Abstract
A patient with multiple sclerosis is reported in whom neck flexion produced a reversible deterioration in gait and an increase in the degree of pyramidal weakness of the lower limbs. The name McArdle's sign is proposed.
Full text
PDF
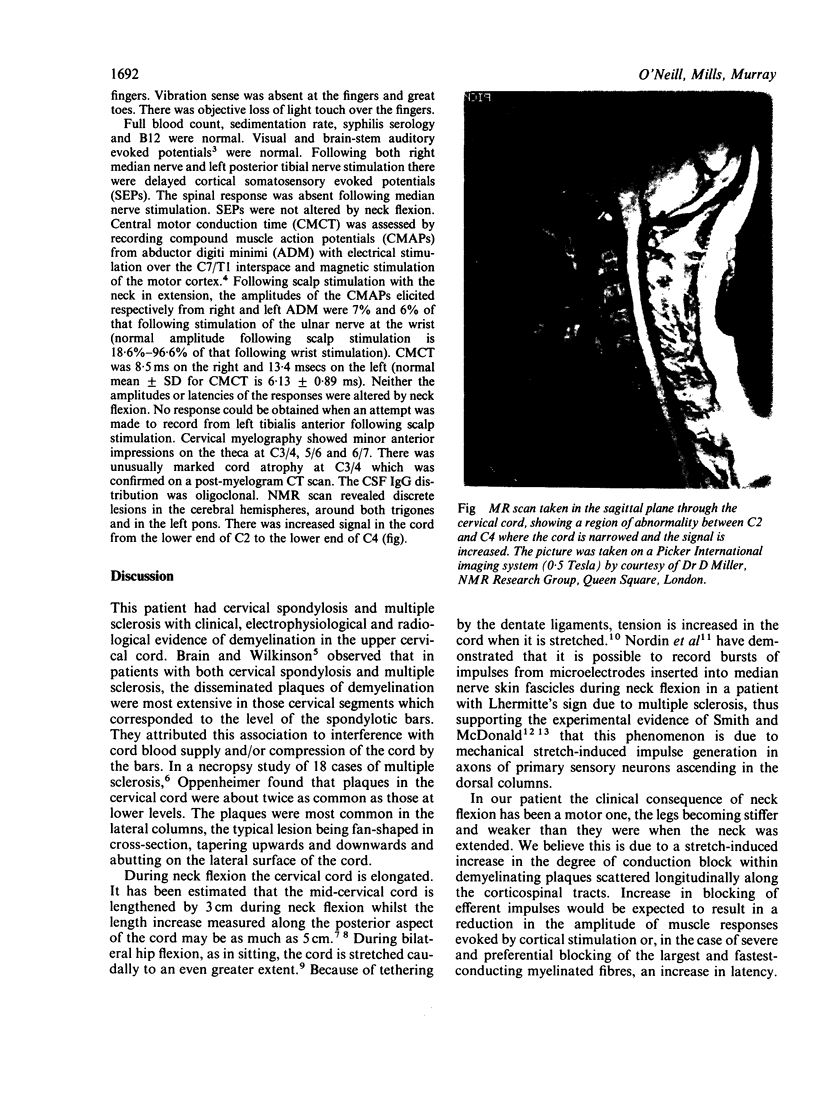

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAIN R., WILKINSON M. The association of cervical spondylosis and disseminated sclerosis. Brain. 1957 Dec;80(4):456–478. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusick J. F., Ackmann J. J., Larson S. J. Mechanical and physiological effects of dentatotomy. J Neurosurg. 1977 Jun;46(6):767–775. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.46.6.0767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess C. W., Mills K. R., Murray N. M. Measurement of central motor conduction in multiple sclerosis by magnetic brain stimulation. Lancet. 1986 Aug 16;2(8503):355–358. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanchandani R., Howe J. G. Lhermitte's sign in multiple sclerosis: a clinical survey and review of the literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Apr;45(4):308–312. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin M., Nyström B., Wallin U., Hagbarth K. E. Ectopic sensory discharges and paresthesiae in patients with disorders of peripheral nerves, dorsal roots and dorsal columns. Pain. 1984 Nov;20(3):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(84)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurick S. The pathogenesis of the spinal cord disorder associated with cervical spondylosis. Brain. 1972;95(1):87–100. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R. The cervical cord in multiple sclerosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Mar-Apr;4(2):151–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE E. E., SPILLANE J. D. The cervical spine; an anatomico-pathological study of 70 specimens (using a special technique) with particular reference to the problem of cervical spondylosis. Brain. 1957 Dec;80(4):571–596. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., McDonald W. I. Spontaneous and evoked electrical discharges from a central demyelinating lesion. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Jul;55(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., McDonald W. I. Spontaneous and mechanically evoked activity due to central demyelinating lesion. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):154–155. doi: 10.1038/286154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. R. Mechanism and treatment of spinal-cord disorders associated with cervical spondylosis. Lancet. 1953 Apr 11;1(6763):717–720. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91847-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



