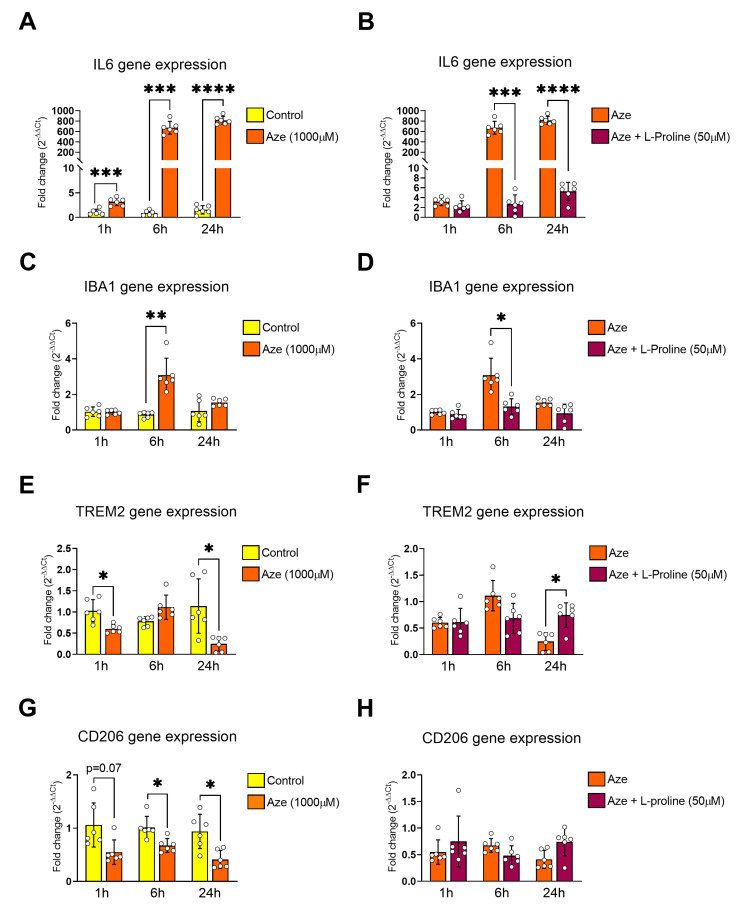
Figure 2.
Effects of L-proline supplementation on the pro- and anti-inflammatory gene expression profile of BV2 cells after exposure to AZE. Gene expression in cells exposed to AZE alone or co-administered with L-proline was measured using real-time qPCR and quantified using the ΔCt method after normalization to the S18 housekeeping gene. Bar graphs display comparative gene expression changes in the following inflammation-related genes: (A,B) IL6, (C,D) IBA1, (E,F) TREM2 and (G,H) CD206. Results are presented as mean fold changes vs. control ± SEM (A,C,E,G) or vs. AZE (B,D,F,H) from n = 6 biological replicates. Statistically significant data (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 or **** p < 0.0001) were determined by repeated measures ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Aze = L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid; IL6 = interleukin 6; IBA1 = ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1; TREM2 = triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; CD206 = cluster of differentiation 206 (also known as mannose receptor C-type 1).