Abstract
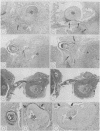
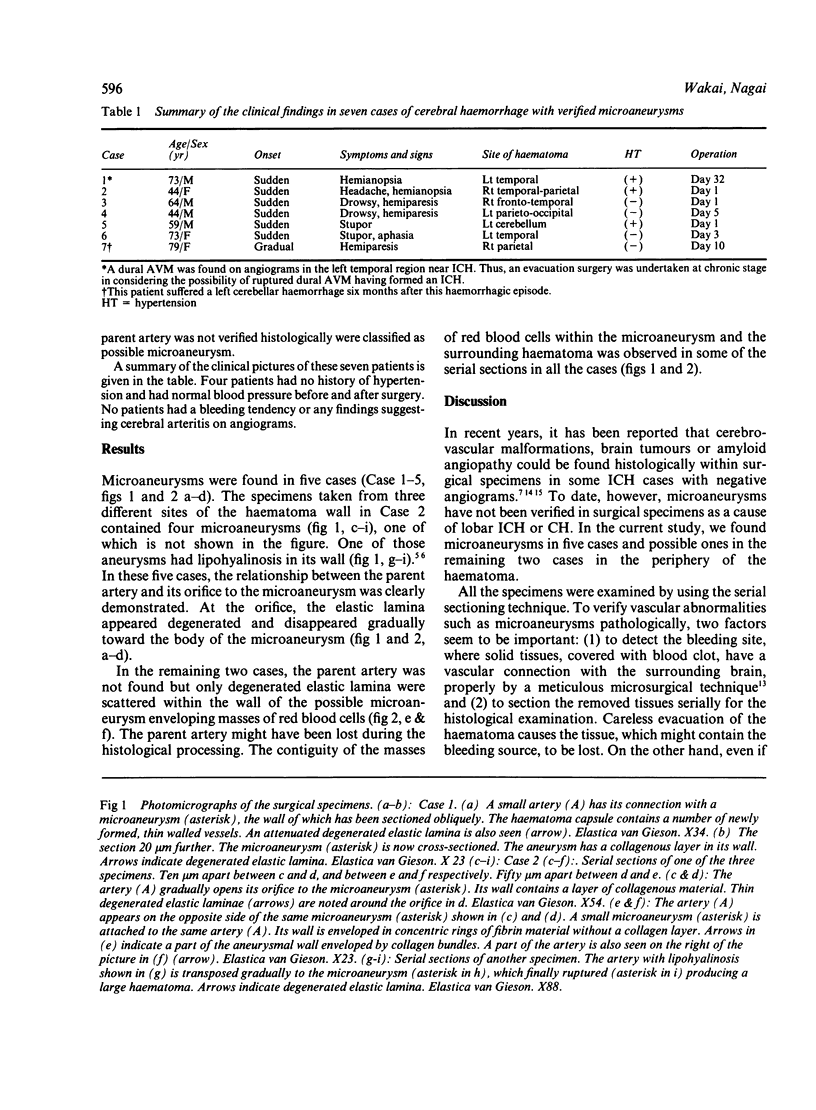
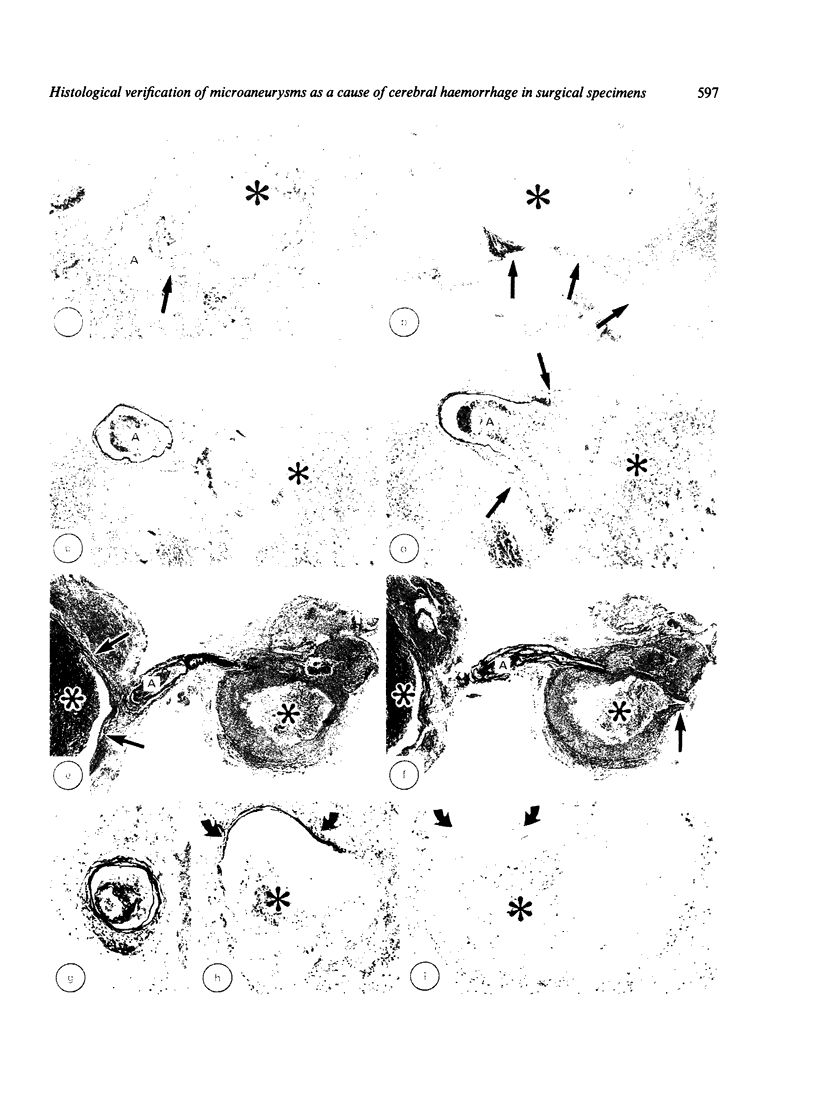
Surgical specimens taken from 14 patients with lobar intracerebral haemorrhage or cerebellar haemorrhage without vascular abnormalities on angiograms were examined histologically. In seven of the 14 patients, arteriovenous malformation or amyloid angiopathy were found by ordinary pathological examinations. Among the remaining seven patients, definite microaneurysms were verified in five and possible ones in two patients by using the technique of serial sectioning of the solid nodular tissues removed from the presumed bleeding site, where an arterial connection between the tissues and the surrounding brain was noted. Four of these seven patients had no history of hypertension and showed normal blood pressure before and after surgery. To verify microaneurysms in surgical specimens, it seems important to search the presumed bleeding site properly by a meticulous microsurgical technique and to section the tissues serially for the histological examination.
Full text
PDF
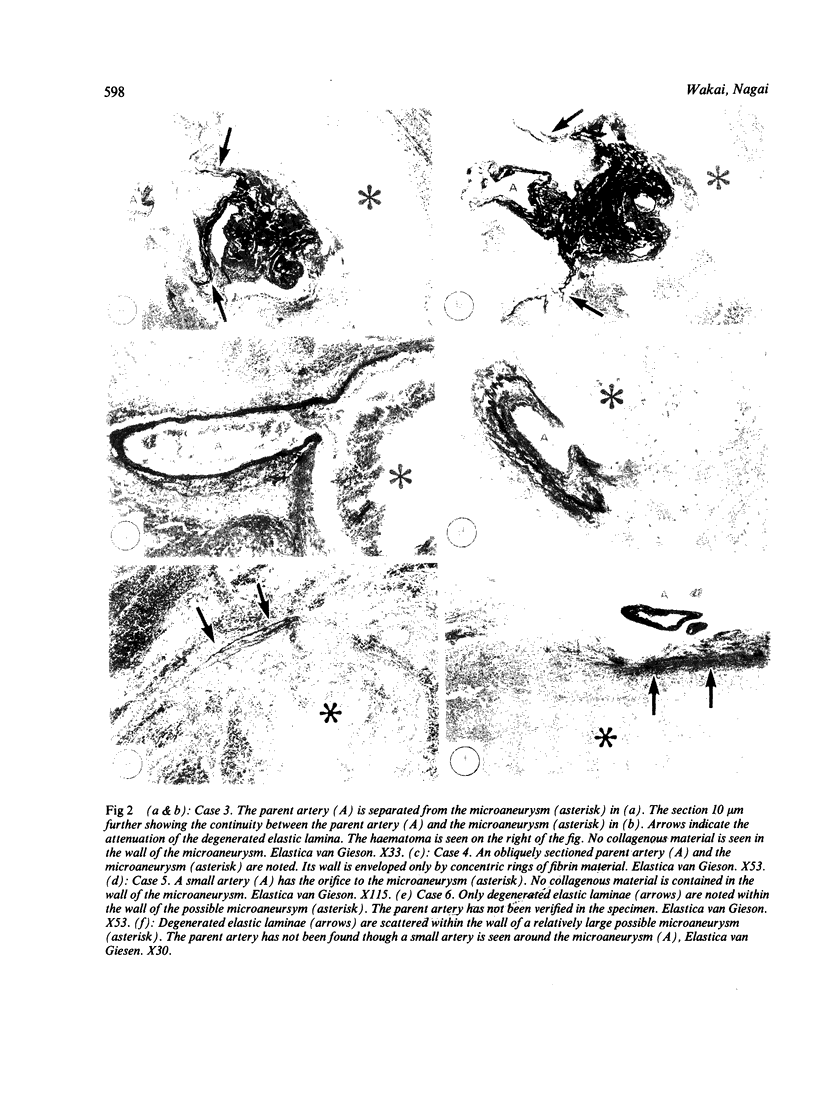

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole F. M., Yates P. O. The occurrence and significance of intracerebral micro-aneurysms. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):393–411. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Cerebral miliary aneurysms in hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):313–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Pathological observations in hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jul;30(3):536–550. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197107000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. R., Dolan E., Sima A. A. The value of histopathological examination of surgically removed blood clot in determining the etiology of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 1984 May-Jun;15(3):517–520. doi: 10.1161/01.str.15.3.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Nishihara Y., Horie A. Amyloid angiopathy and lobar cerebral haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Nov;47(11):1203–1210. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.11.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase C. S., Williams J. P., Wyatt D. A., Mohr J. P. Lobar intracerebral hematomas: clinical and CT analysis of 22 cases. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1146–1150. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick W. F., Rosenfield D. B. Massive brain hemorrhage: a review of 144 cases and an examination of their causes. Stroke. 1973 Nov-Dec;4(6):946–954. doi: 10.1161/01.str.4.6.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooneda G., Yoshida Y., Suzuki K., Shinkai H. Plasmatic arterionecrosis and its thrombotic occlusion. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(2 Suppl):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSRUSSELL R. W. OBSERVATIONS ON INTRACEREBRAL ANEURYSMS. Brain. 1963 Sep;86:425–442. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropper A. H., Davis K. R. Lobar cerebral hemorrhages: acute clinical syndromes in 26 cases. Ann Neurol. 1980 Aug;8(2):141–147. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Furuse M., Iwasa H., Masuzawa T., Saito K., Sato F., Mizuno Y. Lobar intracerebral hemorrhage: etiology and a long-term follow-up study of 32 patients. Stroke. 1986 Jan-Feb;17(1):51–57. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakai S., Ueda Y., Inoh S., Nagai M. Angiographically occult angiomas: a report of thirteen cases with analysis of the cases documented in the literature. Neurosurgery. 1985 Oct;17(4):549–556. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198510000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakai S., Yamakawa K., Manaka S., Takakura K. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage caused by brain tumor: its incidence and clinical significance. Neurosurgery. 1982 Apr;10(4):437–444. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198204000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]