Abstract
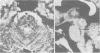
Two cases of unusual cheiro-oral syndrome due to small pontine haemorrhage are described, in which both sides of the mouth were involved in the initial stage. High resolution magnetic resonance imaging revealed a small lesion at the paramedian pontine tegmentum in both cases and suggested involvement of the medial portion of the medial lemniscus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araga S., Fukada M., Kagimoto H., Takahashi K. Pure sensory stroke due to pontine haemorrhage. J Neurol. 1987 Dec;235(2):116–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00718022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIN R., LAPRESLE J. Syndrome sensitif de type thalamique et à topographie chéiro-orale par lésion localisée du thalamus. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1954;90(2):124–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIN R., LAPRESLE J. [2d personal observation of a sensory syndrome of the thalamic type with cheiro-oral topography caused by localized lesion of the thalamus]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1960 Nov;103:474–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Inoue K. Cheiro-oral syndrome following midbrain haemorrhage. J Neurol. 1985;232(5):304–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00313870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara S., Terao A., Araki S., Shirabe T. [Unilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus (MFL) syndrome with palmar-oral symptoms]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1974 Sep;14(9):745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]