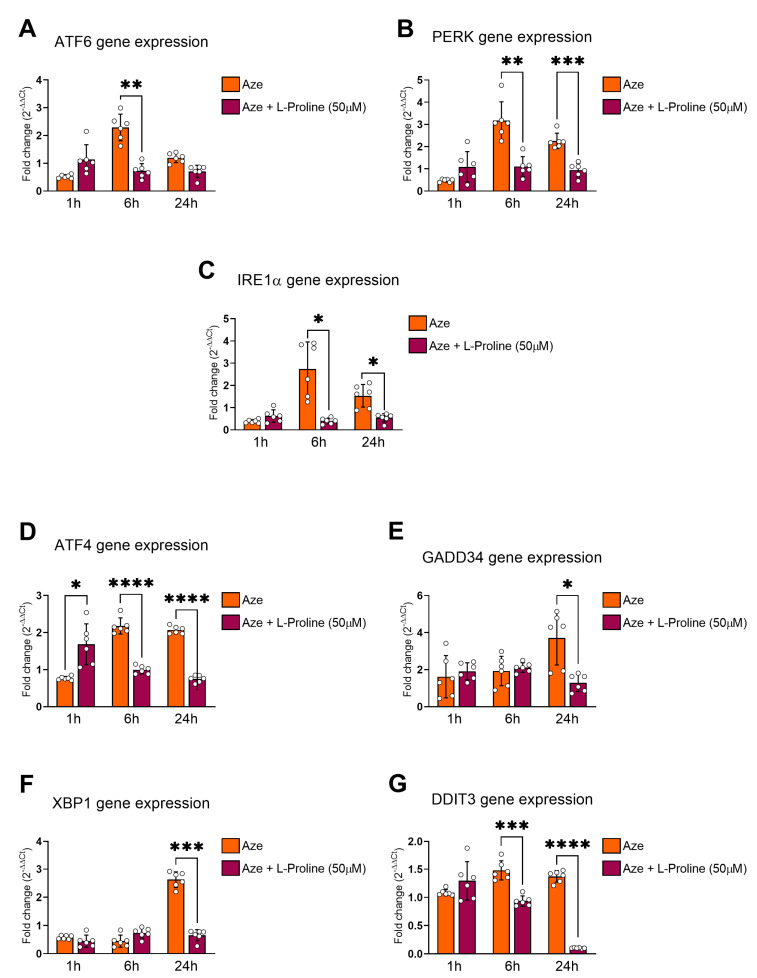
Figure 4.
Effects of L-proline co-administration on the expression of ER stress/UPR genes in AZE-treated BV2 microglia. Gene expression was measured using real-time qPCR and quantified using the ΔCt method after normalization to the S18 housekeeping gene. Bar graphs show the differential expression of the following upstream and downstream regulators of the ER stress/UPR response: ATF6, PERK (also known as EIF2AK3), IRE1α (also known as ERN1), ATF4, GADD34, XBP1 and DDIT3. Relative expression levels of (A) ATF6, (B) PERK, (C) IRE1α, (D) ATF4, (E) GADD34, (F) XBP1 and (G) DDIT3 transcripts were measured in AZE-treated cells in the absence (Aze) or presence of L-proline (Aze + L-Proline) at various times (1, 6 and 24 h, respectively). Results are presented as mean fold changes in controls ± SEM of three independent experiments, each run using two biological replicates per experiment (n = 6). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 or **** p < 0.0001 vs. control, as determined by repeated measures ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test. Aze = L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid; ATF6 = Activating transcription factor 6; PERK = protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (also known as EIF2AK3 = eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3); IRE1α = inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase/endoribonuclease 1α (also known as ERN1 = endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1); ATF4 = activating transcription factor 4; GADD34 = growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein (also known as PPP1R15A = protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 15A); XBP1 = X-box binding protein 1; DDIT3 = DNA damage inducible transcript 3 (also known as CHOP = C/EBP homologous protein).