Abstract
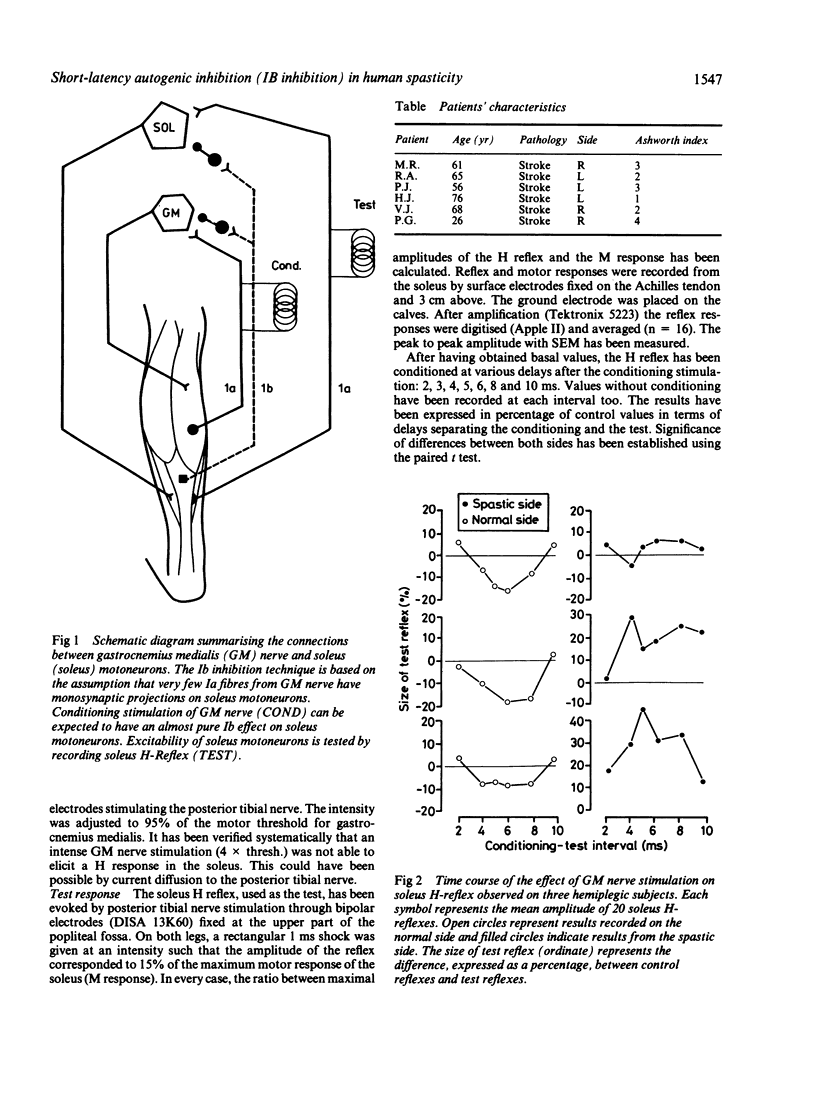
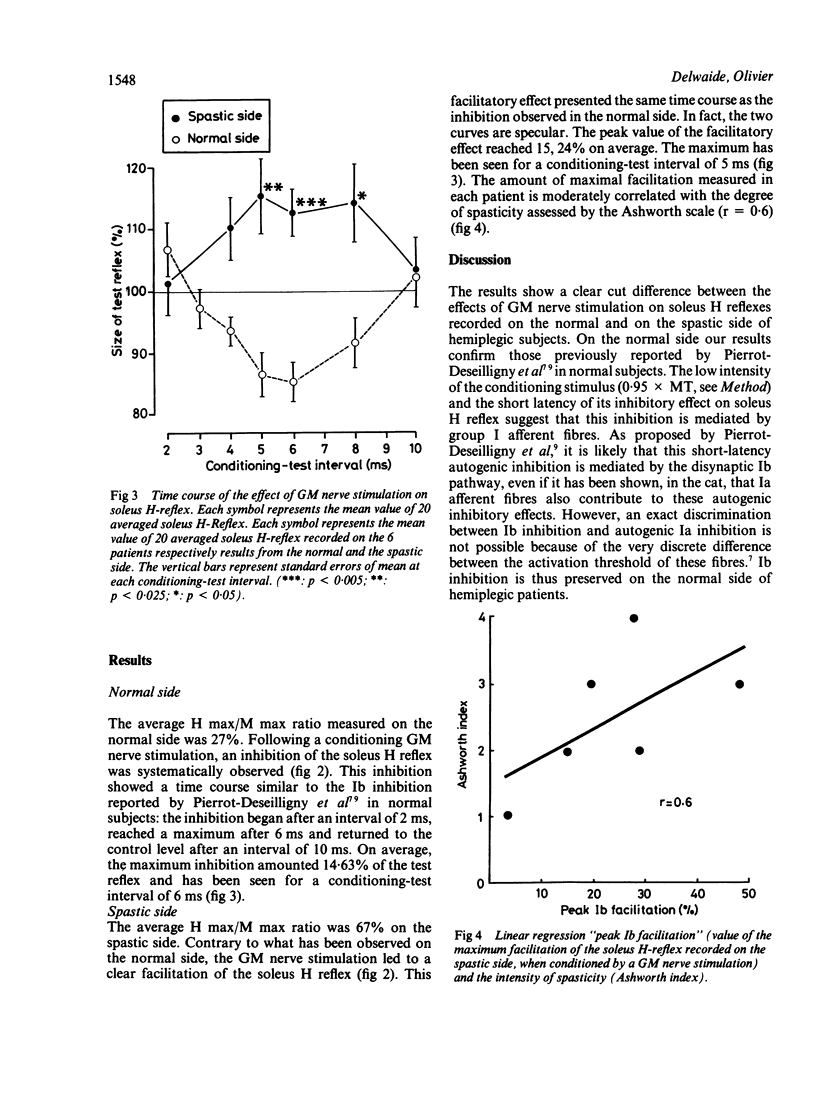
The inhibitory effect of IB interneurons on motoneurons was tested in both legs of six hemiplegic adults. On the normal side, an inhibition of 10 ms, (14.6%) was observed in all cases and was similar to that described previously. On the spastic side, the same technique results in a facilitation of same duration reaching a maximum of 15%. Hence the IB inhibitory effect is, at least functionally, absent in spasticity. Disappearance of IB inhibition is an additional mechanism to be considered in interpreting spasticity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH B. PRELIMINARY TRIAL OF CARISOPRODOL IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Practitioner. 1964 Apr;192:540–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gandevia S. C., McKeon B. Monosynaptic and oligosynaptic contributions to human ankle jerk and H-reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Sep;52(3):435–448. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J. C. Regulation of stiffness by skeletomotor reflexes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:99–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A. Multisensory control of spinal reflex pathways. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:11–28. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60803-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., McDOUGAL D. B., Jr Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. I. Identification of certain reflexes in the electromyogram and the conduction velocity of peripheral nerve fibers. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 May;86(5):265–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. H. Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1933 Apr 13;78(1):1–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. R., Houk J. C. Improvement in linearity and regulation of stiffness that results from actions of stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):119–142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Katz R., Morin C. Evidence of Ib inhibition in human subjects. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 20;166(1):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Morin C., Bergego C., Tankov N. Pattern of group I fibre projections from ankle flexor and extensor muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):337–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00237499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymer W. Z., Houk J. C., Crago P. E. Mechanisms of the clasp-knife reflex studied in an animal model. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Sep;37(1):93–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01474257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville J., Ashby P. Hemiplegic spasticity: neurophysiologic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1978 Dec;59(12):592–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B., Hagbarth K. E., Torebjörk H. E., Wallin B. G. Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):919–957. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt D. G., Stauffer E. K., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 1. Spindle primary and tendon organ afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1375–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


