Abstract
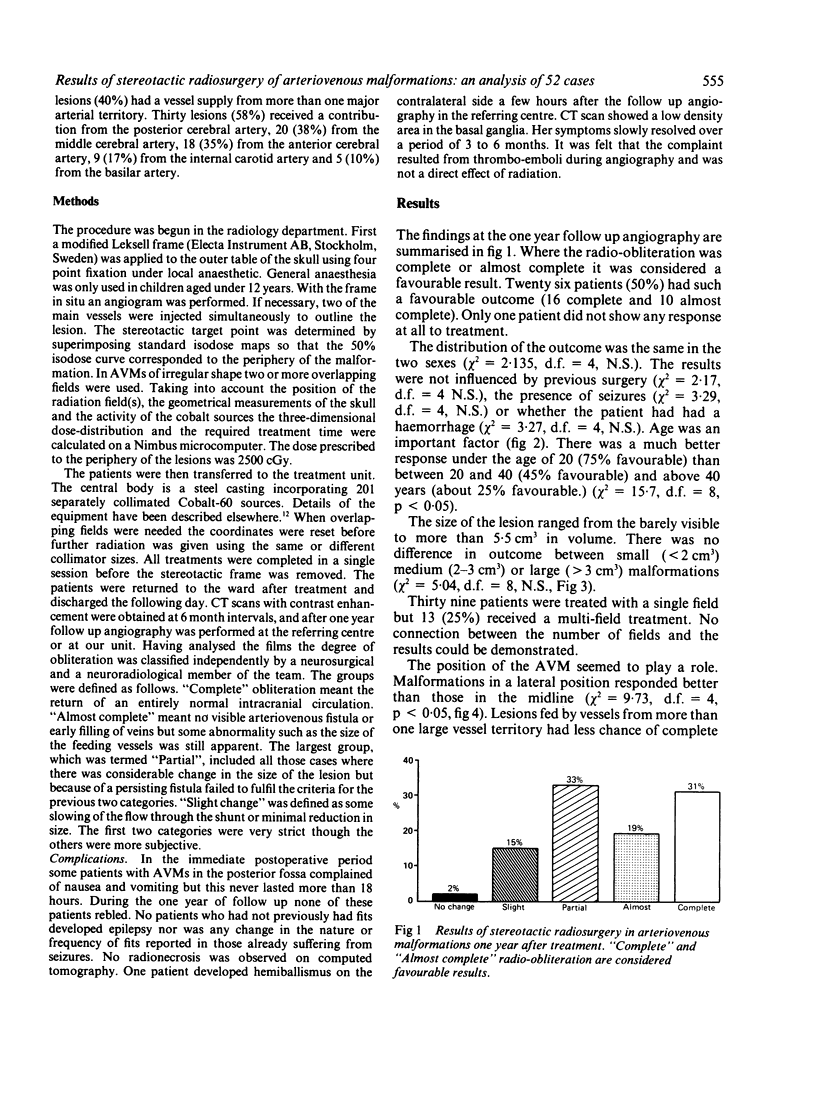
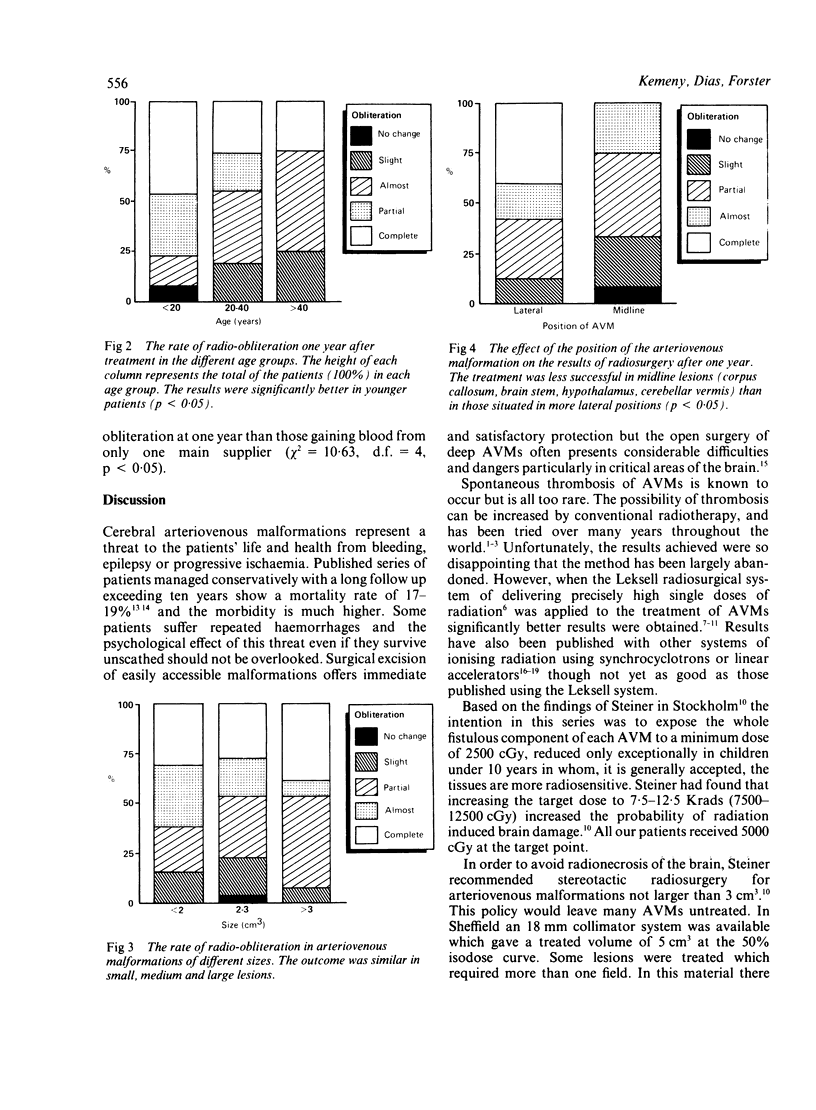
The stereotactic radiosurgery unit in Sheffield became operational in September 1985 and over 180 patients harbouring AVMs have been treated. The first 52 patients underwent one year follow up angiography and comprise the material for this study. At one year 26 patients (50%) already had a favourable outcome (16 complete and 10 almost complete obliteration). The results were the same in the two sexes. There was a better response in younger patients: under 20 years 75% favourable, between 20 and 40 years 45% favourable and above 40 years about 25% favourable. Malformations in a lateral position appeared to respond better than those in the midline. Lesions fed by vessels from more than one large vessel territory had less chance of complete obliteration at one year than those gaining blood from only one main supply. There was no difference in outcome between small malformations (less than 2 cm3) medium (2-3 cm3) or large (greater than 3 cm3). No immediate morbidity or late side effects were encountered in these patients. Stereotactic radiosurgery is a safe and effective method in the treatment of arteriovenous malformations but there is a relatively long latency. The number of malformations obliterated is expected to be much higher when two years have elapsed after treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colombo F., Benedetti A., Pozza F., Avanzo R. C., Marchetti C., Chierego G., Zanardo A. External stereotactic irradiation by linear accelerator. Neurosurgery. 1985 Feb;16(2):154–160. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198502000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrikant J. I., Lyman J. T., Hosobuchi Y. Stereotactic heavy-ion Bragg peak radiosurgery for intra-cranial vascular disorders: method for treatment of deep arteriovenous malformations. Br J Radiol. 1984 Jun;57(678):479–490. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-57-678-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster D. M., Steiner L., Håkanson S. Arteriovenous malformations of the brain. A long-term clinical study. J Neurosurg. 1972 Nov;37(5):562–570. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.5.0562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSSON B., LEKSELL L., REXED B., SOURANDER P., MAIR W., ANDERSSON B. The high-energy proton beam as a neurosurgical tool. Nature. 1958 Nov 1;182(4644):1222–1223. doi: 10.1038/1821222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOL J. L. Treatment of arteriovenous malformations of the cerebral hemispheres. J Neurosurg. 1962 Feb;19:136–141. doi: 10.3171/jns.1962.19.2.0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVIEN H. J., PESERICO L. Regression in size of arterovenous anomaly. J Neurosurg. 1960 May;17:493–496. doi: 10.3171/jns.1960.17.3.0493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L., Leksell L., Greitz T., Forster D. M., Backlund E. O. Stereotaxic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Report of a case. Acta Chir Scand. 1972;138(5):459–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognetti F., Andreoli A., Cuscini A., Testa C. Successful management of an intracranial arteriovenous malformation by conventional irradiation. J Neurosurg. 1985 Aug;63(2):193–195. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.63.2.0193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton L., Bomford C. K., Ramsden D. The Sheffield stereotactic radiosurgery unit: physical characteristics and principles of operation. Br J Radiol. 1987 Sep;60(717):897–906. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-60-717-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


