Abstract
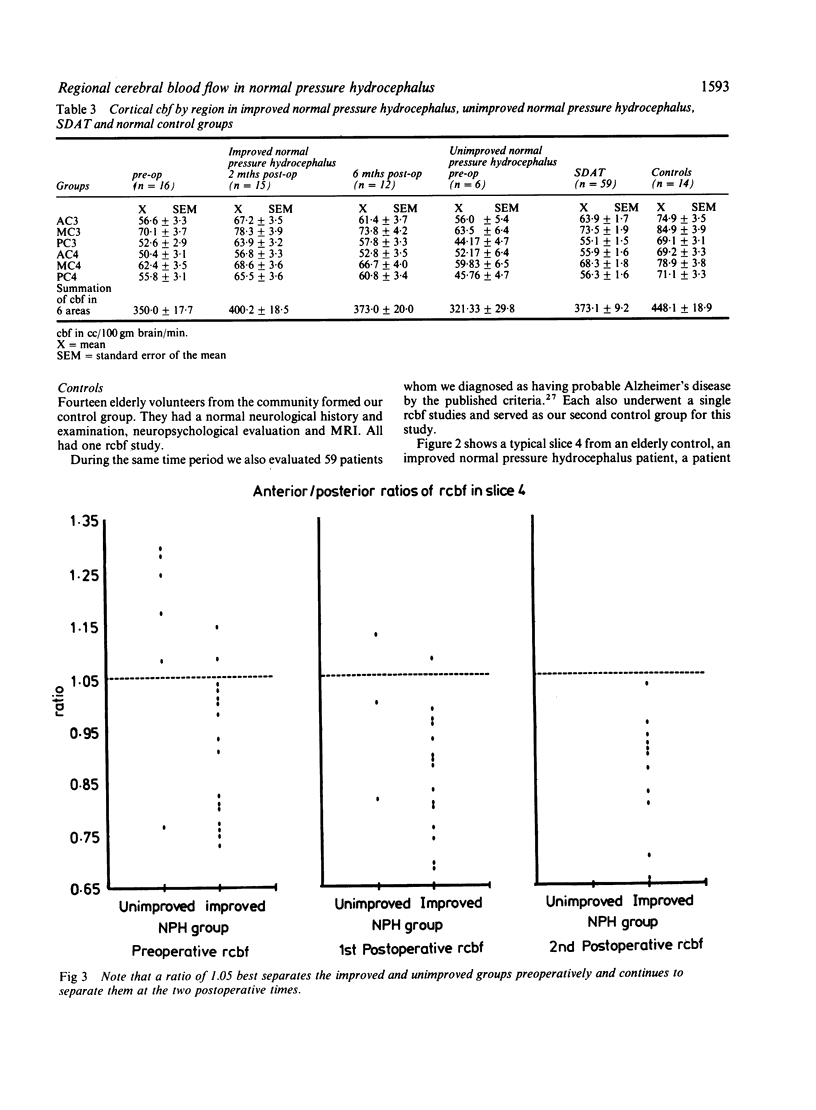
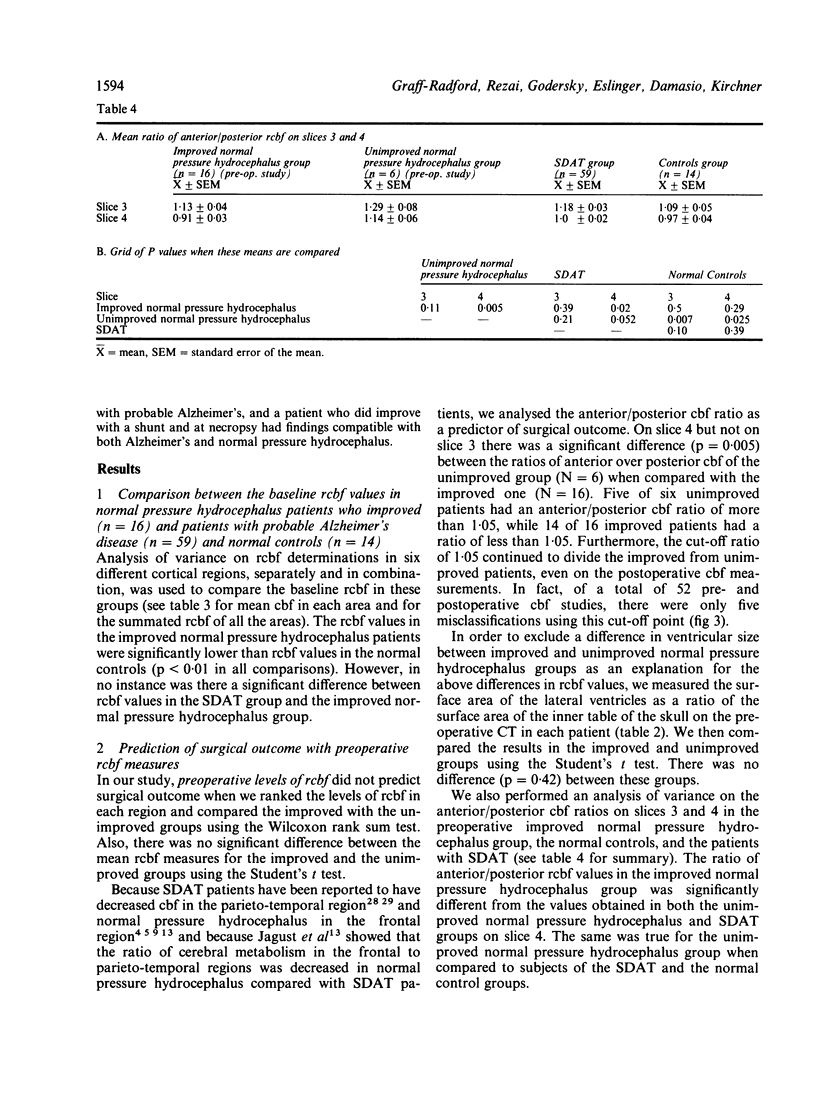
Regional cerebral blood flow (rcbf) was studied preoperatively and at 2 and 6 months postoperatively in 22 normal pressure hydrocephalus patients using xenon-133 inhalation and single photon emission computed tomography. Sixteen of the 22 patients improved (improved group) and six did not (unimproved group). The following comparisons were made: (1) preoperative rcbf in the improved group, to 14 normal elderly volunteers and to that in 59 SDAT (senile dementia of the Alzheimer type) patients; (2) preoperative rcbf in the improved and unimproved groups to determine if rcbf could predict surgical outcome; (3) pre- to postoperative rcbf in the improved group to see if increased cbf accounted for clinical improvement. The findings were: (1) preoperative rcbf in the improved group was lower than that in normal controls but was the same as that in SDAT; however, the ratios of rcbf values in anterior and posterior brain regions were significantly different between improved group and SDAT (p = 0.02); (2) an anterior/posterior ratio of 1.05 correctly classified surgical outcome in 19/22 patients; five of six in the unimproved group were above this cut off while 14/16 in the improved group were below; (3) in the improved group rcbf increased at 2 but not at 6 months after surgery without a corresponding reduction of clinical signs, supporting the notion that increase in cbf probably does not account for clinical improvement in normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks D. J., Beaney R. P., Powell M., Leenders K. L., Crockard H. A., Thomas D. G., Marshall J., Jones T. Studies on cerebral oxygen metabolism, blood flow, and blood volume, in patients with hydrocephalus before and after surgical decompression, using positron emission tomography. Brain. 1986 Aug;109(Pt 4):613–628. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Børgesen S. E., Gjerris F. The predictive value of conductance to outflow of CSF in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain. 1982 Mar;105(Pt 1):65–86. doi: 10.1093/brain/105.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., Chase T. N., Fedio P., Patronas N. J., Brooks R. A., Di Chiro G. Alzheimer's disease: focal cortical changes shown by positron emission tomography. Neurology. 1983 Aug;33(8):961–965. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.8.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff-Radford N. R., Godersky J. C. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Onset of gait abnormality before dementia predicts good surgical outcome. Arch Neurol. 1986 Sep;43(9):940–942. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520090068020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T. V., Grepe A. O., Kalmér M. S., Lopez J. Pre- and postoperative evaluation of cerebral blood flow in low-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1969 Dec;31(6):644–651. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.6.0644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb R. L., Jr, Raichle M. E., Gado M. H., Eichling J. O., Hughes C. P. Cerebral blood flow, oxygen utilization, and blood volume in dementia. Neurology. 1977 Oct;27(10):905–910. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.10.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagust W. J., Friedland R. P., Budinger T. F. Positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose differentiates normal pressure hydrocephalus from Alzheimer-type dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Nov;48(11):1091–1096. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.11.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M., Younkin D., Weinberger J., Hurtig H., Goldberg H., Reivich M. Cerebral hemodynamics in the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurology. 1984 Jan;34(1):96–99. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki T., Kose S., Tamaki N., Matsumoto S., Yamashita H. [Normal pressure hydrocephalus. (Part I). Pre- and post-operative r-CBF]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1982 Jun;22(6):412–416. doi: 10.2176/nmc.22.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lying-Tunell U., Lindblad B. S., Malmlund H. O., Persson B. Cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate of oxygen, glucose, lactate, pyruvate, ketone bodies and amino acids in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus before and after shunting and in normal subjects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1977;64:338–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T., Meyer J. S., Hartmann A., Ott E. O. Abnormal cerebrospinal fluid-blood flow dynamics. Implications in diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arch Neurol. 1975 Oct;32(10):657–664. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490520027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Kitagawa Y., Tanahashi N., Tachibana H., Kandula P., Cech D. A., Rose J. E., Grossman R. G. Pathogenesis of normal-pressure hydrocephalus--preliminary observations. Surg Neurol. 1985 Feb;23(2):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(85)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. H., Timperman A. L. Cerebral blood flow in posttraumatic encephalopathy. The effect of ventriculoatrial shunt. Neurology. 1971 Jan;21(1):33–42. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokely E. M., Sveinsdottir E., Lassen N. A., Rommer P. A single photon dynamic computer assisted tomograph (DCAT) for imaging brain function in multiple cross sections. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980 Apr;4(2):230–240. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198004000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki N., Kusunoki T., Wakabayashi T., Matsumoto S. Cerebral hemodynamics in normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Evaluation by 133Xe inhalation method and dynamic CT study. J Neurosurg. 1984 Sep;61(3):510–514. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.61.3.0510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]