Abstract
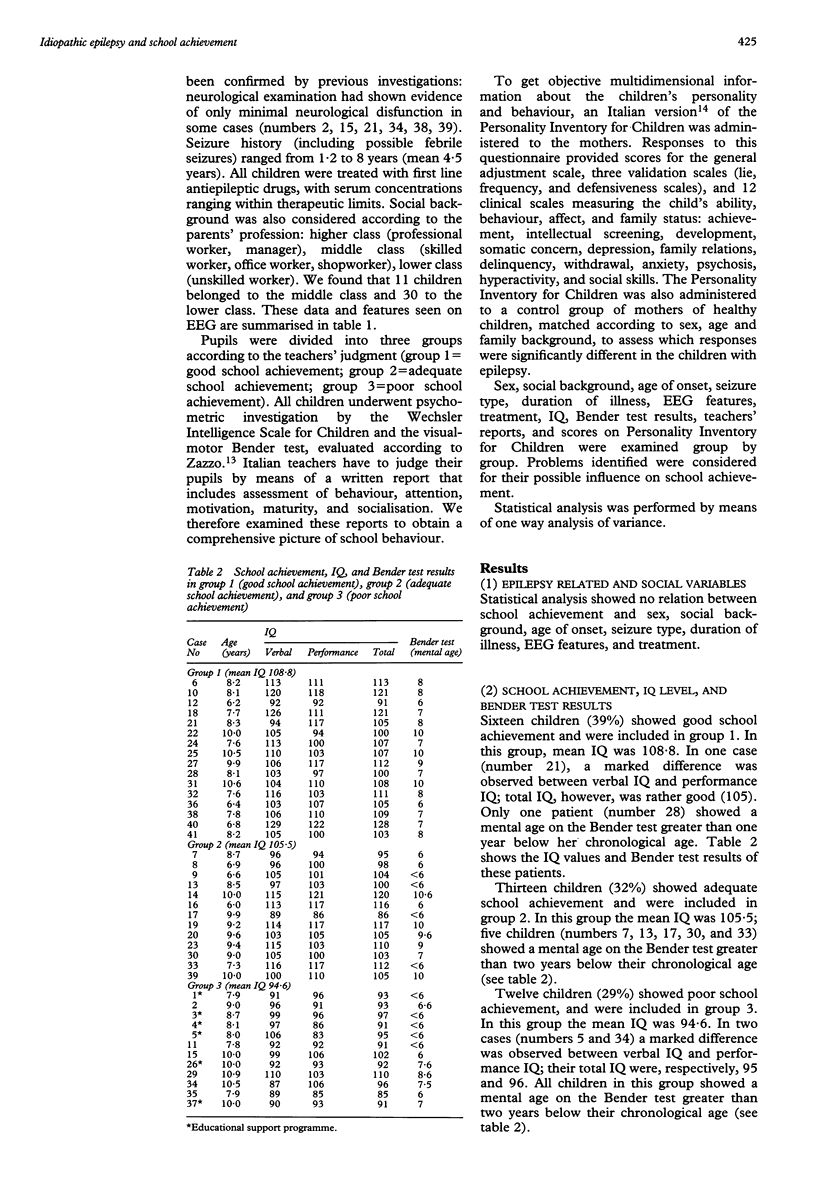
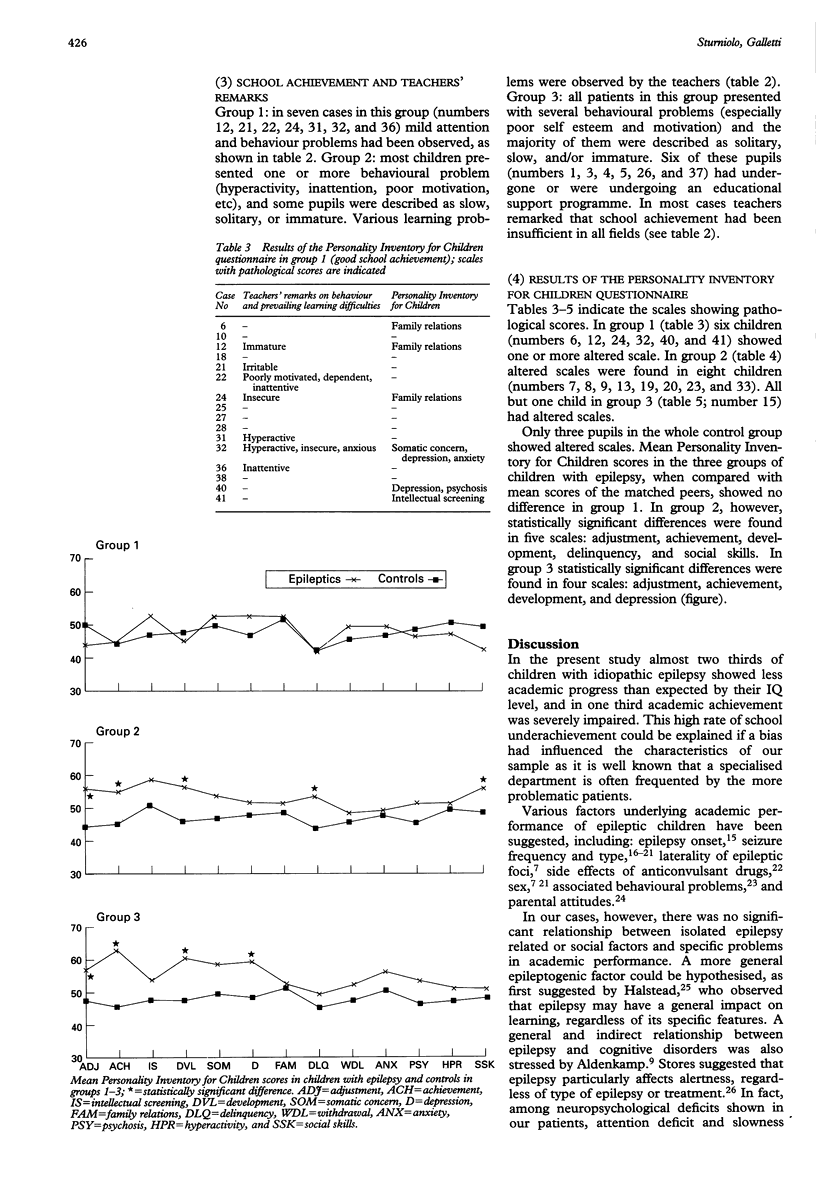
Forty one children (20 boys, 21 girls) aged 6-10.8 years (mean age 8.6 years) who were affected with idiopathic epilepsy underwent neuropsychological (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, Bender test) and behavioural assessment (Personality Inventory for Children; this was also used in a matched control group). Further information was obtained by teachers' reports. School underachievement occurred in 25 children (61%). Statistical analysis showed no influence of sex, social background, age of onset, seizure type, duration of illness, features seen on electroencephalography, and treatment. School failure was due to poor performance in almost all academic fields, and was associated with higher visuomotor impairment; children showing good school performance had a higher mean IQ and less visuomotor impairment. The behaviour of children with epilepsy who had a good academic performance did not differ from that of their healthy peers. Emotional maladjustment (social skill impairment, depression, poor motivation, and low self esteem) was associated with poor school performance. Such problems, that may complicate the course of idiopathic epilepsy and require an appropriate educational programme, should be carefully considered by the clinician.
Full text
PDF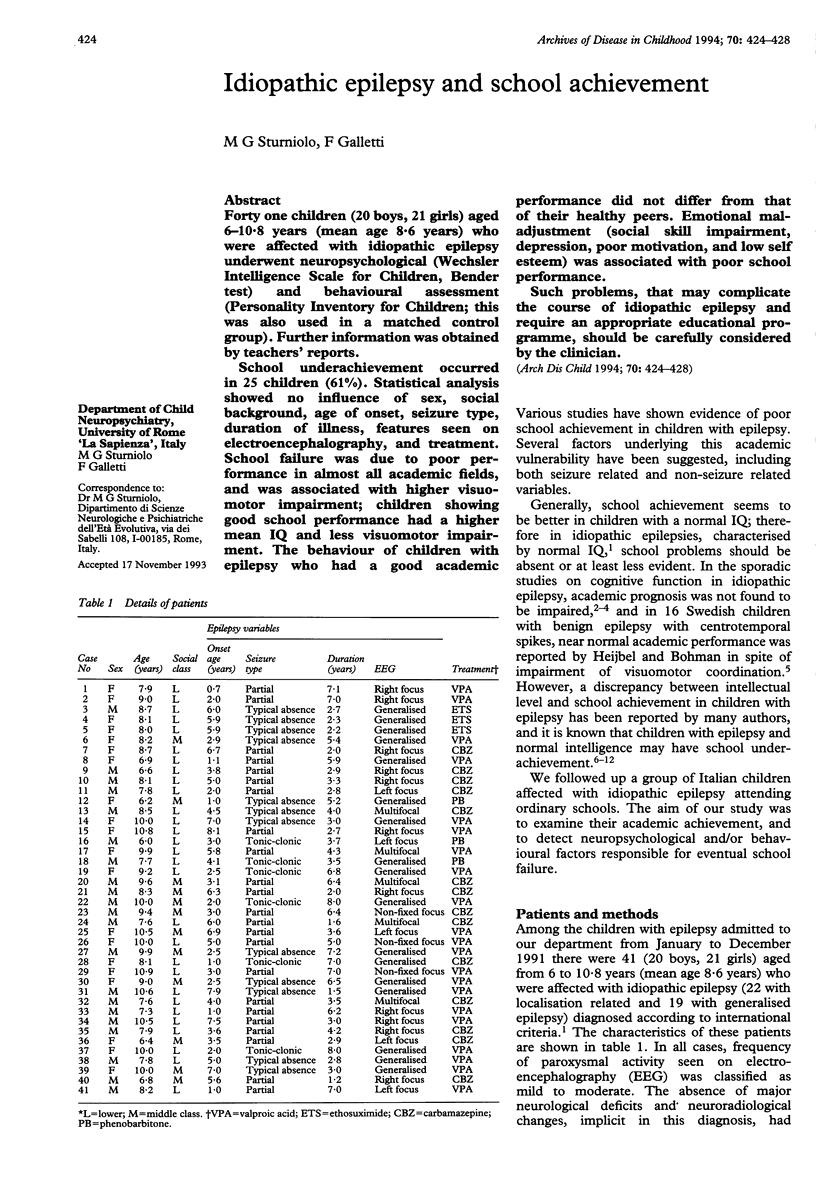


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarts J. H., Binnie C. D., Smit A. M., Wilkins A. J. Selective cognitive impairment during focal and generalized epileptiform EEG activity. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):293–308. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldenkamp A. P., Alpherts W. C., Dekker M. J., Overweg J. Neuropsychological aspects of learning disabilities in epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1990;31 (Suppl 4):S9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1990.tb05874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Wildig C., Jones P. W. Teachers' perceptions of epilepsy. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Dec;67(12):1467–1471. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.12.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodrill C. B. A neuropsychological battery for epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1978 Dec;19(6):611–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1978.tb05041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodrill C. B. Correlates of generalized tonic-clonic seizures with intellectual, neuropsychological, emotional, and social function in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1986 Jul-Aug;27(4):399–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farwell J. R., Dodrill C. B., Batzel L. W. Neuropsychological abilities of children with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1985 Sep-Oct;26(5):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1985.tb05670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallhofer B. Epilepsy and its prejudice. Teachers' knowledge and opinions: are they a response to psychopathological phenomena? Psychopathology. 1984;17(4):187–212. doi: 10.1159/000284053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Hartlage L. C. Comparative performance of epileptic and nonepileptic children and adolescents. (On tests of academic, communicative and social skills). Dis Nerv Syst. 1971 Jun;32(6):418–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteling J. M., Seydel E. R., Wiegman O. Previous experiences with epilepsy and effectiveness of information to change public perception of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1986 Nov-Dec;27(6):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALSTEAD H. Abilities and behaviour of epileptic children. J Ment Sci. 1957 Jan;103(430):28–47. doi: 10.1192/bjp.103.430.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartlage L. C., Green J. B. The relation of parental attitudes to academic and social achievement in epileptic children. Epilepsia. 1972 Jan;13(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1972.tb04544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijbel J., Bohman M. Benign epilepsy of children with centrotemporal EEG foci: intelligence, behavior, and school adjustment. Epilepsia. 1975 Dec;16(5):679–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb04751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare P. Does illness foster dependency? A study of epileptic and diabetic children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1984 Feb;26(1):20–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1984.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth L., Whitmore K. A study of children with epilepsy attending ordinary schools. I: their seizure patterns, progress and behaviour in school. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1974 Dec;16(6):746–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1974.tb03395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennekens-Schinkel A., Linschooten-Duikersloot E. M., Bouma P. A., Peters A. C., Stijnen T. Spelling errors made by children with mild epilepsy: writing-to-dictation. Epilepsia. 1987 Sep-Oct;28(5):555–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb03688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loiseau P., Pestre M., Dartigues J. F., Commenges D., Barberger-Gateau C., Cohadon S. Long-term prognosis in two forms of childhood epilepsy: typical absence seizures and epilepsy with rolandic (centrotemporal) EEG foci. Ann Neurol. 1983 Jun;13(6):642–648. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. G., Moore J. R. Parental expectations for their epileptic children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1979 Oct;20(4):299–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1979.tb00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. S., Barabas G., Ferrari M. Emotional concomitants of childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1982 Dec;23(6):671–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1982.tb05083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary D. S., Seidenberg M., Berent S., Boll T. J. Effects of age of onset of tonic-clonic seizures on neuropsychological performance in children. Epilepsia. 1981 Apr;22(2):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1981.tb04102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazzaglia P., Frank-Pazzaglia L. Record in grade school of pupils with epilepsy: an epidemiological study. Epilepsia. 1976 Dec;17(4):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1976.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penry J. K., Dean J. C. Prevention of intractable partial seizures by intermittent vagal stimulation in humans: preliminary results. Epilepsia. 1990;31 (Suppl 2):S40–S43. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1990.tb05848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenberg M., Beck N., Geisser M., Giordani B., Sackellares J. C., Berent S., Dreifuss F. E., Boll T. J. Academic achievement of children with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1986 Nov-Dec;27(6):753–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenberg M., O'Leary D. S., Berent S., Boll T. Changes in seizure frequency and test-retest scores on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Epilepsia. 1981 Feb;22(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1981.tb04334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stores G. School-children with epilepsy at risk for learning and behaviour problems. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Aug;20(4):502–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturniolo M. G., Giannotti F., Cortesi F., Galletti F. Partial childhood epilepsy and reaction time: the effect of interictal EEG discharges. Neurophysiol Clin. 1992 Sep;22(4):287–299. doi: 10.1016/s0987-7053(05)80261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


