Abstract
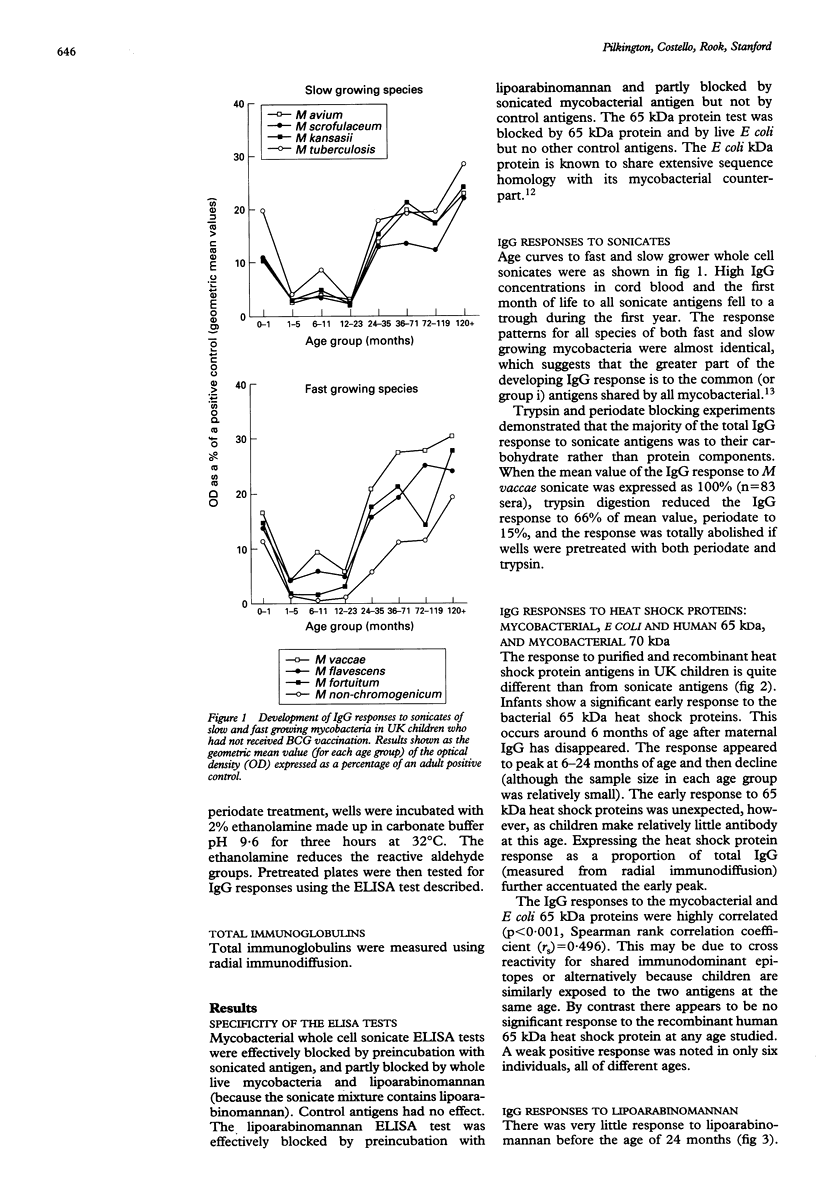
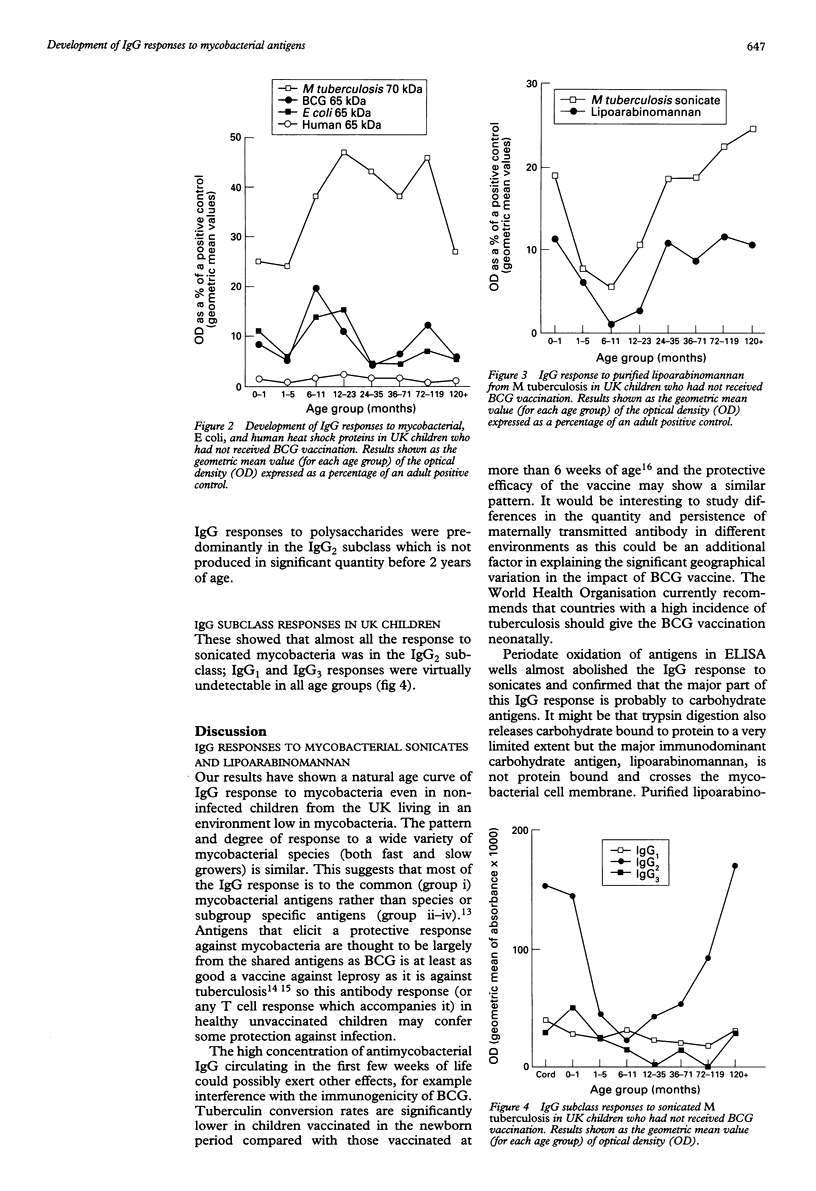
Recent studies link mycobacterial and human heat shock protein antigens with autoimmune diseases. Little is known about the development of antibody responses to these antigens in children. IgG responses to mycobacterial antigens were studied in children living in the UK (an environment low in mycobacteria) who had not received BCG vaccination. Age curves of IgG response to sonicates from different species of mycobacteria were similar suggesting that the greater part of the developing IgG response is to the common antigens shared by all mycobacteria. The major part of the IgG response was to carbohydrate antigens: lipoarabinomannan is a mycobacterial cell wall carbohydrate and was confirmed as a major immunodominant antigen. Infants showed a marked early response to the mycobacterial 65 kilodalton (kDa) and 70 kDa heat shock proteins, but not to the human 65 kDa heat shock protein. The early IgG response to heat shock proteins may reflect cross reactivity to proteins released by a wide variety of bacteria (possibly from breakdown in the gut) or recognition of other immunodominant antigens with high levels of cross reactivity to self.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S. Natural autoantibodies: from 'horror autotoxicus' to 'gnothi seauton'. Immunol Today. 1991 May;12(5):154–159. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr G. M., Rook G. A., al-Saffar M., Van Embden J., Stanford J. L., Behbehani K. Antibody levels to mycobacteria in relation to HLA type: evidence for non-HLA-linked high levels of antibody to the 65 kD heat shock protein of M. bovis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):211–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Young D. B. Autoimmunity, microbial immunity and the immunological homunculus. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. H., Grange J. M., Yates M. D. Mycobacteria in water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;57(2):193–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. M., Kumar A., Narayan V., Akbar M. S., Ahmed S., Abou-Zeid C., Rook G. A., Stanford J., Moreno C. Does antibody to mycobacterial antigens, including lipoarabinomannan, limit dissemination in childhood tuberculosis? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Nov-Dec;86(6):686–692. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Markovits D., Reshef T., van der Zee R., Cohen I. R. Induction and therapy of autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic (NOD/Lt) mouse by a 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B., Coulson A. F., Duff G. W. Sequence homologies between hsp60 and autoantigens. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90210-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Bal V., Mendez-Samperio P., Mehlert A., So A., Rothbard J., Jindal S., Young R. A., Young D. B. Stress proteins may provide a link between the immune response to infection and autoimmunity. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydyard P. M., Tsoulfa G., Sharif M., Bröker B., Smith M., Rook G. A. Immunity to heat shock proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 5):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassau E., Parsons E. R., Johnson G. D. The detection of antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Tubercle. 1976 Mar;57(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(76)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönnighaus J. M., Fine P. E., Sterne J. A., Wilson R. J., Msosa E., Gruer P. J., Jenkins P. A., Lucas S. B., Liomba N. G., Bliss L. Efficacy of BCG vaccine against leprosy and tuberculosis in northern Malawi. Lancet. 1992 Mar 14;339(8794):636–639. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P. C., Schaar C. G., Breedveld F. C., van Eden W., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R., de Vries R. R. Synovial fluid T cell reactivity against 65 kD heat shock protein of mycobacteria in early chronic arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains genes for the major heat shock protein HSP70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L., Grange J. M. The meaning and structure of species as applied to mycobacteria. Tubercle. 1974 Jun;55(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(74)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L., Shield M. J., Rook G. A. How environmental mycobacteria may predetermine the protective efficacy of BCG. Tubercle. 1981 Mar;62(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(81)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styblo K. Overview and epidemiologic assessment of the current global tuberculosis situation with an emphasis on control in developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11 (Suppl 2):S339–S346. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_2.s339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Willeit J., Marosi M., Kleindienst R., Oberhollenzer F., Kiechl S., Stulnig T., Luef G., Wick G. Association of serum antibodies to heat-shock protein 65 with carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1993 Jan 30;341(8840):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92613-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Mehlert A. Serology of mycobacteria: characterization of antigens recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11 (Suppl 2):S431–S435. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_2.s431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Elliott T. J. Stress proteins, infection, and immune surveillance. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90861-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


