Figure 5. Proposed mechanisms of aromatic polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
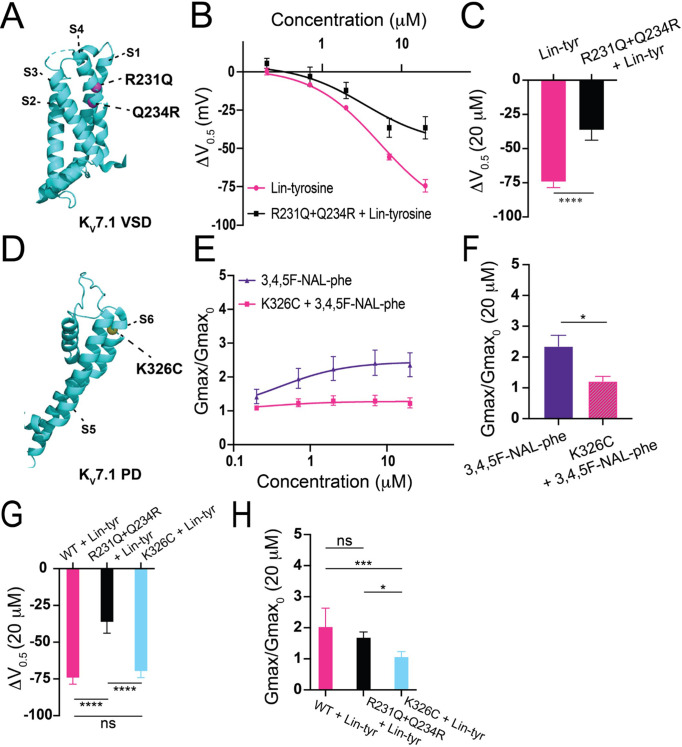
(A) Structure of KV7.1 voltage-sensing domain (VSD) based on PDB: 6V00A projected using PyMOL Software (Schrödinger L and DeLano 2020). Pink spheres indicate mutated residues in the S4 segment, R321Q-Q234R, which are implicated in PUFA-mediated effects on voltage dependent activation. (B) ΔV0.5 dose–response curve for WT KV7.1/KCNE1 + Lin-tyr (pink) (n = 4) and KV7.1-R231Q-Q234R/KCNE1 + Lin-tyr (black) (n = 5). (C) Maximum effects on ΔV0.5 (at 20 μM) for WT KV7.1/KCNE1 + Lin-tyr (n = 4) and KV7.1-R231Q-Q234R/KCNE1 + Lin-tyr (n = 5). (D) Structure of KV7.1 pore domain (PD). Yellow spheres indicate mutated residue in the S6 segment, K326C, which is implicated in PUFA-mediated effects on maximal conductance. (E) Gmax dose–response curve for WT KV7.1/KCNE1 + 3,4,5F-NAL-phe (purple) (n = 5) and KV7.1-K326C/KCNE1 + 3,4,5F-NAL-phe (pink) (n = 3). (F) Maximum effects on Gmax (at 20 μM) for WT KV7.1/KCNE1 + 3,4,5F-NAL-phe (n = 5) and KV7.1-K326C/KCNE1 + 3,4,5F-NAL-phe (n = 3). (G) Maximum effects on ΔV0.5 (at 20 μM) of Lin-tyr on WT KV7.1/KCNE1 (n = 4), KV7.1-R231Q-Q234R/KCNE1 (n = 5), and KV7.1-K326C/KCNE1 (n = 6). (H) Maximum effects on Gmax (at 20 μM) of Lin-tyr on WT KV7.1/KCNE1 (n = 6), KV7.1-R231Q-Q234R/KCNE1 (n = 5), and KV7.1-K326C/KCNE1 (n = 6). Values for all compounds and concentrations available in Figure 5—source data 1.