Abstract
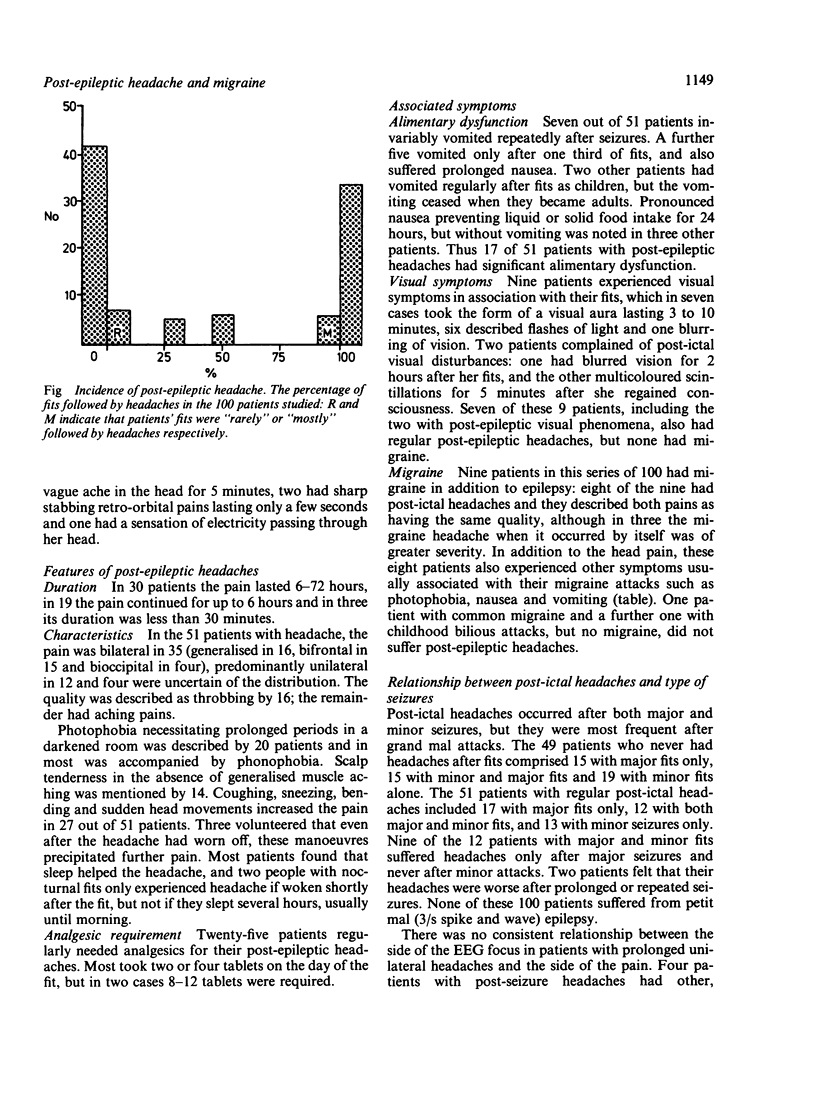
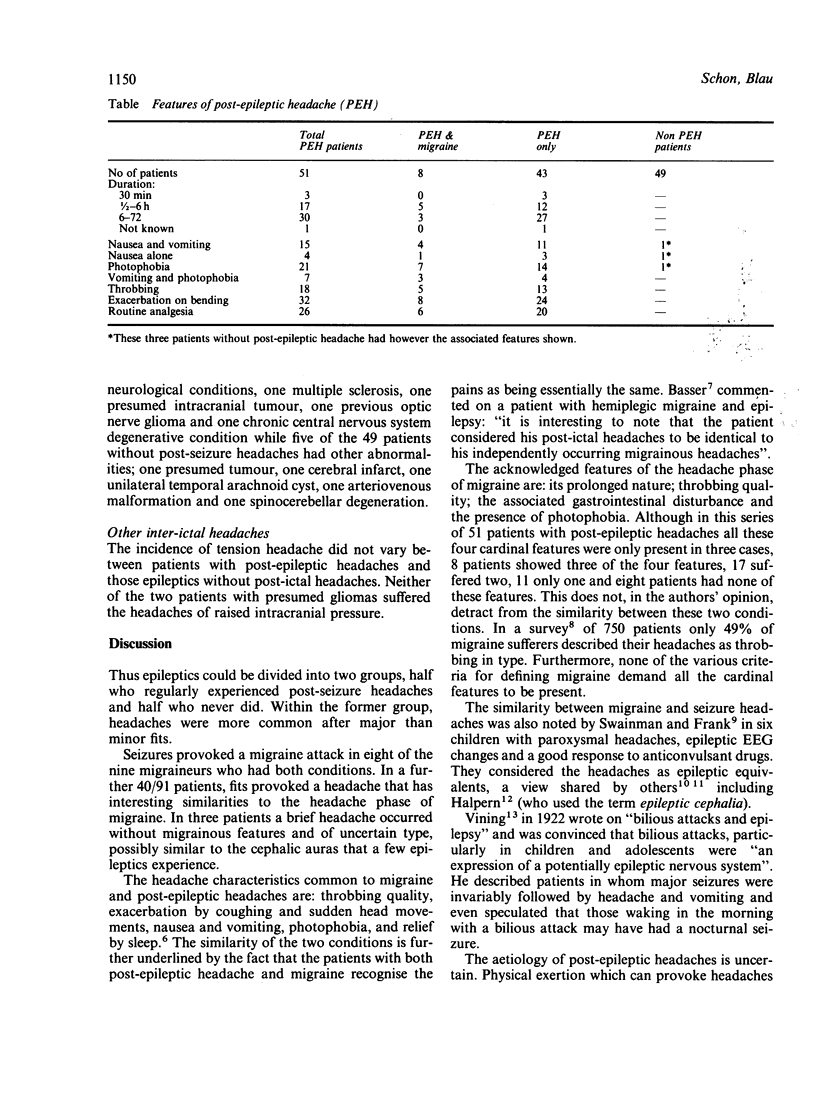
One hundred epileptic patients were questioned about their headaches. Post-ictal headaches occurred in 51 of these patients and most commonly lasted 6-72 hours. Major seizures were more often associated with post-epileptic headaches than minor attacks. Nine patients in this series of 100 also had migraine: in eight of these nine a typical, albeit a mild, migraine attack was provoked by fits. The post-ictal headache in the 40 epileptics who did not have migraine was accompanied by vomiting in 11 cases, photophobia in 14 cases and vomiting with photophobia in 4 cases. Furthermore, post-epileptic headache was accentuated by coughing, bending and sudden head movements and relieved by sleep. It is, therefore, clear that seizures provoke a syndrome similar to the headache phase of migraine in 50% of epileptics. It is proposed that post-epileptic headache arises intracranially and is related to the vasodilatation known to follow seizures. The relationship of post-epileptic headache to migraine is discussed in the light of current ideas on migraine pathogenesis, in particular the vasodilation which accompanies Leao's spreading cortical depression.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basser L. S. The relation of migraine and epilepsy. Brain. 1969;92(2):285–300. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beevers D. G., Erskine E., Robertson M., Beattie A. D., Campbell B. C., Goldberg A., Moore M. R., Hawthorne V. M. Blood-lead and hypertension. Lancet. 1976 Jul 3;2(7975):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N., Dexter S. L. The site of pain origin during migraine attacks. Cephalalgia. 1981 Sep;1(3):143–147. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1981.0103143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N. Migraine pathogenesis: the neural hypothesis reexamined. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 May;47(5):437–442. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.5.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau J. N. Resolution of migraine attacks: sleep and the recovery phase. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Mar;45(3):223–226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN L., BENTAL E. Epileptic cephalea. Neurology. 1958 Aug;8(8):615–620. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.8.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougaard K., Oikawa T., Sveinsdottir E., Skinoj E., Ingvar D. H., Lassen N. A. Regional cerebral blood flow in focal cortical epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1976 Aug;33(8):527–535. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500080005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A. D. Headaches as seizure equivalents. Headache. 1966 Jul;6(2):78–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1966.hed0602078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D. E., Engel J., Jr, Phelps M. E., Selin C. Epileptic patterns of local cerebral metabolism and perfusion in humans determined by emission computed tomography of 18FDG and 13NH3. Ann Neurol. 1980 Oct;8(4):348–360. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W. Headaches related to sexual activity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Dec;39(12):1226–1230. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.12.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplante P., Saint-Hilaire J. M., Bouvier G. Headache as an epileptic manifestation. Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1493–1495. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen M., Jørgensen M. B., Diemer N. H., Gjedde A., Hansen A. J. Persistent oligemia of rat cerebral cortex in the wake of spreading depression. Ann Neurol. 1982 Nov;12(5):469–474. doi: 10.1002/ana.410120510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen M., Olesen J. Regional cerebral blood flow during migraine attacks by Xenon-133 inhalation and emission tomography. Brain. 1984 Jun;107(Pt 2):447–461. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Hata T., Imai A., Zetusky W. J. Migraine and intracranial swelling. Lancet. 1985 Dec 7;2(8467):1308–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. M. Is migraine explained by Leao's spreading depression? Lancet. 1985 Oct 5;2(8458):763–766. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum F., Posner J. B., Troy B. Cerebral metabolic and circulatory responses to induced convulsions in animals. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jan;18(1):1–13. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470310015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke E. D. Benign exertional headache. Med Clin North Am. 1968 Jul;52(4):801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaiman K. F., Frank Y. Seizure headaches in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1978 Oct;20(5):580–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1978.tb15276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. B., Blume W. T. Painful epileptic seizures. Brain. 1983 Sep;106(Pt 3):537–554. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


