Abstract
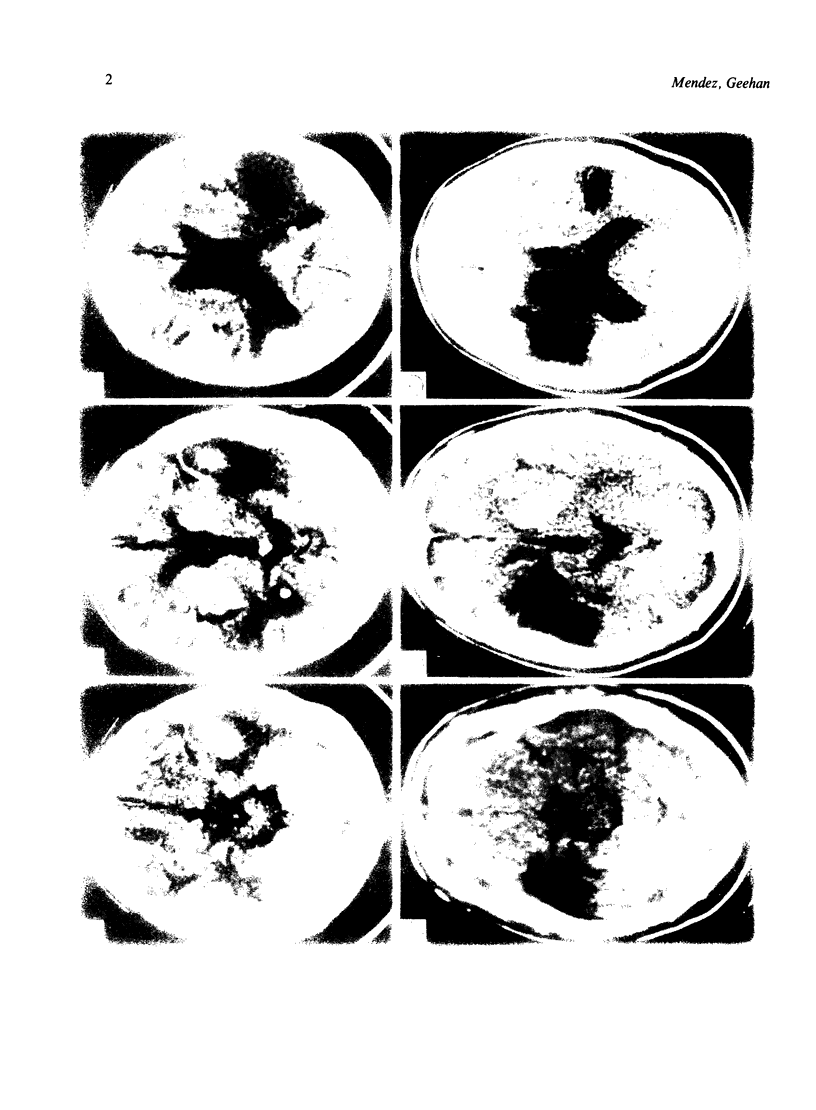
The symptoms of two patients with bilateral cortical auditory lesions evolved from cortical deafness to other auditory syndromes: generalised auditory agnosia, amusia and/or pure word deafness, and a residual impairment of temporal sequencing. On investigation, both had dysacusis, absent middle latency evoked responses, acoustic errors in sound recognition and matching, inconsistent auditory behaviours, and similarly disturbed psychoacoustic discrimination tasks. These findings indicate that the different clinical syndromes caused by cortical auditory lesions form a spectrum of related auditory processing disorders. Differences between syndromes may depend on the degree of involvement of a primary cortical processing system, the more diffuse accessory system, and possibly the efferent auditory system.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Rosenberger K., Winter H., Zöllner C. A case of cortical deafness. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1977 Nov 7;224(3):213–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00348003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert M. L., Bear D. Time to understand. A case study of word deafness with reference to the role of time in auditory comprehension. Brain. 1974 Jun;97(2):373–384. doi: 10.1093/brain/97.1.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert M. L., Sparks R., Von Stockert T., Sax D. A case study of auditory agnosia: linguistic and non-linguistic processing. Cortex. 1972 Dec;8(4):427–443. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(72)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assal G., Despland P. A. Présentation d'un cas d'agnosie auditive. Rev Otoneuroophtalmol. 1973 Jul-Sep;45(4):353–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach S. H., Allard T., Naeser M., Alexander M. P., Albert M. L. Pure word deafness. Analysis of a case with bilateral lesions and a defect at the prephonemic level. Brain. 1982 Jun;105(Pt 2):271–300. doi: 10.1093/brain/105.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. B. [A tribute to Russell DeJong, founding Editor-in-chief]. Neurology. 1977 Jan;27(1):1–2. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. S., Garron D. C., Trost-Cardamone J. E., Wichter M. D., Schwartz M. Word deafness: one hundred years later. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 May;49(5):489–499. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesia G. G. Organization of auditory cortical areas in man. Brain. 1976 Sep;99(3):403–414. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chocholle R., Chedru F., Botte M. C., Chain F., Lhermitte F. Etude psychoacoustique d'un cas de "surdité corticale". Neuropsychologia. 1975 Apr;13(2):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(75)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coslett H. B., Brashear H. R., Heilman K. M. Pure word deafness after bilateral primary auditory cortex infarcts. Neurology. 1984 Mar;34(3):347–352. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzaniga M. S., Glass A. V., Sarno M. T., Posner J. B. Pure word deafness and hemispheric dynamics: a case history. Cortex. 1973 Mar;9(1):136–143. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(73)80022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M. N., Brown M., Hollander J. Auditory agnosia and cortical deafness: analysis of a case with three-year followup. Brain Lang. 1975 Jul;2(3):324–332. doi: 10.1016/s0093-934x(75)80073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J., Greenwood R., Lecky B. Cortical deafness--a case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Oct;48(1):35–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerger J., Lovering L., Wertz M. Auditory disorder following bilateral temporal lobe insult: report of a case. J Speech Hear Disord. 1972 Nov;37(4):523–535. doi: 10.1044/jshd.3704.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN R., HARPER J. The problem of agnosia in the light of a case of pure word deafness. J Ment Sci. 1956 Jan;102(426):112–120. doi: 10.1192/bjp.102.426.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanshepolsky J., Kelley J. J., Waggener J. D. A cortical auditory disorder. Clinical, audiologic and pathologic aspects. Neurology. 1973 Jul;23(7):699–705. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.7.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMOYNE J., MAHOUDEAU D. A propos d'un cas d'agnosie auditive pure avec surdité corticale associée à une dysphonie fonctionnelle; observation anatomo-clinique. Ann Otolaryngol. 1959 Apr-May;76(4-5):293–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen N. A., Larsen B. Cortical activity in the left and right hemispheres during language-related brain functions. Phonetica. 1980;37(1-2):27–37. doi: 10.1159/000259981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier B., Rossa Y., Eustache F., Schupp C., Boner L., Bazin C. Un cas de surdité corticale épargnant en partie la musique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1984;140(3):190–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicester J. Central deafness and subcortical motor aphasia. Brain Lang. 1980 Jul;10(2):224–242. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(80)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASPETIOL R., MESSIMY R., SEMETTE D. [A case of central deafness]. Ann Otolaryngol. 1959 Dec;76:1103–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. C., Rappaport B. Z., Garcia-Bunuel L. Self-monitoring behavior in a case of severe auditory agnosia with aphasia. Brain Lang. 1985 Mar;24(2):297–313. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(85)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz-Lutz M. N., North P., Dufour P., Eber A. M., Gentine A., Rohmer F. Troubles auditifs d'origine corticale. A propos de deux cas. Rev Otoneuroophtalmol. 1980 May-Jun;52(3):231–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli G. The processing of speech sounds in a patient with cortical auditory disorder. Neuropsychologia. 1982;20(1):5–20. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(82)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Peronnet F., Schott B. A case of cortical deafness: clinical and electrophysiological data. Brain Lang. 1980 Jul;10(2):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(80)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motomura N., Yamadori A., Mori E., Tamaru F. Auditory agnosia. Analysis of a case with bilateral subcortical lesions. Brain. 1986 Jun;109(Pt 3):379–391. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi M., Suzuki J. Auditory agnosia due to incision of splenium corporis callosi. Acta Otolaryngol. 1973 Aug-Sep;76(2):109–113. doi: 10.3109/00016487309121488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R., Newcombe F. Clinical and anatomic findings in a case of auditory agnosia. Arch Neurol. 1978 Nov;35(11):712–719. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500350016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving A., Salomon G., Elberling C., Larsen B., Lassen N. A. Middle components of the auditory evoked response in bilateral temporal lobe lesions. Report on a patient with auditory agnosia. Scand Audiol. 1980;9(3):161–167. doi: 10.3109/01050398009076350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINHOLD M. A case of auditory agnosia. Brain. 1950 Jun;73(2):203–223. doi: 10.1093/brain/73.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPREEN O., BENTON A. L., FINCHAM R. W. AUDITORY AGNOSIA WITHOUT APHASIA. Arch Neurol. 1965 Jul;13:84–92. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1965.00470010088012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo M., Kaga K., Tanaka Y. [Auditory agnosia following bilateral temporal lobe lesions-report of a case (author's transl)]. No To Shinkei. 1981 Feb;33(2):139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA Y., TAGUCHI K., SAKABE N., IGARASHI E. PURE AUDITORY AGNOSIA ASSOCIATED WITH ALTERATION OF VOICE AND PERSONAL CHARACTER. A CASE REPORT. Folia Phoniatr (Basel) 1965;17:185–194. doi: 10.1159/000263041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabira T., Tsuji S., Nagashima T., Nakajima T., Kuroiwa Y. Cortical deafness in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 May;44(5):433–436. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich G. Das syndrom der akustischen Agnosie. Fallbericht und Versuch einer neuropsychologischen Qualifizierung. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1977 Nov 7;224(3):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich G. Interhemispheric functional relationships in auditory agnosia. An analysis of the preconditions and a conceptual model. Brain Lang. 1978 May;5(3):286–300. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(78)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignolo L. A. Auditory agnosia. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 25;298(1089):49–57. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLFART G., LINDGREN A., JERNELIUS B. Clinical picture and morbid anatomy in a case of pure word deafness. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1952 Dec;116(6):818–827. doi: 10.1097/00005053-195212000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. L., Knight R. T., Neville H. J. Bitemporal lesions dissociate auditory evoked potentials and perception. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1984 Mar;57(3):208–220. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(84)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIEGLER D. K. Word deafness and Wernicke's aphasia; report of cases and discussion of the syndrome. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1952 Mar;67(3):323–331. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1952.02320150056005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]