Abstract
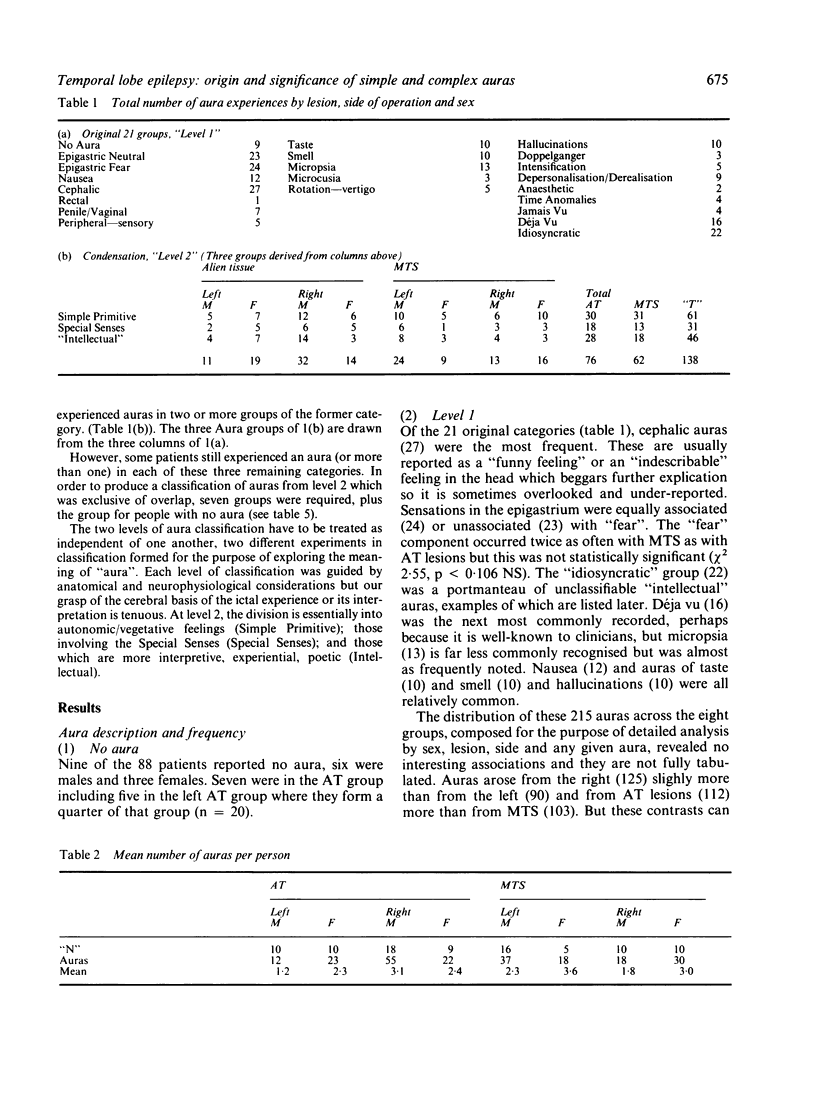
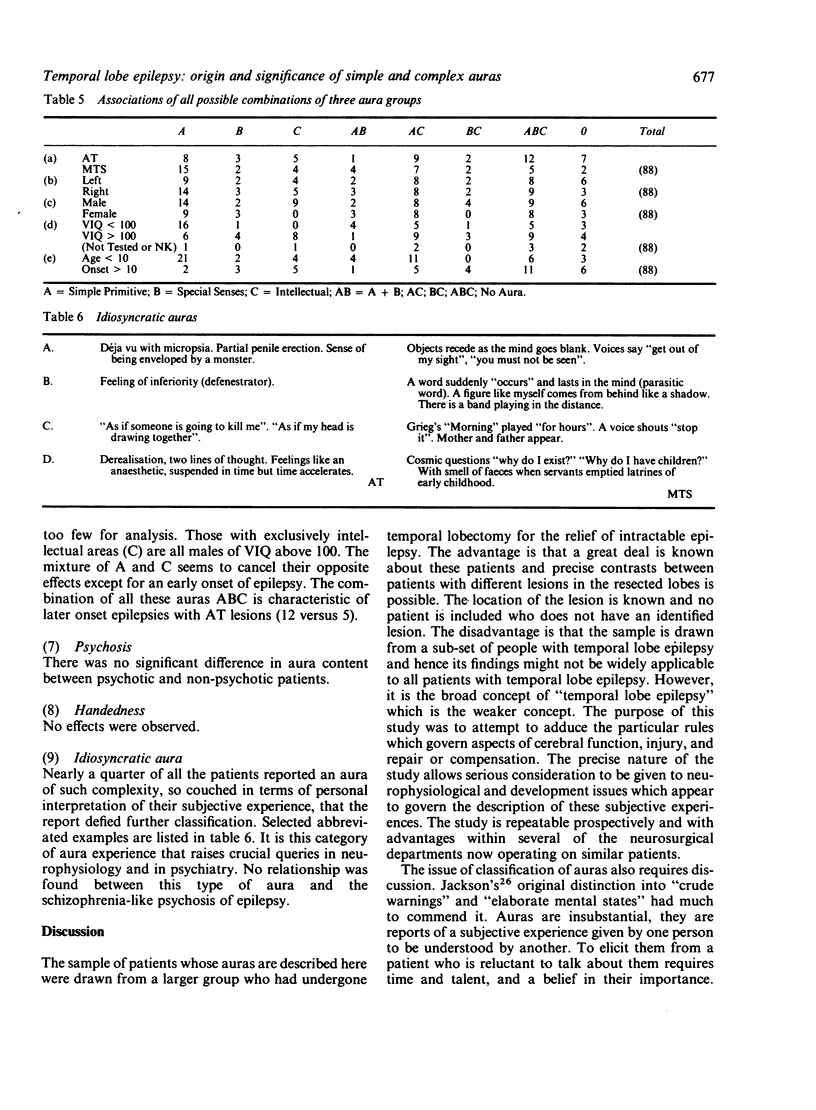
The aura experience of 88 patients with temporal lobe epilepsy was recorded, classified and analysed. Despite the great richness of the 215 experiences described, correlations with left or right brain, nature of lesion, age of onset, etc. were only apparent when a classification into three aura groups was used. "Simple primitive" auras as sole auras were more likely with early onset epilepsy, in lower IQ patients, in males, from the right temporal lobe, and with mesial temporal sclerosis. Exclusively "intellectual" auras were confined to a group of high IQ males. The number of aura experiences described per person correlated with Verbal IQ for males but not females, but also varied with side, sex, and nature of lesion. The results are discussed in terms of the necessary conditions for aura and their relevance and in relationship to the results of brain stimulation studies by Penfield and others.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DELGADO J. R., HAMLIN H., HIGGINS J. W., MAHL G. F. Behavioral changes during intracerebral electrical stimulation. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1956 Oct;76(4):399–419. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1956.02330280057006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devinsky O., Hafler D. A., Victor J. Embarrassment as the aura of a complex partial seizure. Neurology. 1982 Nov;32(11):1284–1285. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.11.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer M. A., Taylor D. C. Surgical treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy due to mesial temporal sclerosis. Etiology and significance. Arch Neurol. 1968 Oct;19(4):353–361. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480040019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor P., Olivier A., Quesney L. F., Andermann F., Horowitz S. The role of the limbic system in experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1982 Aug;12(2):129–144. doi: 10.1002/ana.410120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Jeavons P. M., Hughes R. C., Covanis A. Aura in temporal lobe epilepsy: clinical and electroencephalographic correlation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Dec;46(12):1079–1083. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.12.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL D., MITCHELL W. Epileptic anamnesis. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir Neerl. 1953 Oct;56(5):718–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halgren E., Walter R. D., Cherlow D. G., Crandall P. H. Mental phenomena evoked by electrical stimulation of the human hippocampal formation and amygdala. Brain. 1978 Mar;101(1):83–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann B. P., Dikmen S., Schwartz M. S., Karnes W. E. Interictal psychopathology in patients with ictal fear: a quantitative investigation. Neurology. 1982 Jan;32(1):7–11. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M. J., Adams J. E., Rutkin B. B. Visual imagery on brain stimulation. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;19(4):469–486. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1968.01740100085013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBIE L. S. Some implications for psychoanalysis of modern concepts of the organization of the brain. Psychoanal Q. 1953 Jan;22(1):21–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHL G. F., ROTHENBERG A., DELGADO J. M., HAMLIN H. PSYCHOLOGICAL RESPONSES IN THE HUMAN TO INTRACEREBRAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION. Psychosom Med. 1964 Jul-Aug;26:337–368. doi: 10.1097/00006842-196407000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLAN S., PENFIELD W. Illusions of comparative interpretation and emotion; production by epileptic discharge and by electrical stimulation in the temporal cortex. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959 Mar;81(3):269–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENFIELD W., PEROT P. THE BRAIN'S RECORD OF AUDITORY AND VISUAL EXPERIENCE. A FINAL SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION. Brain. 1963 Dec;86:595–696. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C. Aggression and epilepsy. J Psychosom Res. 1969 Sep;13(3):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(69)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C. Factors influencing the occurrence of schizophrenia-like psychosis in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Psychol Med. 1975 Aug;5(3):249–254. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700056609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C., Falconer M. A. Clinical, socio-economic, and psychological changes after temporal lobectomy for epilepsy. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;114(515):1247–1261. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.515.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C., Marsh S. M. Hughlings Jackson's Dr Z: the paradigm of temporal lobe epilepsy revealed. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Sep;43(9):758–767. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.9.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C. Mental state and temporal lobe epilepsy. A correlative account of 100 patients treated surgically. Epilepsia. 1972 Dec;13(6):727–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1972.tb05160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C. Sexual behavior and temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Nov;21(5):510–516. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480170082008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore W. H., Porter R. J., Penry J. K. Complex partial seizures: clinical characteristics and differential diagnosis. Neurology. 1983 Sep;33(9):1115–1121. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.9.11515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN BUREN J. M. The abdominal aura. A study of abdominal sensations occurring in epilepsy and produced by depth stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1963 Feb;15:1–19. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(63)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


