Abstract
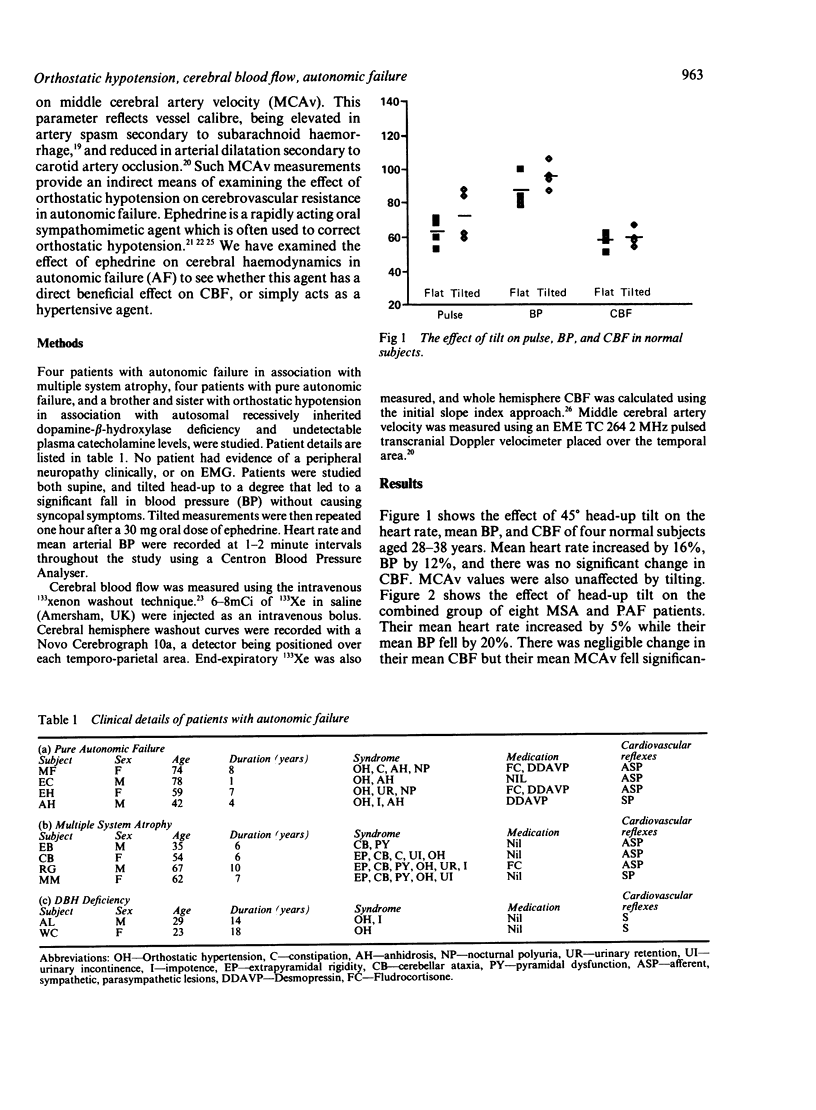
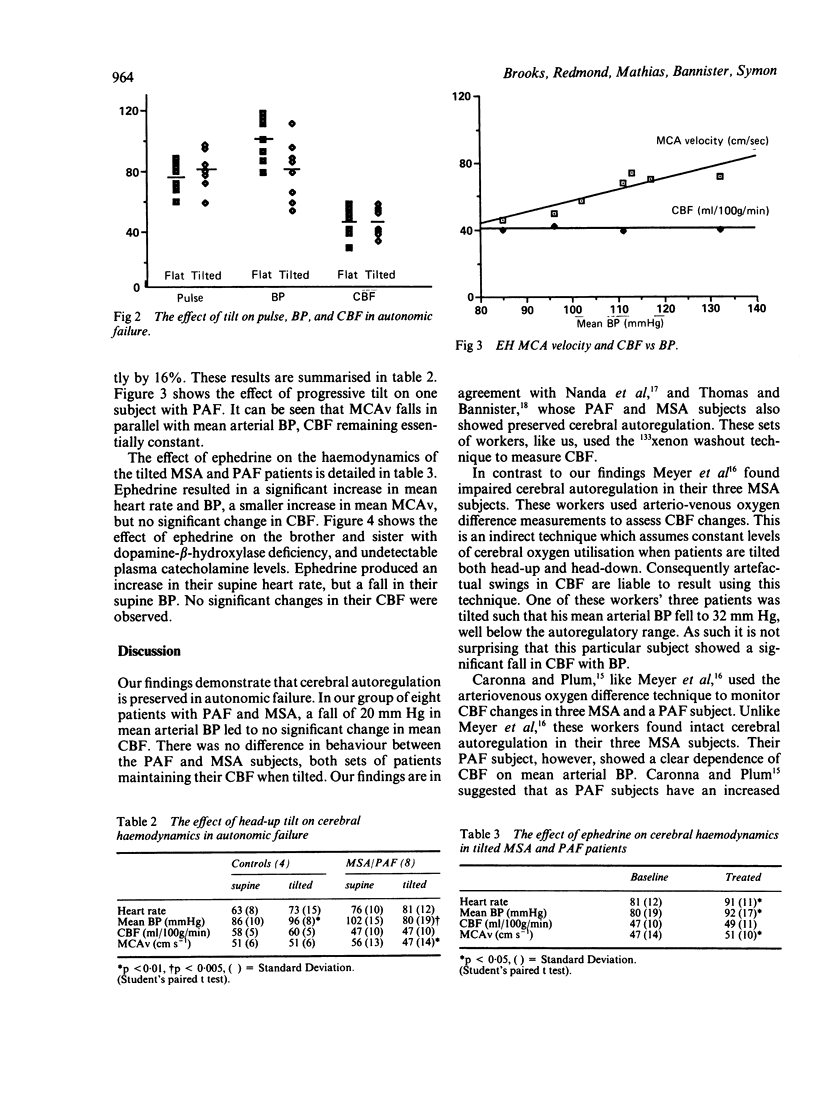
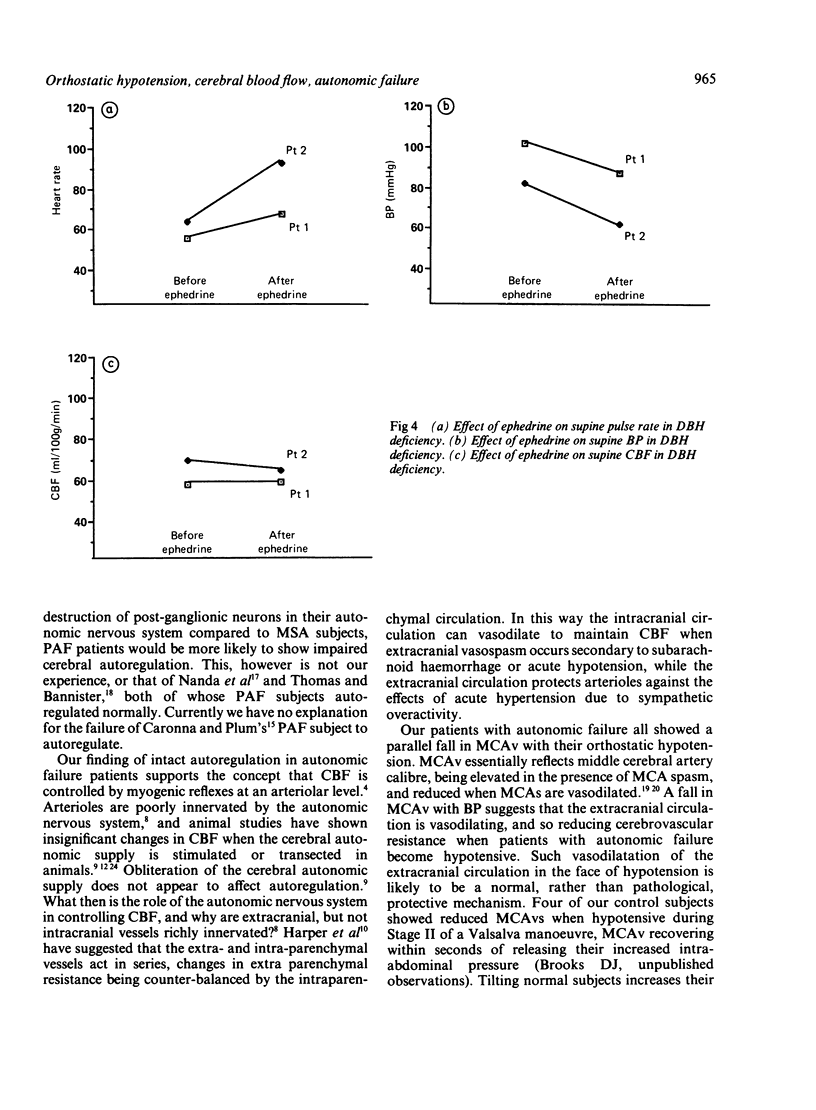
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) and middle cerebral artery velocity (MCAv) have been measured using 133xenon washout and transcranial Doppler in ten patients with autonomic failure. Four pure autonomic failure and four multiple system atrophy patients behaved similarly: tilting them sufficiently to induce significant orthostatic hypotension without causing syncopal symptoms led to a significant fall in their mean MCAv, but no change in their mean CBF. These findings suggest that cerebral autoregulation is preserved in autonomic failure, orthostatic hypotension resulting in a reactive vasodilatation which lowers MCAv, reduces vascular resistance, and maintains CBF. Ephedrine helped to correct the orthostatic hypotension, but had no direct effect on CBF. Two siblings with orthostatic hypotension secondary to dopamine-beta-hydroxylase deficiency also had preserved cerebral autoregulation, but ephedrine led to paradoxical hypotension in these patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaslid R., Huber P., Nornes H. Evaluation of cerebrovascular spasm with transcranial Doppler ultrasound. J Neurosurg. 1984 Jan;60(1):37–41. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.1.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNETT A. J., WAGNER G. R. Severe orthostatic hypotension: case report and description of response to sympatheticomimetic drugs. Am Heart J. 1958 Sep;56(3):412–424. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(58)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach G. L., Heistad D. D. Effects of sympathetic stimulation and changes in arterial pressure on segmental resistance of cerebral vessels in rabbits and cats. Circ Res. 1983 May;52(5):527–533. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.5.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. C., Powell S., Rutt D., Browse N. L. Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity: a validation study. Stroke. 1986 Sep-Oct;17(5):913–915. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.5.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caronna J. J., Plum F. Cerebrovascular regulation in preganglionic and postganglionic autonomic insufficiency. Stroke. 1973 Jan-Feb;4(1):12–19. doi: 10.1161/01.str.4.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B., Bannister R., Sever P. Pressor amines and monoamine-oxidase inhibitors for treatment of postural hypotension in autonomic failure. Limitations and hazards. Lancet. 1978 Jan 28;1(8057):172–175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90610-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSTEIN U. PHYSIOLOGIE UND PATHOPHYSIOLOGIE DES HIRNKREISLAUFS. Med Welt. 1965 Apr 10;15:715–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield J. C., Jr, Tindall G. T. Effect of norepinephrine, epinephrine, and angiotensin on blood flow in the internal carotid artery of man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1672–1684. doi: 10.1172/JCI105858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow: influence of the arterial blood pressure on the blood flow through the cerebral cortex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Oct;29(5):398–403. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.5.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M., Deshmukh V. D., Rowan J. O., Jennett W. B. The influence of sympathetic nervous activity on cerebral blood flow. Arch Neurol. 1972 Jul;27(1):1–6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490130003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. M., Millar R. A., Purves M. J. Observations on the extrinsic neural control of cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Circ Res. 1969 Jul;25(1):77–93. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen N. A. Control of cerebral circulation in health and disease. Circ Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):749–760. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.6.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Shimazu K., Fukuuchi Y., Ouchi T., Okamoto S., Koto A., Ericsson A. D. Cerebral dysautoregulation in central neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (Shy-Drager syndrome). Neurology. 1973 Mar;23(3):262–273. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.3.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda R. N., Wyper D. J., Harper A. M., Johnson R. H. Cerebral blood flow in paraplegia. Paraplegia. 1974 Nov;12(3):212–218. doi: 10.1038/sc.1974.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E., Rennels M. Innervation of intracranial arteries. Brain. 1970;93(3):475–490. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks V. J., Sandison A. G., Skinner S. L., Whelan R. F. Sympathomimetic drugs in orthostatic hypotension. Lancet. 1961 May 27;1(7187):1133–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. J., Bannister R. Preservation of autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in autonomic failure. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Jan;44(2-3):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. J., Zilkha E., Redmond S., Du Boulay G. H., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. An intravenous 133xenon clearance technique for measuring cerebral blood flow. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Jan;40(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Fujita Y. Responsiveness of isolated cerebral and peripheral arteries to serotonin, norepinephrine, and transmural electrical stimulation. Circ Res. 1973 Jul;33(1):98–104. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagerle L. C., Kumar S. P., Delivoria-Papadopoulos M. Effect of sympathetic nerve stimulation on cerebral blood flow in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res. 1986 Feb;20(2):131–135. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198602000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


