Abstract
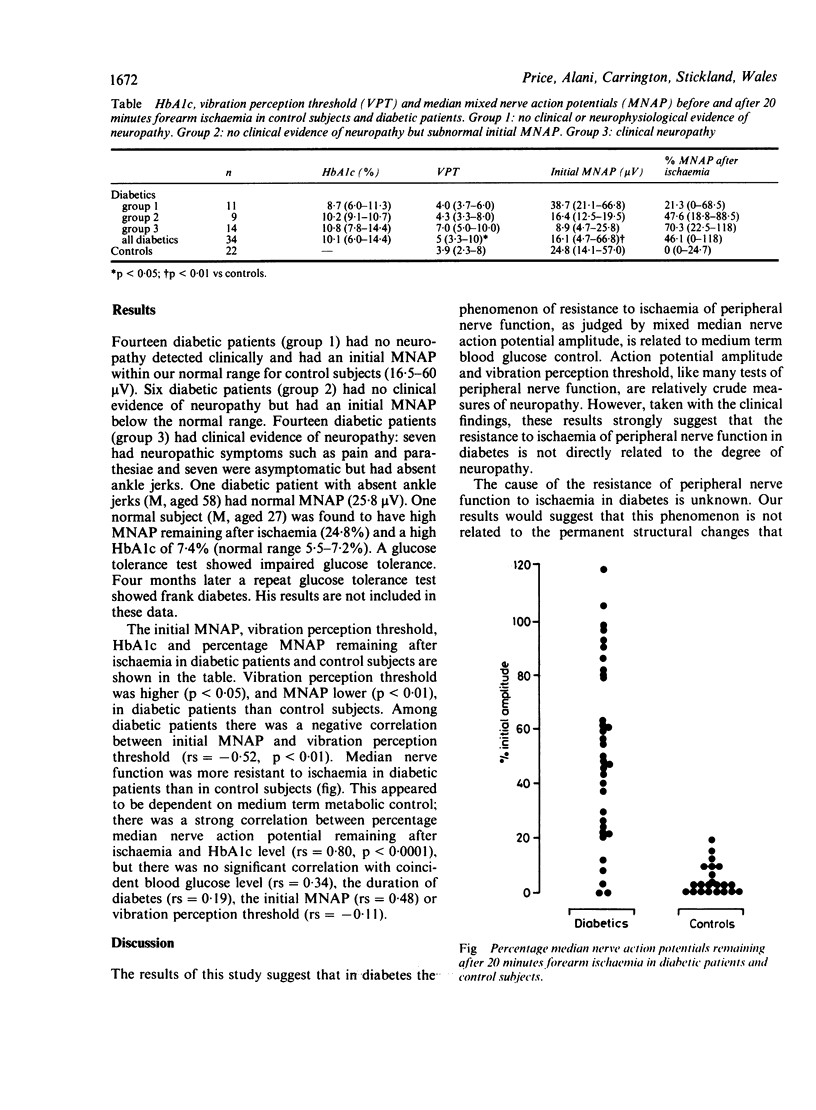
The cause of the abnormal resistance to ischaemia of peripheral nerve function in diabetes is unknown. Median nerve function was more resistant to ischaemia in diabetic patients than in control subjects. In diabetic patients the degree of resistance to ischaemia correlated closely with HbAlc but not with the coincident blood glucose level, the duration of diabetes, the vibration perception threshold at the thumb or the initial median nerve action potential amplitude. Thus in diabetes the resistance of peripheral nerve function to ischaemia is dependent on medium term metabolic control and is not directly related to the presence or absence of neuropathy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castaigne P., Cathala H. P., Beaussart-Boulengé L., Petrover M. Effect of ischaemia on peripheral nerve function in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing dialysis treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Oct;35(5):631–637. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Orskov H. Vibratory perception during ischaemia in uraemic patients and in subjects with mild carbohydrate intolerance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;32(6):519–524. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.6.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen G., Pilgaard S. The effect of ischaemia on vibration sense in hypo- or hypercalcaemia and in demyelinated nerves. Acta Neurol Scand. 1971;47(1):71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1971.tb07465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. H., Ginsberg-Fellner F. Ischemia and sensory nerve conduction in diabetes mellitus. Neurology. 1979 May;29(5):695–704. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo J., Simard-Duquesne N., Dvornik D. Resistance of the diabetic rat nerve to ischemic inactivation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;63(7):773–777. doi: 10.1139/y85-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Schmelzer J. D. Peripheral nerve conduction studies in galactose-poisoned rats. Demonstration of increased resistance to ischemic conduction associated with endoneurial edema due to sugar alcohol accumulation. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Jun;59(3):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Schmelzer J. D., Ward K. K., Yao J. K. Experimental chronic hypoxic neuropathy: relevance to diabetic neuropathy. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):E94–E99. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.1.E94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Ward K., Schmelzer J. D., Brimijoin S. Ischemic conduction failure and energy metabolism in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):E457–E462. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.4.E457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrick P. G., Wilson A. J., Jakubowski J., Boulton A. J., Ward J. D. Sural nerve oxygen tension in diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Oct 25;293(6554):1053–1054. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6554.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen V. K., Kardel T. Delayed decrement of the nerve impulse propagation during induced limb ischaemia in chronic hepatic failure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;38(10):966–976. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.10.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock I. Glycosylated haemoglobin: measurement and clinical use. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Aug;37(8):841–851. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINESS I. Influence of diabetic status on vibratory perception during ischaemia. Acta Med Scand. 1961 Sep;170:319–338. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINESS I. Vibratory perception in diabetics during arrested blood flow to the limb. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Mar 4;163(3):195–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1959.tb10400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne K. N., Peiris O. A. Peripheral nerve function in chronic liver disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;33(5):609–614. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.5.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne K. N., Peiris O. A. The effect of ischaemia on the excitability of sensory nerves in diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):348–353. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Sherman W. R., Kurien M. M., Moonsammy G. I., Wisgerhof M. Polyol accumulations in nervous tissue of rats with experimental diabetes and galactosaemia. J Neurochem. 1967 Nov;14(11):1057–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickland M. H., Perkins C. M., Wales J. K. The Measurement of Haemoglobin A1c by isoelectric focussing in diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1982 May;22(5):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00253573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. K., Hanwell M. A., Satchell P. M., Turtle J. R. The effect of aldose reductase inhibition on motor nerve conduction velocity in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):789–794. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


