, 38, 59–62). Our results show that adaptation can have important consequences on the emergence of lasR mutations, which could significantly change the evolutionary landscape of the community. Thus, adaptive mutations are important to the evolution of quorum sensing and may play a critical role in shaping quorum-sensing populations in communities under strong selective pressure, such as those found in infections.
The effects of fusA1 G61A mutations on ΔlasR selection by tobramycin are consistent with a type of epistasis called sign epistasis. Epistasis describes a phenomenon in which the phenotypic effects of one gene mutation are modified by mutations in other genes (38), and sign epistasis is a type of interaction that reverses mutational effects on phenotype (63–65). Sign epistatic effects change the direction of selection; thus, they do not require large changes in phenotype or MIC to cause significant effects on evolution (66, 67). For example, sign epistatic interactions permit the emergence of new traits in a population, as illustrated by our study. Some prior studies have demonstrated sign epistatic effects in bacteria, for example, in the development of cefotaxime resistance in Escherichia coli (68) and the evolution of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (69) and also in P. aeruginosa in the context of rifampicin resistance (70). In the P. aeruginosa study, epistatic and sign epistatic interactions were surprisingly common, with ~50% of those interactions tested showing epistatic effects and 84% of epistatic interactions showing sign epistatic effects. These studies suggest that sign epistatic interactions are prevalent in P. aeruginosa. The studies also highlight the potential importance of adaptive mutations that have small antibiotic resistance effects for the evolution of new traits in a population.
Our study provides new information on the effects of fusA1 mutations on antibiotic resistance. The fusA1-encoded protein EF-G1A is important for recycling ribosomes during translation (71). Mutations in EF-G1A are thought to cause ribosomes to get stuck on the mRNA and back up other ribosomes behind them (72). These translation disruptions could cause ribosome stress and subsequently activate the MexXY regulator ArmZ through translation attenuation (53–55). In support of this idea, at least some of the other fusA1 mutants increase transcription of the mexXY genes, and MexXY is important for increased resistance of these strains (41, 51). The fusA1 G61A mutation seems to cause similar effects but only in combination with ΔlasR (Fig. 2 and 5A). These results suggest LasR can somehow ameliorate the effects of the G61A mutation possibly by protecting against ribosome stress. LasR may do this by activating specific effectors or in coordination with other stress responses, for example, through the stress-responsive sigma factor RpoS (73). We find it interesting that LasR does not have interactive effects on tobramycin resistance with any other fusA1 mutations (Fig. 4B), which suggests either that LasR cannot sufficiently overcome the effects of those other mutations or there are unknown mechanistic differences in the mutational effects.
Our results suggest there may be a variety of epistatic gene interactions with fusA1 that have previously unappreciated contributions to antibiotic resistance and gene evolution. For example, the fusA1 G61A mutation increased resistance in the T1 variant by ~4-fold, which was not observed in wild type (Fig. S2). This result suggested other mutations in the T1 isolate enhance the effects of the fusA1 G61A mutation on tobramycin resistance. The particular mutations in T1 that have interaction effects on fusA1 G61A remain to be discovered. One other fusA1 mutation (A1366G) also had interesting effects in our studies. This mutation further enhanced the sensitivity of ΔlasR to tobramycin (Fig. 4B). Such genetic interactions that enhance antibiotic sensitivity are particularly relevant to therapeutics because they could pave a path toward developing novel disease interventions that increase the efficacy of existing antibiotics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Culture conditions and reagents.
Routine growth was in Luria-Bertani broth (LB) for Escherichia coli or in LB buffered to pH 7 with 50 mM 3-(morpholino)-propanesulfonic acid (LB-MOPS) for Pseudomonas aeruginosa or on LB agar (LBA; 1.5% wt/vol Bacto Agar). Liquid growth media for specific experiments were M9-caseinate (casein broth: 6 g L−1 Na2HPO4, 3 g L−1 KH2PO4, 0.5 g L−1 NaCl, 1 g L−1 NH4Cl, pH 7.4, and 1% sodium caseinate) (17) or a MOPS minimal medium [25 mM d-glucose, freshly prepared 5 μM FeSO4, 15 mM NH4Cl, and 2 mM K2HPO4 added to a 1× MOPS base buffer consisting of 50 mM MOPS, 4 mM Tricine, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM K2SO4, 50 μM MgCl2, 10 μM CaCl2, 0.3 μM (NH4)6Mo7O24, 40 μM H3BO3, 3 μM cobalt(II) acetate, 1 μM CuSO4, 8 μM MnSO4, and 1 μM ZnSO4] (17, 74). Four percent skim milk agar (SMA) was used for identifying ΔlasR mutants in competition experiments. All growth was at 37°C, and liquid cultures were grown with shaking at 250 rpm in 18-mm culture tubes (2-mL cultures), 125-mL baffled flasks (10-mL cultures), or 250-mL baffled flasks (60-mL cultures). For strain construction, we used 100 μg mL−1 carbenicillin, 15 μg mL−1 gentamicin, and 2.5–10 μg mL−1 tetracycline for E. coli and 150 to 300 μg mL−1 carbenicillin, 50 to 200 μg mL−1 gentamicin, and 15 to 100 μg mL−1 tetracycline for P. aeruginosa. 3OC12-HSL was purchased from Cayman Chemicals (MI, USA), dissolved in acidified ethyl acetate with glacial acetic acid (0.1 mL l−1), and added to an empty sterile conical tube and dried by evaporation before adding liquid media.
Genomic or plasmid DNA was extracted using Qiagen Puregene Core A kit (Hilden, Germany) or IBI Scientific plasmid purification mini-prep kit (IA, USA) while PCR products were purified using IBI Scientific PCR cleanup/gel extraction kits, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Antibiotics were purchased from GoldBio (MO, USA) except for tetracycline, which is from Fisher Scientific (PA, USA).
Bacterial strains and strain construction.
All bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers used in this study are provided in the supplemental material. P. aeruginosa strain UCBPP-PA14 (“PA14”) and PA14 derivatives were used for these studies. Markerless deletions in specific loci of P. aeruginosa PA14 were generated using allelic exchange as described previously (75). To generate plasmids for allelic exchange, DNA fragments with the mutated or deleted gene allele plus 500-bp flanking DNA were synthesized (Genscript, NJ) or generated by PCR using primer-incorporated restriction enzyme sites. The synthesized or PCR products were moved to plasmid pEXG2 (76) using restriction enzyme digestion and ligation or isothermal assembly. The subsequent plasmids were transformed into the appropriate P. aeruginosa strain using described methods (77). The plasmids for ΔlasR (17), ΔmexY (78), and ΔarmZ (56) are described elsewhere. Merodiploids were selected on Pseudomonas isolation agar (PIA)-carbenicillin (150 to 300 μg mL−1) for ΔlasR; PIA-gentamicin (50 to 200 μg mL−1) for fusA1 G61A, ΔlasI, and ptsP 1547T; and PIA-tetracycline (15 to 100 μg mL−1) for ΔmexY and ΔarmZ. Deletion mutants were counterselected using NaCl-free 15% sucrose. Putative mutants were verified through antibiotic sensitivity tests and gene-targeted Sanger sequencing. It was of note that in some cases we had difficulty with genetic manipulations involving fusA1 mutations. In most cases, we found success by optimizing the concentration of antibiotics used for selecting plasmid integrants. For introducing the fusA1 G61A mutation to the genome of P. aeruginosa by allelic exchange, we found success only when we introduced the full-length fusA1 rather than shorter fragments, possibly because this approach helped to avoid creating disruptions that were not viable. To make the Prha-fusA1 expression cassette, we PCR-amplified the wild-type fusA1 gene from PA14 using primer-encoded restriction enzyme sites. The PCR product was digested and ligated to pJM253 (miniCTX1-rhaSR-PrhaBAD) (79). This plasmid was moved into P. aeruginosa by conjugation as described previously (79). Transformants were selected on LBA with 200 μg mL−1 tetracycline, and the insertion of the cassette in the attB site was verified by PCR.
Antimicrobial susceptibility assays.
Antibiotic susceptibility was determined by MIC using a modified method from the 2022 guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CSLI) (80), similar to that previously described (17). Briefly, two antibiotic dilution series were made from staggered starting antibiotic concentrations to cover a broader range of concentrations. These were as follows (in μg mL−1): tobramycin, 20 and 7; ceftazidime, 100 and 75; ciprofloxacin 1 and 0.375; piperacillin 100 and 75; imipenem 10 and 3.5; and tetracycline 20 and 7. These were successively diluted in MOPS minimal medium 2-fold in a 200-μL volume in 2-mL tubes. The starter cultures were prepared by growing P. aeruginosa in LB-MOPS to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 4. The starter cultures were subsequently diluted 1:40 into each tube containing tobramycin to start the MIC experiment. After 20 h of incubation with shaking, turbidity was measured using a Biotek Synergy 2 plate reader. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of antibiotic (μg mL−1) in which bacterial growth was not measurable.
Coculture assays.
Overnight (18 h) pure cultures were grown in LB-MOPS, diluted to an OD600 of 0.025 for LasR− or 0.05 to 0.15 for LasR+ into LB-MOPS, and grown to an OD600 of ~3.5 before combining at a 99:1 (LasR+:LasR−) ratio and used to start the coculture by diluting 1:40 into casein broth in 18-mm test tubes. In some cases as indicated, tobramycin was added to the casein broth coculture. At 24 h, cocultures were diluted 1:40 into fresh casein broth in a new test tube and the experiment was ended at 48 h. The initial and final total population counts (CFU mL−1) were determined by dilution plating and viable plate counts. The percent ΔlasR mutant was determined by patching 200 colonies on SMA where ΔlasR mutants form distinct colony phenotypes (17, 22, 23, 81).
Droplet digital PCR.
Overnight (18 h) pure cultures were grown in LB-MOPS, subcultured in LB-MOPS, and grown to an OD600 of ~4. Stationary-phase P. aeruginosa (OD600 of 4) was diluted to OD600 0.1 in MOPS minimal medium and grown 2.5 to 3 h (OD600 ~0.20 to 0.45). RNA was harvested using the RNeasy minikit (Qiagen), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) was performed on a Bio-Rad QX200 ddPCR system using Eva Green supermix. Each reaction mixture contained 1.8 ng μL−1 cDNA template, 0.8 μM each primer, and 10 μL Eva Green supermix in a 20-μL final volume. After generating 40 μL of oil droplets, 40 rounds of PCR were conducted using the following cycling conditions: 95°C for 30s, 62°C for 30s, and 68°C for 30s. Absolute transcript levels were determined using Bio-Rad QuantaSoft software. In all cases, a no-template control was run with no detectable transcripts. The reference gene used was the proline biosynthetic gene (proC), and the results are reported as the calculated transcript amount of a given gene per calculated proC transcript.
Growth curve.
Overnight (18 h) pure cultures were grown in LB-MOPS, subcultured in LB-MOPS, and grown to an OD600 of ~4. Stationary-phase P. aeruginosa (OD600 of 4) was diluted to OD600 0.1 in MOPS minimal medium, and OD600 was measured in a Jenway spectrophotometer every hour for 8 h. An exponential-fit trendline was fit to the data used to calculate the doubling time.
Statistical analysis.
All statistical analyses were carried out using GraphPad Prism version 9.4.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). Unless otherwise noted, antibiotic MICs, cocultures, mexX transcripts, and growth rates were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The significance of LasR− or antibiotic-dependent effects among strains was determined by finding the interaction term with alpha = 0.05 in pairwise comparisons of each strain/isolate with PA14. The significance of differences between LasR+ and LasR− within each strain was determined using Sidak’s multiple-comparison test in a post hoc analysis. Statistically significant differences are defined in the figure legends.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the NIH through grants R35GM133572, CMADP COBRE (P20 GM103638), and K-INBRE (P20 GM103418) and by Inez Jay Fund to J.R.C. V.D.C. was supported by an Undergraduate Research Award from the KU Center for Undergraduate Research and a K-INBRE fellowship (P20 GM103418). K.A.T. was supported by KU Center for Undergraduate Research Emerging Scholars Program, U.S. Department of Education McNair Scholars Program, and Maximizing Access to Research Careers (MARC) (T34GM136453-01). R.G.A.-D. was supported by the Fulbright Foreign Student Program (15160174). B.M.M. was supported by the NIH Chemical Biology Training Program (T32 GM132061). A.J.H. was supported by the NIH Bridges to Baccalaureate Program (R25 GM060182).
The authors also acknowledge Keith Poole (Queen’s University) and Katy Jeannot (Université de Franche-Comté) for providing plasmids; Nicole E. Smalley and Ajai A. Dandekar (University of Washington), and Robert Unckless (University of Kansas) for the insightful suggestions; and Rishita Yadali, Isabelle Parisi, Emma Norris, and Benjamin Smith for their technical support. Molecular graphics and analyses were performed with the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) ChimeraX, developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at UCSF, with support from National Institutes of Health grant R01-GM129325 and the Office of Cyber Infrastructure and Computational Biology, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available online only.
Contributor Information
Josephine R. Chandler, Email: jrchandler@ku.edu.
Conrad W. Mullineaux, Queen Mary University of London
REFERENCES
- 1.Diggle SP, Whiteley M. 2020. Microbe Profile: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: opportunistic pathogen and lab rat. Microbiology (Reading) 166:30–33. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fuqua WC, Winans SC, Greenberg EP. 1994. Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J Bacteriol 176:269–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.269-275.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Papenfort K, Bassler BL. 2016. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:576–588. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schuster M, Sexton DJ, Diggle SP, Greenberg EP. 2013. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing: from evolution to application. Annu Rev Microbiol 67:43–63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fuqua C, Greenberg EP. 2002. Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:685–695. doi: 10.1038/nrm907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fuqua C, Winans SC, Greenberg EP. 1996. Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: the LuxR-LuxI family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:727–751. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pesci EC, Pearson JP, Seed PC, Iglewski BH. 1997. Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 179:3127–3132. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.10.3127-3132.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pearson JP, Passador L, Iglewski BH, Greenberg EP. 1995. A second N-acylhomoserine lactone signal produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1490–1494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee J, Zhang L. 2015. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 6:26–41. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pearson JP, Feldman M, Iglewski BH, Prince A. 2000. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-to-cell signaling is required for virulence in a model of acute pulmonary infection. Infect Immun 68:4331–4334. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.4331-4334.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Azimi S, Klementiev AD, Whiteley M, Diggle SP. 2020. Bacterial quorum sensing during infection. Annu Rev Microbiol 74:201–219. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032020-093845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tang HB, DiMango E, Bryan R, Gambello M, Iglewski BH, Goldberg JB, Prince A. 1996. Contribution of specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors to pathogenesis of pneumonia in a neonatal mouse model of infection. Infect Immun 64:37–43. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.37-43.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bjarnsholt T, Jensen PO, Burmolle M, Hentzer M, Haagensen JA, Hougen HP, Calum H, Madsen KG, Moser C, Molin S, Hoiby N, Givskov M. 2005. Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum-sensing dependent. Microbiology (Reading) 151:373–383. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Popat R, Crusz SA, Messina M, Williams P, West SA, Diggle SP. 2012. Quorum-sensing and cheating in bacterial biofilms. Proc Biol Sci 279:4765–4771. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rasmussen TB, Skindersoe ME, Bjarnsholt T, Phipps RK, Christensen KB, Jensen PO, Andersen JB, Koch B, Larsen TO, Hentzer M, Eberl L, Hoiby N, Givskov M. 2005. Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology (Reading) 151:1325–1340. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shih PC, Huang CT. 2002. Effects of quorum-sensing deficiency on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother 49:309–314. doi: 10.1093/jac/49.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abisado RG, Kimbrough JH, McKee BM, Craddock VD, Smalley NE, Dandekar AA, Chandler JR. 2021. Tobramycin adaptation enhances policing of social cheaters in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 87:e0002921. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00029-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Evans KC, Benomar S, Camuy-Velez LA, Nasseri EB, Wang X, Neuenswander B, Chandler JR. 2018. Quorum-sensing control of antibiotic resistance stabilizes cooperation in Chromobacterium violaceum. ISME J 12:1263–1272. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0047-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gabrielaite M, Johansen HK, Molin S, Nielsen FC, Marvig RL. 2020. Gene loss and acquisition in lineages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa evolving in cystic fibrosis patient airways. mBio 11:e02359-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02359-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rossi E, La Rosa R, Bartell JA, Marvig RL, Haagensen JAJ, Sommer LM, Molin S, Johansen HK. 2021. Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation and evolution in patients with cystic fibrosis. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:331–342. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00477-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Feltner JB, Wolter DJ, Pope CE, Groleau MC, Smalley NE, Greenberg EP, Mayer-Hamblett N, Burns J, Déziel E, Hoffman LR, Dandekar AA. 2016. LasR variant cystic fibrosis isolates reveal an adaptable quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 7:e01513-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01513-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hoffman LR, Kulasekara HD, Emerson J, Houston LS, Burns JL, Ramsey BW, Miller SI. 2009. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants are associated with cystic fibrosis lung disease progression. J Cyst Fibros 8:66–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.D'Argenio DA, Wu M, Hoffman LR, Kulasekara HD, Déziel E, Smith EE, Nguyen H, Ernst RK, Larson Freeman TJ, Spencer DH, Brittnacher M, Hayden HS, Selgrade S, Klausen M, Goodlett DR, Burns JL, Ramsey BW, Miller SI. 2007. Growth phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants adapted to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Mol Microbiol 64:512–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Smith EE, Buckley DG, Wu Z, Saenphimmachak C, Hoffman LR, D'Argenio DA, Miller SI, Ramsey BW, Speert DP, Moskowitz SM, Burns JL, Kaul R, Olson MV. 2006. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8487–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602138103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang Y, Gao L, Rao X, Wang J, Yu H, Jiang J, Zhou W, Wang J, Xiao Y, Li M, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Shen L, Hua Z. 2018. Characterization of lasR-deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 8:13344. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30813-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lore NI, Cigana C, De Fino I, Riva C, Juhas M, Schwager S, Eberl L, Bragonzi A. 2012. Cystic fibrosis-niche adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reduces virulence in multiple infection hosts. PLoS One 7:e35648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lelong E, Marchetti A, Simon M, Burns JL, van Delden C, Kohler T, Cosson P. 2011. Evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence in infected patients revealed in a Dictyostelium discoideum host model. Clin Microbiol Infect 17:1415–1420. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lesprit P, Faurisson F, Join-Lambert O, Roudot-Thoraval F, Foglino M, Vissuzaine C, Carbon C. 2003. Role of the quorum-sensing system in experimental pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1478–1482. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200207-736BC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hennemann LC, LaFayette SL, Malet JK, Bortolotti P, Yang T, McKay GA, Houle D, Radzioch D, Rousseau S, Nguyen D. 2021. LasR-deficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa variants increase airway epithelial mICAM-1 expression and enhance neutrophilic lung inflammation. PLoS Pathog 17:e1009375. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.LaFayette SL, Houle D, Beaudoin T, Wojewodka G, Radzioch D, Hoffman LR, Burns JL, Dandekar AA, Smalley NE, Chandler JR, Zlosnik JE, Speert DP, Bernier J, Matouk E, Brochiero E, Rousseau S, Nguyen D. 2015. Cystic fibrosis-adapted quorum sensing mutants cause hyperinflammatory responses. Sci Adv 1:e1500199. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mateu-Borras M, Gonzalez-Alsina A, Domenech-Sanchez A, Querol-Garcia J, Fernandez FJ, Vega MC, Alberti S. 2022. Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation in cystic fibrosis patients increases C5a levels and promotes neutrophil recruitment. Virulence 13:215–224. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2028484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hammond JH, Hebert WP, Naimie A, Ray K, Van Gelder RD, DiGiandomenico A, Lalitha P, Srinivasan M, Acharya NR, Lietman T, Hogan DA, Zegans ME. 2016. Environmentally endemic pseudomonas aeruginosa strains with mutations in lasR are associated with increased disease severity in corneal ulcers. mSphere 1:e00140-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00140-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Scribner MR, Stephens AC, Huong JL, Richardson AR, Cooper VS. 2022. The nutritional environment is sufficient to select coexisting biofilm and quorum sensing mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 204:e0044421. doi: 10.1128/JB.00444-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mould DL, Stevanovic M, Ashare A, Schultz D, Hogan DA. 2022. Metabolic basis for the evolution of a common pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa variant. Elife 11:e76555. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Clay ME, Hammond JH, Zhong F, Chen X, Kowalski CH, Lee AJ, Porter MS, Hampton TH, Greene CS, Pletneva EV, Hogan DA. 2020. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutant fitness in microoxia is supported by an Anr-regulated oxygen-binding hemerythrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:3167–3173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917576117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jean-Pierre F, Hampton TH, Schultz D, Hogan DA, Groleau M-C, Déziel E, O’Toole GA. 2022. Community composition shapes microbial-specific phenotypes in a cystic fibrosis polymicrobial model system. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2022.06.23.497319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Hoffman LR, Richardson AR, Houston LS, Kulasekara HD, Martens-Habbena W, Klausen M, Burns JL, Stahl DA, Hassett DJ, Fang FC, Miller SI. 2010. Nutrient availability as a mechanism for selection of antibiotic tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa within the CF airway. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000712. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gros P-A, Le Nagard H, Tenaillon O. 2009. The evolution of epistasis and its links with genetic robustness, complexity and drift in a phenotypic model of adaptation. Genetics 182:277–293. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.099127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rodnina MV, Savelsbergh A, Katunin VI, Wintermeyer W. 1997. Hydrolysis of GTP by elongation factor G drives tRNA movement on the ribosome. Nature 385:37–41. doi: 10.1038/385037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang D, Yan K, Zhang Y, Liu G, Cao X, Song G, Xie Q, Gao N, Qin Y. 2015. New insights into the enzymatic role of EF-G in ribosome recycling. Nucleic Acids Res 43:10525–10533. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bolard A, Plesiat P, Jeannot K. 2018. Mutations in gene fusA1 as a novel mechanism of aminoglycoside resistance in clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e01835-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01835-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chung JC, Becq J, Fraser L, Schulz-Trieglaff O, Bond NJ, Foweraker J, Bruce KD, Smith GP, Welch M. 2012. Genomic variation among contemporary Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chronically infected cystic fibrosis patients. J Bacteriol 194:4857–4866. doi: 10.1128/JB.01050-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Feliziani S, Marvig RL, Lujan AM, Moyano AJ, Di Rienzo JA, Krogh Johansen H, Molin S, Smania AM. 2014. Coexistence and within-host evolution of diversified lineages of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in long-term cystic fibrosis infections. PLoS Genet 10:e1004651. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lopez-Causape C, Rubio R, Cabot G, Oliver A. 2018. Evolution of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa aminoglycoside mutational resistome in vitro and in the cystic fibrosis setting. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e02583-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02583-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lopez-Causape C, Sommer LM, Cabot G, Rubio R, Ocampo-Sosa AA, Johansen HK, Figuerola J, Canton R, Kidd TJ, Molin S, Oliver A. 2017. Evolution of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutational resistome in an international Cystic Fibrosis clone. Sci Rep 7:5555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05621-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Scribner MR, Santos-Lopez A, Marshall CW, Deitrick C, Cooper VS. 2020. Parallel evolution of tobramycin resistance across species and environments. mBio 11:e00932-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00932-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Romero Romero ML, Yang F, Lin YR, Toth-Petroczy A, Berezovsky IN, Goncearenco A, Yang W, Wellner A, Kumar-Deshmukh F, Sharon M, Baker D, Varani G, Tawfik DS. 2018. Simple yet functional phosphate-loop proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E11943–E11950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812400115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Winsor GL, Griffiths EJ, Lo R, Dhillon BK, Shay JA, Brinkman FS. 2016. Enhanced annotations and features for comparing thousands of Pseudomonas genomes in the Pseudomonas genome database. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D646–D653. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Greipel L, Fischer S, Klockgether J, Dorda M, Mielke S, Wiehlmann L, Cramer N, Tummler B. 2016. Molecular epidemiology of mutations in antimicrobial resistance loci of pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:6726–6734. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00724-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Markussen T, Marvig RL, Gómez-Lozano M, Aanæs K, Burleigh AE, Høiby N, Johansen HK, Molin S, Jelsbak L. 2014. Environmental heterogeneity drives within-host diversification and evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 5:e01592-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01592-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Maunders EA, Triniman RC, Western J, Rahman T, Welch M. 2020. Global reprogramming of virulence and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a single nucleotide polymorphism in elongation factor, fusA1. J Biol Chem 295:16411–16426. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Matsuo Y, Eda S, Gotoh N, Yoshihara E, Nakae T. 2004. MexZ-mediated regulation of mexXY multidrug efflux pump expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by binding on the mexZ-mexX intergenic DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 238:23–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2004.tb09732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Morita Y, Gilmour C, Metcalf D, Poole K. 2009. Translational control of the antibiotic inducibility of the PA5471 gene required for mexXY multidrug efflux gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 191:4966–4975. doi: 10.1128/JB.00073-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jones AK, Woods AL, Takeoka KT, Shen X, Wei JR, Caughlan RE, Dean CR. 2017. Determinants of antibacterial spectrum and resistance potential of the elongation factor G inhibitor argyrin B in key Gram-negative pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e02400-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02400-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Guenard S, Muller C, Monlezun L, Benas P, Broutin I, Jeannot K, Plesiat P. 2014. Multiple mutations lead to MexXY-OprM-dependent aminoglycoside resistance in clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:221–228. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01252-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Morita Y, Sobel ML, Poole K. 2006. Antibiotic inducibility of the MexXY multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of the antibiotic-inducible PA5471 gene product. J Bacteriol 188:1847–1855. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.5.1847-1855.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Feng Y, Likos JJ, Zhu L, Woodward H, Munie G, McDonald JJ, Stevens AM, Howard CP, De Crescenzo GA, Welsch D, Shieh HS, Stallings WC. 2002. Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the catalytic domain of matrix metalloproteinase-2 complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1598:10–23. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(02)00307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hou Y, Lin YP, Sharer JD, March PE. 1994. In vivo selection of conditional-lethal mutations in the gene encoding elongation factor G of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 176:123–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.123-129.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kostylev M, Kim DY, Smalley NE, Salukhe I, Greenberg EP, Dandekar AA. 2019. Evolution of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing hierarchy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:7027–7032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819796116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen R, Déziel E, Groleau M-C, Schaefer AL, Greenberg EP. 2019. Social cheating in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing variant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:7021–7026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819801116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Oshri RD, Zrihen KS, Shner I, Omer Bendori S, Eldar A. 2018. Selection for increased quorum-sensing cooperation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through the shut-down of a drug resistance pump. ISME J 12:2458–2469. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0205-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Jayakumar P, Figueiredo ART, Kümmerli R. 2022. Evolution of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa can occur via loss of function and regulon modulation. mSystems 26:e0035422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Weinreich DM, Watson RA, Chao L. 2005. Perspective: sign epistasis and genetic constraint on evolutionary trajectories. Evolution 59:1165–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jerison ER, Desai MM. 2015. Genomic investigations of evolutionary dynamics and epistasis in microbial evolution experiments. Curr Opin Genet Dev 35:33–39. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wong A. 2017. Epistasis and the evolution of antimicrobial resistance. Front Microbiol 8:246. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Phillips PC. 2008. Epistasis–the essential role of gene interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic systems. Nat Rev Genet 9:855–867. doi: 10.1038/nrg2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Poelwijk FJ, Kiviet DJ, Weinreich DM, Tans SJ. 2007. Empirical fitness landscapes reveal accessible evolutionary paths. Nature 445:383–386. doi: 10.1038/nature05451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Weinreich D, Delaney NF, DePristo MA, Hartl D. 2006. Darwinian evolution can follow only very few mutational paths to fitter proteins. Science 312:111–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1123539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Borrell S, Teo Y, Giardina F, Streicher EM, Klopper M, Feldmann J, Müller B, Victor TC, Gagneux S. 2013. Epistasis between antibiotic resistance mutations drives the evolution of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Evol Med Public Health 2013:65–74. doi: 10.1093/emph/eot003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hall AR, MacLean RC. 2011. Epistasis buffers the fitness effects of rifampicin- resistance mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Evolution 65:2370–2379. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Palmer SO, Rangel EY, Hu Y, Tran AT, Bullard JM. 2013. Two homologous EF-G proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibit distinct functions. PLoS One 8:e80252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ferrin MA, Subramaniam AR. 2017. Kinetic modeling predicts a stimulatory role for ribosome collisions at elongation stall sites in bacteria. Elife 6:e23629. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schuster M, Hawkins AC, Harwood CS, Greenberg EP. 2004. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa RpoS regulon and its relationship to quorum sensing. Mol Microbiol 51:973–985. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Welsh MA, Blackwell HE. 2016. Chemical genetics reveals environment-specific roles for quorum sensing circuits in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cell Chem Biol 23:361–369. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hmelo LR, Borlee BR, Almblad H, Love ME, Randall TE, Tseng BS, Lin C, Irie Y, Storek KM, Yang JJ, Siehnel RJ, Howell PL, Singh PK, Tolker-Nielsen T, Parsek MR, Schweizer HP, Harrison JJ. 2015. Precision-engineering the Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome with two-step allelic exchange. Nat Protoc 10:1820–1841. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rietsch A, Vallet-Gely I, Dove SL, Mekalanos JJ. 2005. ExsE, a secreted regulator of type III secretion genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8006–8011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503005102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Choi KH, Kumar A, Schweizer HP. 2006. A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J Microbiol Methods 64:391–397. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.De Kievit TR, Parkins MD, Gillis RJ, Srikumar R, Ceri H, Poole K, Iglewski BH, Storey DG. 2001. Multidrug efflux pumps: expression patterns and contribution to antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1761–1770. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.6.1761-1770.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Meisner J, Goldberg JB. 2016. The Escherichia coli rhaSR-PrhaBAD inducible promoter system allows tightly controlled gene expression over a wide range in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:6715–6727. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02041-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.CLSI. 2022. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing—32nd ed. CLSI supplement M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sandoz KM, Mitzimberg SM, Schuster M. 2007. Social cheating in Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15876–15881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705653104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Meng EC, Couch GS, Croll TI, Morris JH, Ferrin TE. 2021. UCSF ChimeraX: structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci 30:70–82. doi: 10.1002/pro.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material. Download jb.00114-23-s0001.docx, DOCX file, 0.1 MB (137.9KB, docx)