Abstract
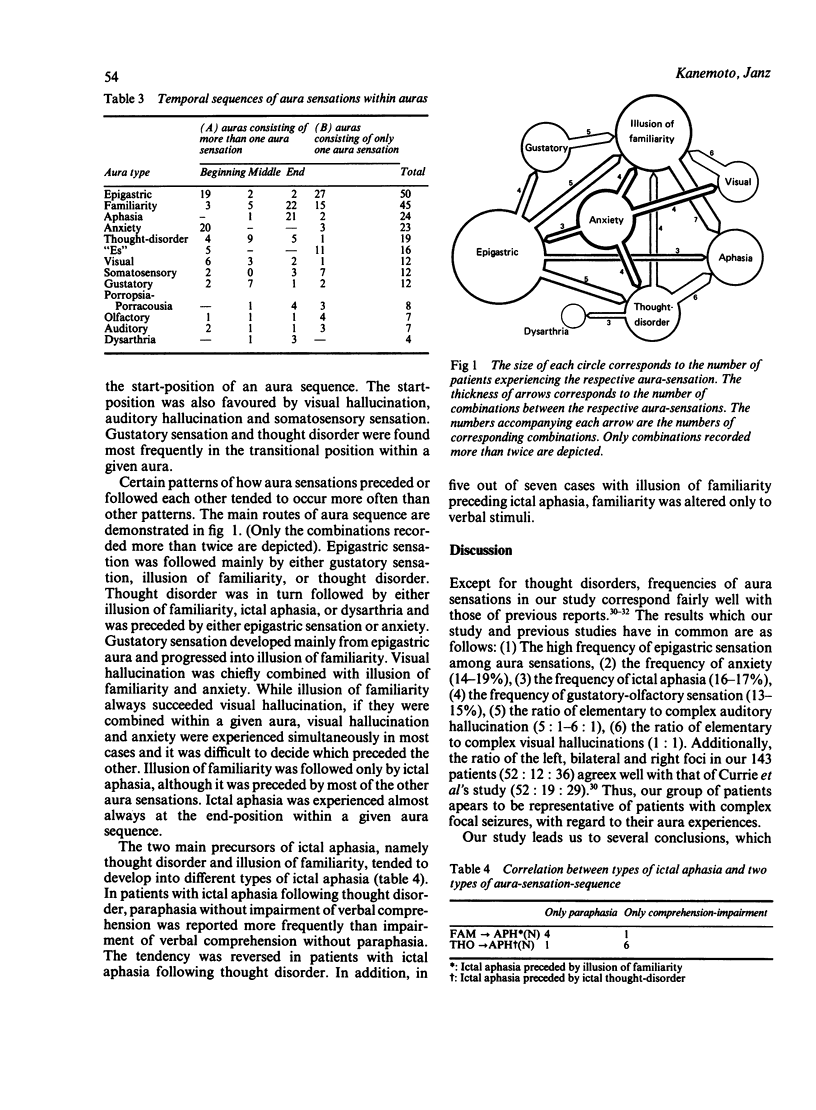
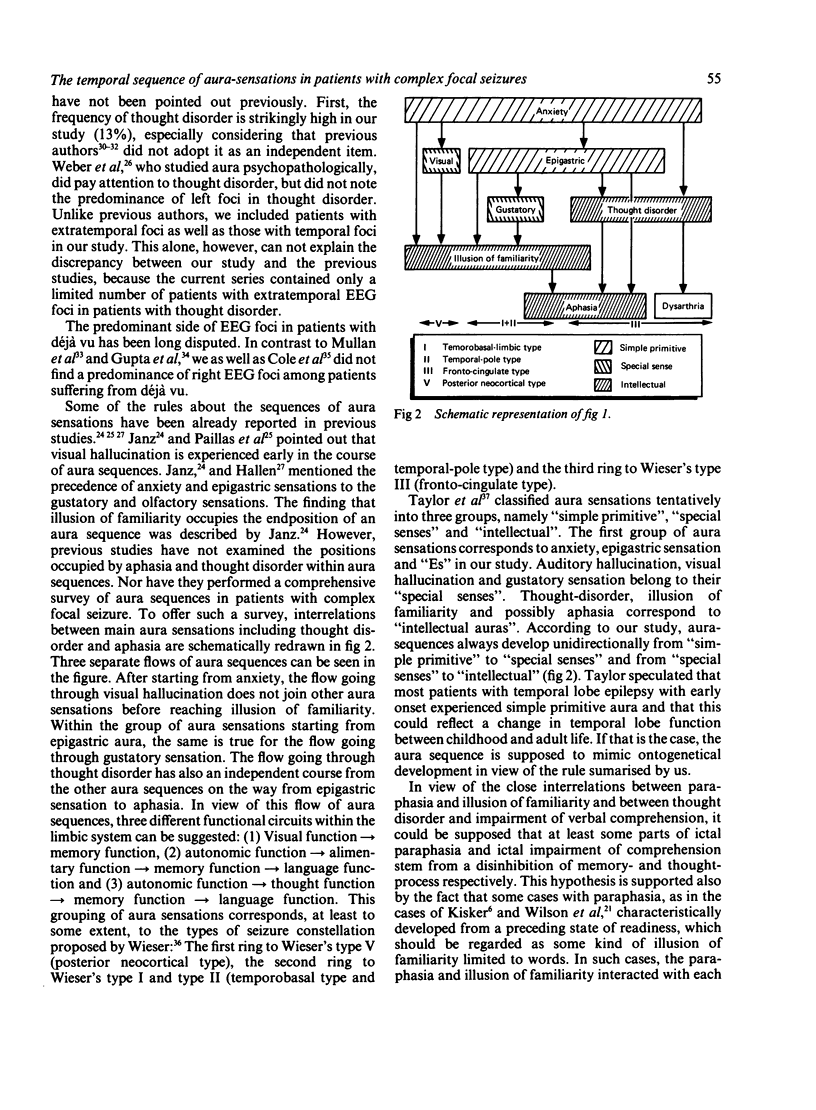
The sequences of aura sensations in 143 patients with complex partial seizures, were analysed with special emphasis on aphasic symptoms. Anxiety, epigastric sensation and visual hallucination were experienced early in the course of the aura, while illusion of familiarity and aphasia occurred late in the course of the aura. Three groups of interconnections of aura sensations were found which corresponded possibly to the types of seizure constellations proposed by Weiser. Close interconnections between impairment of verbal comprehension during seizures and paroxysmal thought disorder, as well as between paroxysmal paraphasia and illusion of familiarity were noted. Paroxysmal aphasia in patients with complex partial seizures was characterised as a positive symptom in contrast to stable aphasia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALAJOUANINE T., SABOURAUD O. [Paroxysmal disorders of speech in epilepsy. (Clinical study)]. Encephale. 1960;49:95–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAVANY J. A., HAGENMULLER D., LOBEL G. Etude clinique des troubles du langage d'essence epileptique. Presse Med. 1956 Sep 1;64(63):1449–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE M., ZANGWILL O. L. Deja vu in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Feb;26:37–38. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRITCHLEY M. [Speech disorders in cases of epilepsy]. Encephale. 1960;49:134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie S., Heathfield K. W., Henson R. A., Scott D. F. Clinical course and prognosis of temporal lobe epilepsy. A survey of 666 patients. Brain. 1971;94(1):173–190. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pasquet E. G., Gaudin E. S., Bianchi A., De Mendilaharsu S. A. Prolonged and monosymptomatic dysphasic status epilepticus. Neurology. 1976 Mar;26(3):244–247. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.3.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinner D. S., Lueders H., Lederman R., Gretter T. E. Aphasic status epilepticus: a case report. Neurology. 1981 Jul;31(7):888–891. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.7.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R. L., Heilman K. M. Speech arrest in partial seizures: evidence of an associated language disorder. Neurology. 1981 Aug;31(8):1016–1019. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.8.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Jeavons P. M., Hughes R. C., Covanis A. Aura in temporal lobe epilepsy: clinical and electroencephalographic correlation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Dec;46(12):1079–1083. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.12.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECAEN H., ANGELERGUES R. [Epilepsy and speech disorders]. Encephale. 1960;49:138–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECAEN H., PIERCY M. Paroxysmal dysphasia and the problem of cerebral dominance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Aug;19(3):194–201. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.3.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton N. G., Matthews T. Aphasia: the sole manifestation of focal status epilepticus. Neurology. 1979 May;29(5):745–748. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.5.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISKER K. P. Sprachliche Stereotypien bei Temporallappen-Epilepsie; ein Beitrag zur Konstitution verbaler Sprachanteile. Nervenarzt. 1957 Aug 20;28(8):366–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER-MICKELEIT R. W. Die Dämmerattacken als charakteristischer Anfallstyp der temporalen Epilepsie (psychomotorische Anfälle, Aquivalente, Automatismen). Nervenarzt. 1953 Aug 20;24(8):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLAN S., PENFIELD W. Illusions of comparative interpretation and emotion; production by epileptic discharge and by electrical stimulation in the temporal cortex. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959 Mar;81(3):269–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrosu F., Brundu A., Rachele M. G., Marrosu G. Epileptic aphasia as dynamic disturbance. A case report. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1983 Feb;5(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeever M., Holmes G. L., Russman B. S. Speech abnormalities in seizures: a comparison of absence and partial complex seizures. Brain Lang. 1983 May;19(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(83)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAILLAS J. E., VIGOUROUX R., DARCOURT G., NAQUET R. Considérations sur l'épilepsie occipitale; à propos de 12 observations de lésions occipitales opérées. Neurochirurgie. 1959 Jan-Mar;5(1):3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racy A., Osborn M. A., Vern B. A., Molinari G. F. Epileptic aphasia. First onset of prolonged monosymptomatic status epilepticus in adults. Arch Neurol. 1980 Jul;37(7):419–422. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500560049004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum D. H., Siegel M., Barr W. B., Rowan A. J. Epileptic aphasia. Neurology. 1986 Jun;36(6):822–825. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERAFETINIDES E. A., FALCONER M. A. Speech disturbances in temporal lobe seizures: a study in 100 epileptic patients submitted to anterior temporal lobectomy. Brain. 1963 Jun;86:333–346. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.2.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. C., Lochery M. Temporal lobe epilepsy: origin and significance of simple and complex auras. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jun;50(6):673–681. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.6.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A., Petty R., Perry A., Rose F. C. Paroxysmal language disturbance in an epileptic treated with clobazam. Neurology. 1983 May;33(5):652–654. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.5.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


