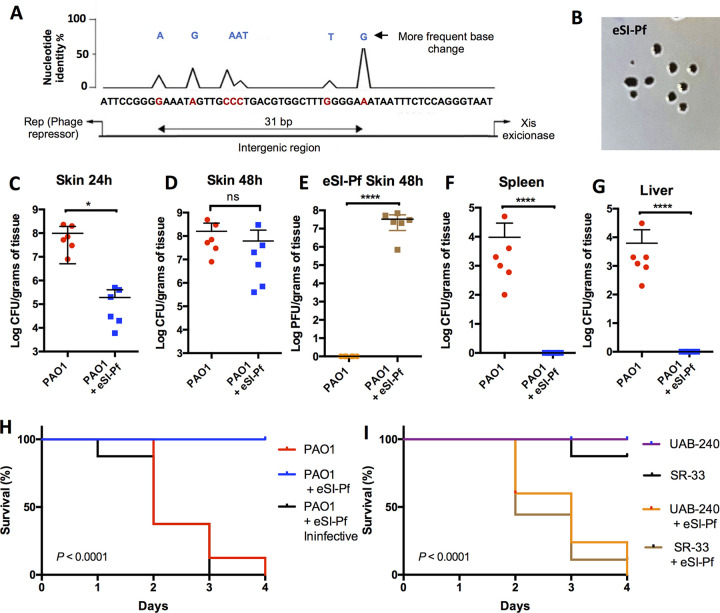
FIG 1.
eSI-Pf leads to decreased P. aeruginosa virulence in a mouse burn model. (A) Sequence analysis of 40 SI-Pf individual clones isolated from single plaques. All mutations were localized in the intergenic region between the phage repressor and the excisionase genes. (B) eSI-Pf formed plaques on a PAO1 lawn. Image were obtained with a handheld camera. (C) Mice infected for 24 h with PAO1 were treated with eSI-Pf. At 24 h posttreatment, the skin showed reduced bacterial load compared to control. (D) However, no significant difference was detected 48 h posttreatment. (E) Mice with burn skin injury were infected with PAO1 and treated with eSI-Pf. The skin was homogenized 48 h postinfection and PFU were quantified by plotting on top of a PAO1 lawn. (F and G) PAO1 infected with eSI-Pf showed impaired dissemination to the spleen (F) and to the liver (G). (H) Kaplan Meier survival curves of mice infected with PAO1 and subsequently treated with eSI-Pf or a deactivated eSI-Pf control. (I) Kaplan Meier survival curves of mice infected with a clinical strain, UAB-240, or an environment isolate, SR-30, and subsequently treated with eSI-Pf. Student's t test was used to analyze data in panels C to G; a Mantel-Cox test was used for the data in panels H and I. Each dot is a biological replicate. Errors bars represent the standard errors of the means.