Abstract
Diffuse Lewy body disease is an important pathological substrate of the common syndrome of parkinsonian dementia. The new technique of anti-ubiquitin immunocytochemistry has been used in a correlative quantitative neuropathological study of fifteen cases of diffuse Lewy body disease, showing that the severity of dementia is related to cortical Lewy body density, whilst subcortical abnormalities make a much less significant contribution. Cortical senile plaques also appear to be part of the pathology of diffuse Lewy body disease and should not therefore be used as an isolated diagnostic criterion for Alzheimer's disease. Diagnostic criteria for diffuse Lewy body disease are discussed.
Full text
PDF






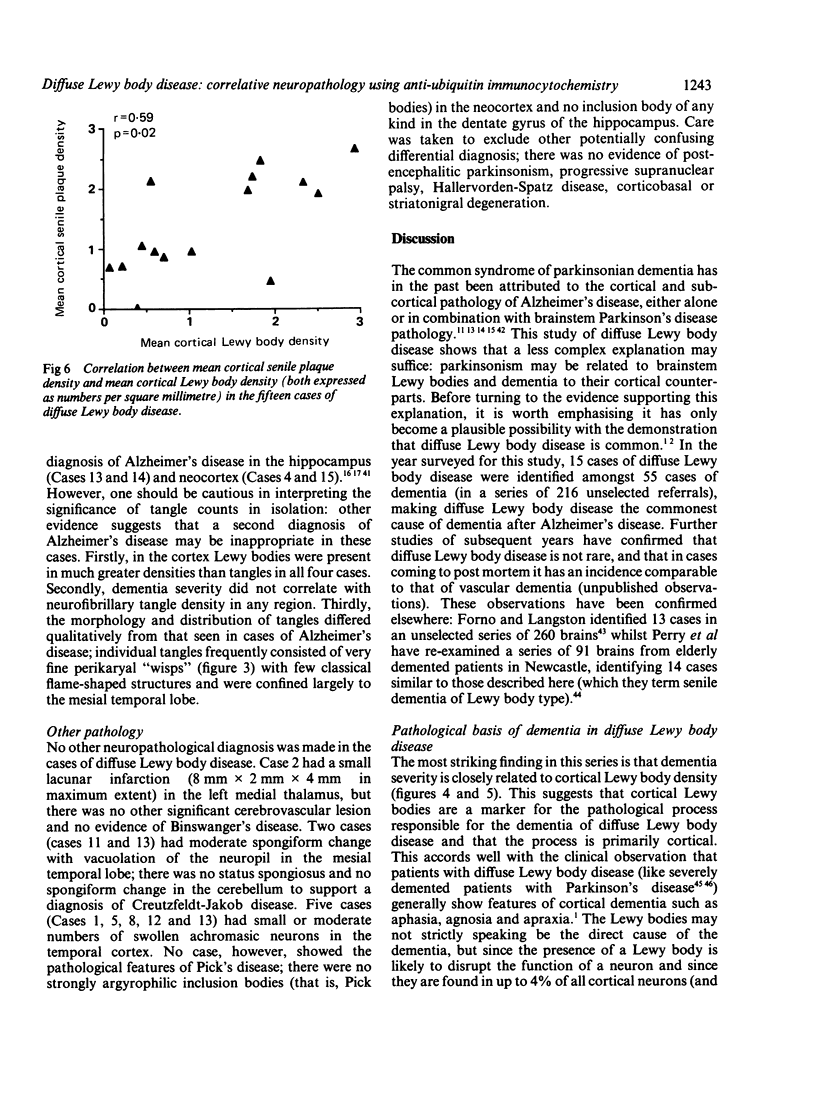




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball M. J., Griffin-Brooks S., MacGregor J. A., Nagy B., Ojalvo-Rose E., Fewster P. H. Neuropathological definition of Alzheimer disease: multivariate analyses in the morphometric distinction between Alzheimer dementia and normal aging. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2(1):29–37. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198802010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. J. The morphological basis of dementia in Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):180–184. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancher C., Lassmann H., Budka H., Jellinger K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Wiche G., Seitelberger F., Wisniewski H. M. An antigenic profile of Lewy bodies: immunocytochemical indication for protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jan;48(1):81–93. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198901000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller F., Mizutani T., Roessmann U., Gambetti P. Parkinson disease, dementia, and Alzheimer disease: clinicopathological correlations. Ann Neurol. 1980 Apr;7(4):329–335. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. G., Marsden C. D. How common is dementia in Parkinson's disease? Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1262–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92807-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt C. R., Filley C. M., Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B. K., de la Monte S., Norenberg M. D., Schneck S. A. Diffuse Lewy body disease and progressive dementia. Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1520–1528. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chui H. C., Mortimer J. A., Slager U., Zarow C., Bondareff W., Webster D. D. Pathologic correlates of dementia in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1986 Oct;43(10):991–995. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520100013007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chui H. C., Teng E. L., Henderson V. W., Moy A. C. Clinical subtypes of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurology. 1985 Nov;35(11):1544–1550. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.11.1544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., White C. L., 3rd, Manz H. J., Parhad I. M., Curry B., Whitehouse P. J., Lehmann J., Coyle J. T. Primary degenerative dementia without Alzheimer pathology. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):462–470. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Timiras P. S. Ubiquitin-protein conjugates in Alzheimer's lesions. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 18;79(1-2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. B. Demonstration of neurofibrillary tangles in paraffin sections: a quick and simple method using a modification of Palmgren's method. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Jan;39(1):67–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Davies P., Mayeux R., Crystal H., Horoupian D. S., Thompson A., Goldman J. E. Diffuse Lewy body disease. Neuropathological and biochemical studies of six patients. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(1):8–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00686786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditter S. M., Mirra S. S. Neuropathologic and clinical features of Parkinson's disease in Alzheimer's disease patients. Neurology. 1987 May;37(5):754–760. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.5.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. A., Stahl S. Letter: Extrapyramidal dementia and levodopa. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):809–809. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. The organization and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mammalian forebrain. Brain Res. 1982 Nov;257(3):327–388. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(82)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forno L. S. The Lewy body in Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim A. M., Mathieson G. Dementia in Parkinson disease: a neuropathologic study. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1209–1214. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. V., McKinney M., Coyle J. T. Evidence for a cholinergic projection to neocortex from neurons in basal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka K., Yoshimura M., Ikeda K., Budka H. Diffuse type of Lewy body disease: progressive dementia with abundant cortical Lewy bodies and senile changes of varying degree--a new disease? Clin Neuropathol. 1984 Sep-Oct;3(5):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuhara S., Mori H., Izumiyama N., Yoshimura M., Ihara Y. Lewy bodies are ubiquitinated. A light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(4):345–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00687787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox G., Lowe J., Morrell K., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Anti-ubiquitin immunocytochemistry is more sensitive than conventional techniques in the detection of diffuse Lewy body disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jan;52(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox G., Lowe J., Morrell K., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a component of neurofibrillary tangles in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leverenz J., Sumi S. M. Parkinson's disease in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1986 Jul;43(7):662–664. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520070020010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Blanchard A., Morrell K., Lennox G., Reynolds L., Billett M., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Lennox G., Jefferson D., Morrell K., McQuire D., Gray T., Landon M., Doherty F. J., Mayer R. J. A filamentous inclusion body within anterior horn neurones in motor neurone disease defined by immunocytochemical localisation of ubiquitin. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O. Pathological basis for neurotransmitter changes in Parkinson's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):3–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1983.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Rosen J., Benson F. Is "subcortical dementia" a recognizable clinical entity? Ann Neurol. 1983 Sep;14(3):278–283. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Spanton S. Heterogeneity in dementia of the Alzheimer type: evidence of subgroups. Neurology. 1985 Apr;35(4):453–461. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama Y., Fukunaga H., Yamashita M. Alzheimer's disease with widespread presence of Lewy bodies. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1984;38(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1984.tb00357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölsä P. K., Marttila R. J., Rinne U. K. Extrapyramidal signs in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1984 Aug;34(8):1114–1116. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.8.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano I., Hirano A. Parkinson's disease: neuron loss in the nucleus basalis without concomitant Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1984 May;15(5):415–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAZAKI H., LIPKIN L. E., ARONSON S. M. Diffuse intracytoplasmic ganglionic inclusions (Lewy type) associated with progressive dementia and quadriparesis in flexion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1961 Apr;20:237–244. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196104000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. The extrapyramidal disorder of Alzheimer's disease. Eur Neurol. 1974;12(2):94–103. doi: 10.1159/000114608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. C., Esiri M. M., Hiorns R. W., Wilcock G. K., Powell T. P. Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4531–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Friedman R., Shaw G., Chau V. Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3033–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. H., Blessed G., Perry E. K., Tomlinson B. E. Histochemical observations on cholinesterase activities in the brains of elderly normal and demented (Alzheimer-type) patients. Age Ageing. 1980 Feb;9(1):9–16. doi: 10.1093/ageing/9.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. H., Irving D., Blessed G., Perry E. K., Fairbairn A. F. Clinically and neuropathologically distinct form of dementia in the elderly. Lancet. 1989 Jan 21;1(8630):166–166. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. H. Recent advances in neuropathology. Br Med Bull. 1986 Jan;42(1):34–41. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn N. P., Rossor M. N., Marsden C. D. Dementia and Parkinson's disease--pathological and neurochemical considerations. Br Med Bull. 1986 Jan;42(1):86–90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisberg B., Ferris S. H., de Leon M. J., Crook T. The Global Deterioration Scale for assessment of primary degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;139(9):1136–1139. doi: 10.1176/ajp.139.9.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Clark A. W., Sternberger N. A., Sternberger L. A. Lewy body dementia without Alzheimer changes. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):490–497. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern Y., Mayeux R., Sano M., Hauser W. A., Bush T. Predictors of disease course in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1987 Oct;37(10):1649–1653. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.10.1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkava R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of Alzheimer type. A comparative study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jun;65(6):636–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Pilleri G. Basal nucleus of Meynert. A neuropathological study in Alzheimer's disease, simple senile dementia, Pick's disease and Huntington's chorea. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):243–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Hansen L. A., DeTeresa R., Davies P., Tobias H., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type without neocortical neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 May;46(3):262–268. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198705000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Sep;11(3):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of non-demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Sep-Oct;7(2):331–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J. Clinical and neurochemical consequences of neuronal loss in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M. Plaques, tangles and dementia. A quantitative study. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M. Cortical changes in the parkinsonian brain: a contribution to the delineation of "diffuse Lewy body disease". J Neurol. 1983;229(1):17–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00313493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





