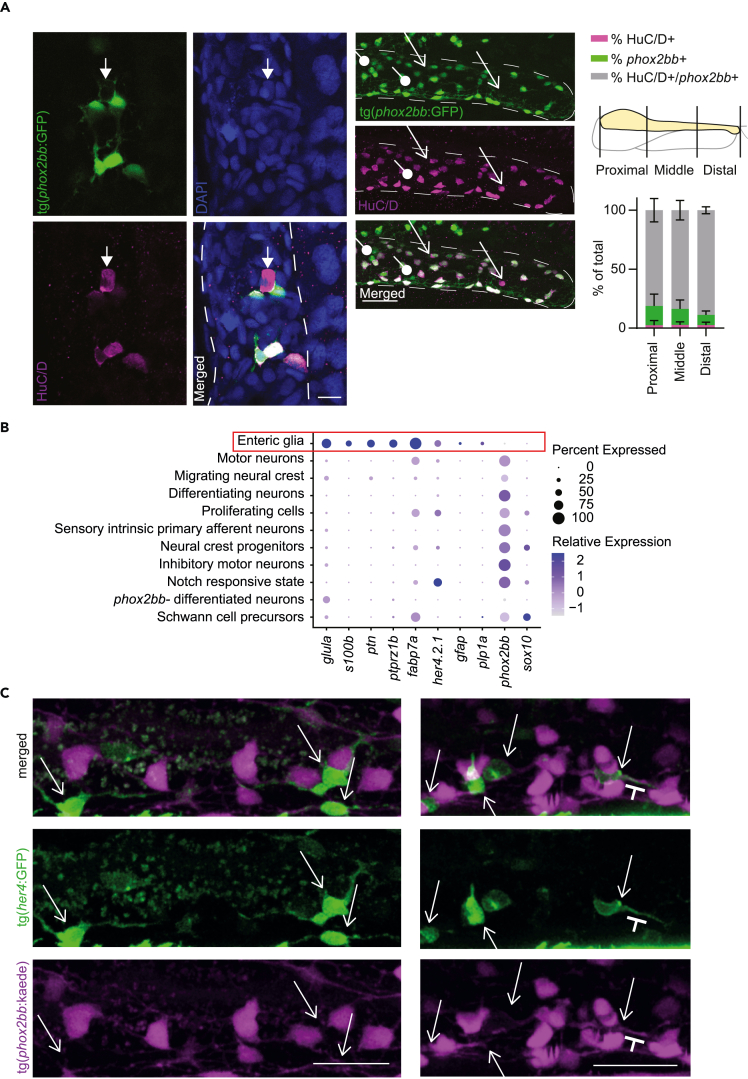
Figure 3.
One small cluster expresses genes typical for enteric glia in mammalians
(A) Left: Single plane recording showing a HuC/D+phox2bb-neuron. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Right: Maximum projections of HuC/D antibody staining shows that most HuC/D+ cells in the intestine express phox2bb, but also show phox2bb+/HuC/D-cells (progenitors) depicted by the arrows with a circle end, and phox2bb-;HuC/D+ cells (differentiated neurons) depicted by arrows. Scale bar represents 40 μm. Quantification of the relative amount of double and single positive cells, relative to the total number of enteric neurons (HuC/D only, phox2bb only and double-positives combined)(n=9; 5 dpf, error bars show standard deviation).
(B) Dotplot showing selective expression of some known enteric glia and radial glia markers and lack of expression of phox2bb and sox10 in the cluster of enteric glia depicted by the red box.
(C) Maximum projections of live-imaging recordings of 5 dpf photoconverted tg(8.3phox2bb:kaede);tg(her4:GFP) intestines shows phox2bb-;her4+ cell depicted by the arrows, that are in close proximity to, or seem to interact with phox2bb+ neurons (magenta; close interaction between extensions is depicted by the T mark). Scale bar represents 20 μm.