Abstract
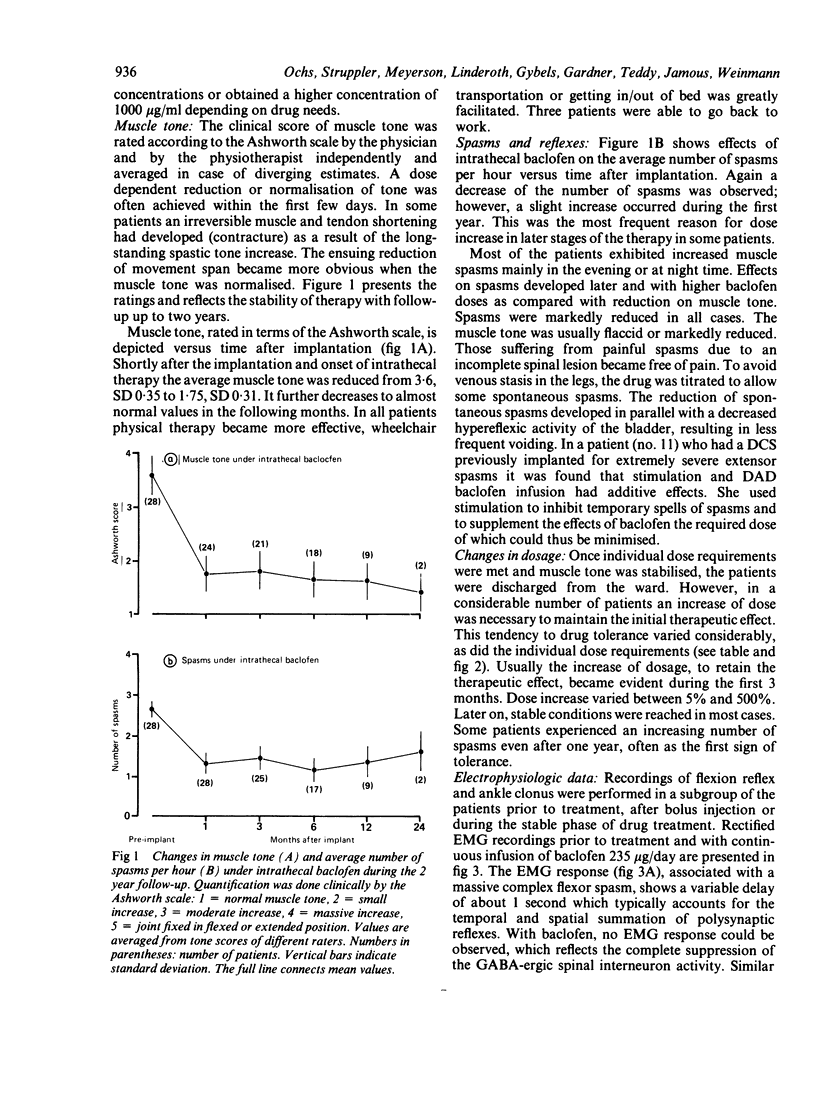
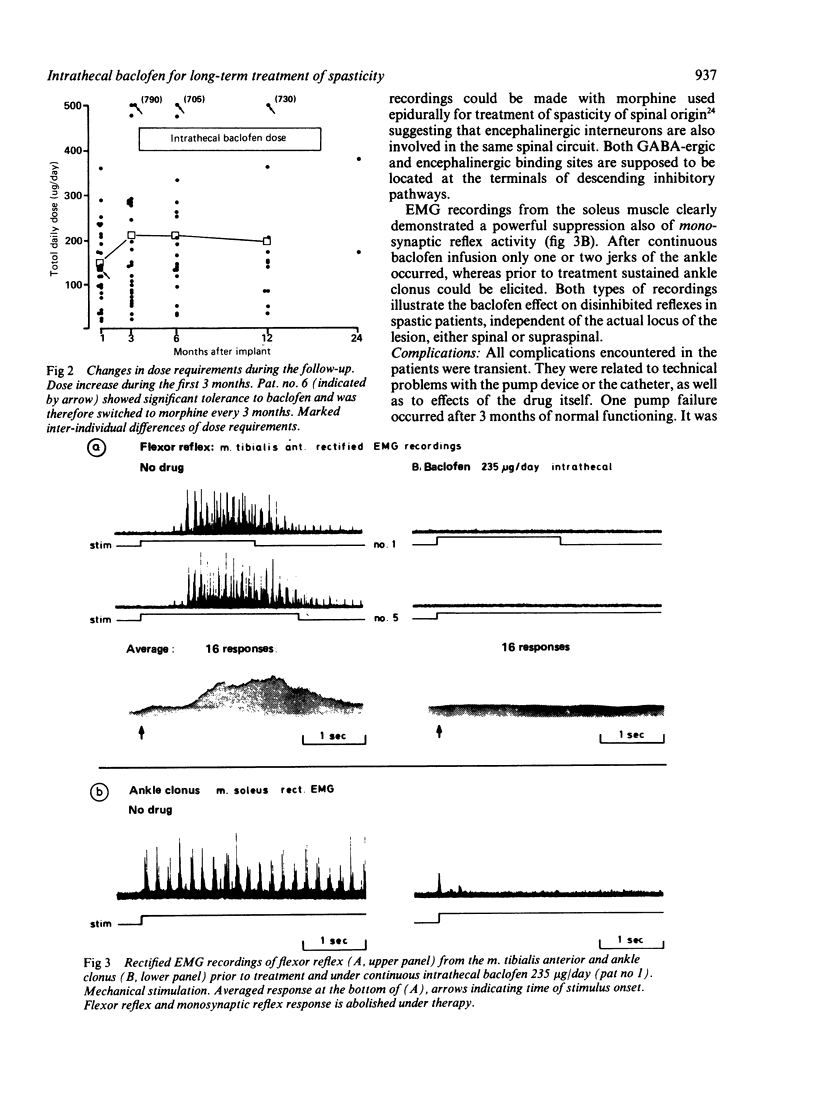
Twenty eight patients with severe, intractable spasticity have been treated by chronic intrathecal administration of baclofen. An implantable programmable drug-administration-device (DAD) was used with a permanent intrathecal catheter. Infusion of 50 to 800 micrograms/day of baclofen completely abolished spasticity. Follow-up was up to two years. Therapeutic effect was documented by clinical assessment of tone, spasms and reflexes and by electrophysiological recordings of mono- and polysynaptic reflex activity. Complications and untoward side-effects of the procedure were few. This procedure is recommended for spasticity of spinal origin refractory to physiotherapy and oral medication. It is a preferable alternative to ablative surgical intervention.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davidoff R. A. Antispasticity drugs: mechanisms of action. Ann Neurol. 1985 Feb;17(2):107–116. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm G. H., Terrence C. F., Chattha A. S. Baclofen in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: double-blind study and long-term follow-up. Ann Neurol. 1984 Mar;15(3):240–244. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W., Olpe H. R. Stereoselectivity of L-baclofen in hippocampal slices of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 22;55(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Effects of intravenously administered enantiomers of baclofen on functionally identified units in lumbar dorsal horn of the spinal cat. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Nov;21(11):1073–1083. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Zieglgänsberger W. D-baclofen does not antagonize the actions of L-baclofen on rat neocortical neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 3;72(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90626-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. F., Burke D., Marosszeky J. E., Gillies J. D. A new agent for the control of spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Aug;33(4):464–468. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsson E., Lindblom U., Mårtensson A. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of baclofen (Lioresal) at optimal therapeutic responses in spastic paresis. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Nov;23(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroin J. S., Penn R. D., Beissinger R. L., Arzbaecher R. C. Reduced spinal reflexes following intrathecal baclofen in the rabbit. Exp Brain Res. 1984;54(1):191–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00235831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan D. L., Selwyn M., Cooper I. S. Time course of clinical and physiological effects of stimulation of the cerebellar surface in patients with spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Feb;41(2):150–160. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H., Zierski J., Dralle D., Börner U., Hoffmann O. The effect of intrathecal baclofen on electrical muscle activity in spasticity. J Neurol. 1987 Jun;234(5):348–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00314294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen E., Petersen T., Schrøder H. D. Relation between flexor spasms, uninhibited detrusor contractions and anal sphincter activity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Mar;49(3):273–277. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Kroin J. S. Continuous intrathecal baclofen for severe spasticity. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):125–127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Kroin J. S. Intrathecal baclofen alleviates spinal cord spasticity. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1078–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91487-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Paice J. A. Chronic intrathecal morphine for intractable pain. J Neurosurg. 1987 Aug;67(2):182–186. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.2.0182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawal N., Arnér S., Gustafsson L. L., Allvin R. Present state of extradural and intrathecal opioid analgesia in Sweden. A nationwide follow-up survey. Br J Anaesth. 1987 Jun;59(6):791–799. doi: 10.1093/bja/59.6.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Dickson C. D-Baclofen is an antagonist at baclofen receptors mediating antinociception in the spinal cord. Pharmacology. 1985;31(5):248–259. doi: 10.1159/000138129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindou M., Abdennebi B., Sharkey P. Microsurgical selective procedures in peripheral nerves and the posterior root-spinal cord junction for spasticity. Appl Neurophysiol. 1985;48(1-6):97–104. doi: 10.1159/000101110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steardo L., Leo A., Marano E. Efficacy of baclofen in trigeminal neuralgia and some other painful conditions. A clinical trial. Eur Neurol. 1984;23(1):51–55. doi: 10.1159/000115677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struppler A., Burgmayer B., Ochs G. B., Pfeiffer H. G. The effect of epidural application of opioids on spasticity of spinal origin. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90576-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. R., Yaksh T. L. Baclofen is antinociceptive in the spinal intrathecal space of animals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 15;51(4):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


