Abstract
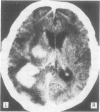
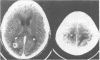
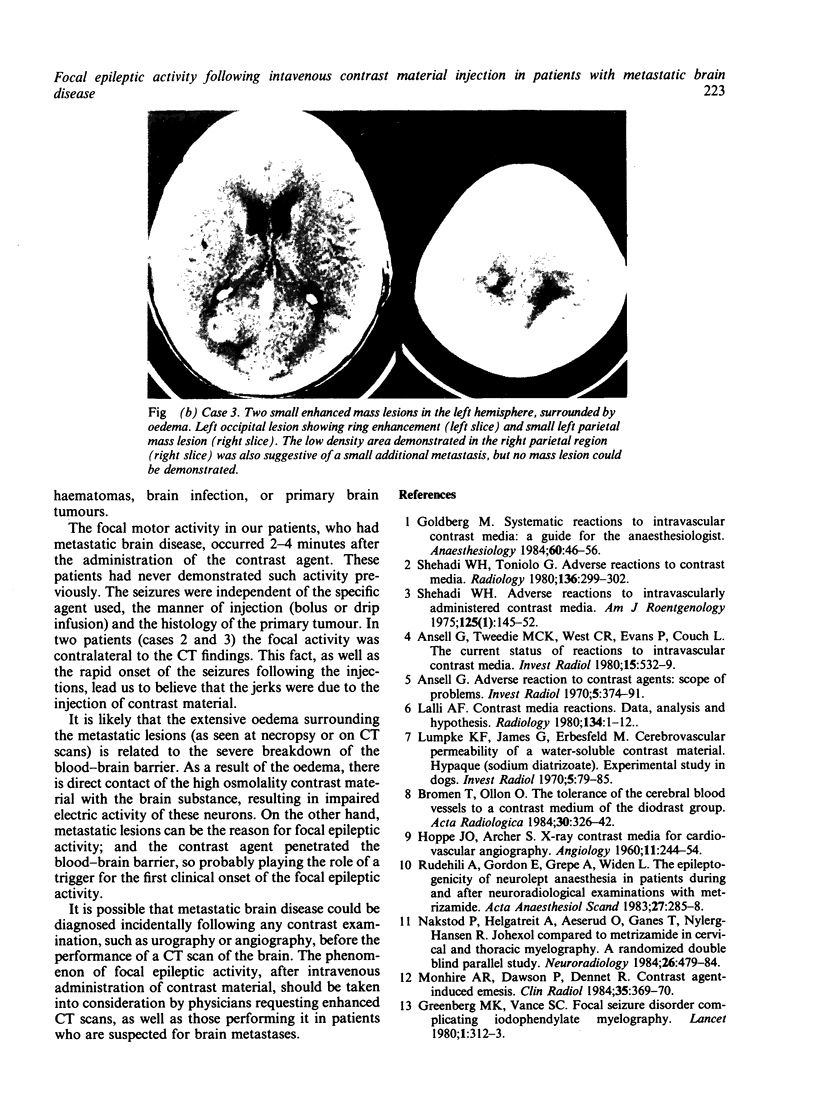
Four patients with metastatic brain disease were referred for computed tomographic (CT) examination with contrast material injection. Within 2 to 4 minutes after the intravenous administration of water soluble contrast agent, focal epileptic activity occurred. The seizures became generalised in two of the patients who later died following status epilepticus. In the other two patients the focal seizures correlated with the localisation of the metastatic mass lesions. None of the patients had a previous history of epilepsy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansell G. Adverse reactions to contrast agents. Scope of problem. Invest Radiol. 1970 Nov-Dec;5(6):374–391. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197011000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. Systemic reactions to intravascular contrast media. A guide for the anesthesiologist. Anesthesiology. 1984 Jan;60(1):46–56. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198401000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. K., Vance S. C. Focal seizure disorder complicating iodophendylate myelography. Lancet. 1980 Feb 9;1(8163):312–313. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90808-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPE J. O., ARCHER S. X-ray contrast media for cardiovascular angiography. Angiology. 1960 Jun;11:244–254. doi: 10.1177/000331976001100318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalli A. F. Contrast media reactions: data analysis and hypothesis. Radiology. 1980 Jan;134(1):1–12. doi: 10.1148/radiology.134.1.6985735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe K. F., James G., Erbesfeld M., Mende T. J., Viamonte M., Jr Cerebrovascular permeability of a water-soluble contrast material, Hypaque (sodium diatrizoate). Experimental study in dogs. Invest Radiol. 1970 Mar-Apr;5(2):79–85. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhire A. R., Dawson P., Dennet R. Contrast agent-induced emesis. Clin Radiol. 1984 Sep;35(5):369–370. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(84)80186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakstad P., Helgetveit A., Aaserud O., Ganes T., Nyberg-Hansen R. Iohexol compared to metrizamide in cervical and thoracic myelography. A randomized double blind parallel study. Neuroradiology. 1984;26(6):479–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00342685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudehill A., Gordon E., Grepe A., Widén L. The epileptogenicity of neurolept anaesthesia in patients during and after neuroradiological examinations with metrizamide. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1983 Aug;27(4):285–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1983.tb01952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehadi W. H., Toniolo G. Adverse reactions to contrast media: a report from the Committee on Safety of Contrast Media of the International Society of Radiology. Radiology. 1980 Nov;137(2):299–302. doi: 10.1148/radiology.137.2.7433658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]