Fig. 2 |. Variovorax maintains stereotypic root development.
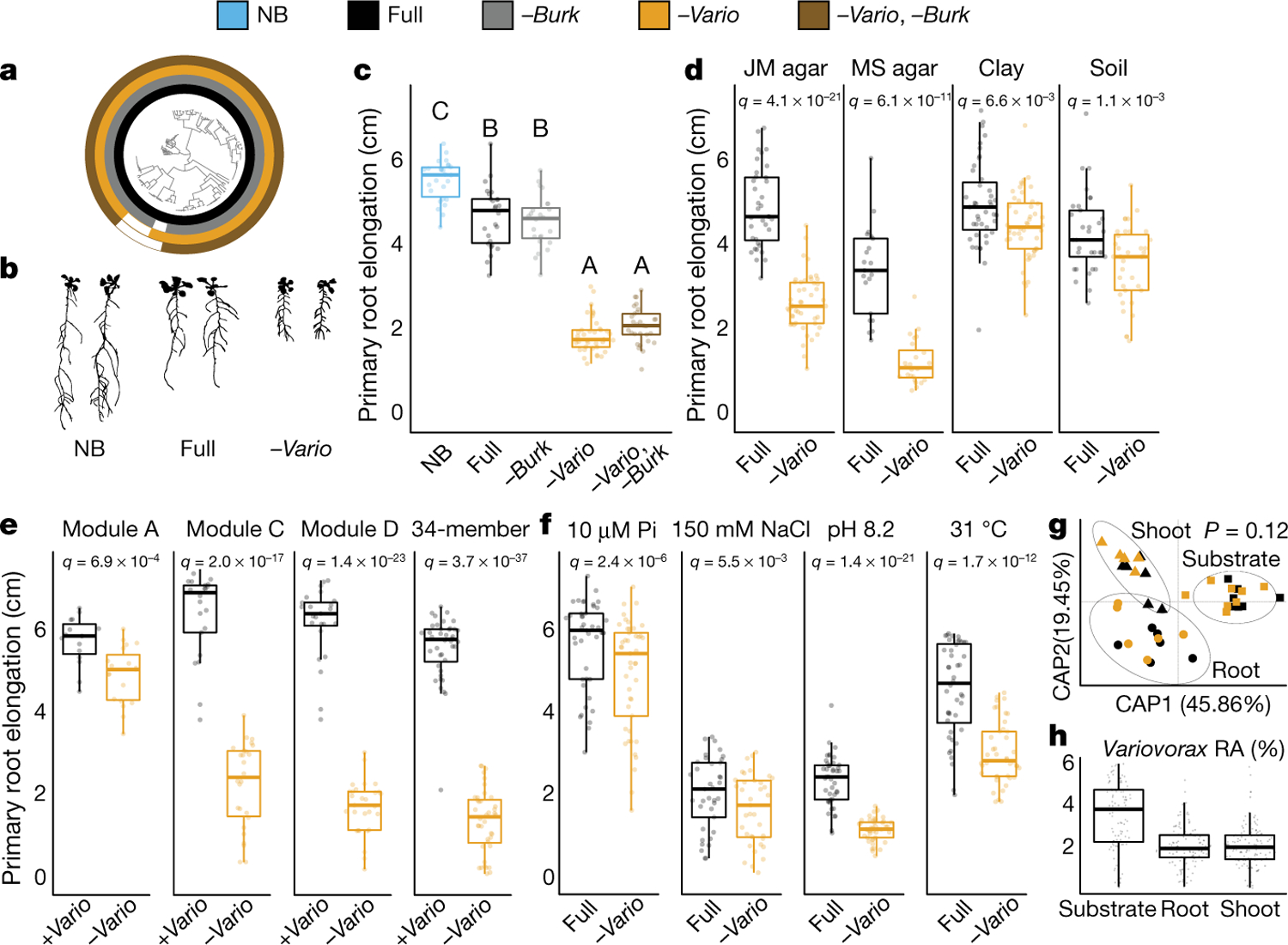
a, Phylogenetic tree of 185 bacterial isolates. Concentric rings represent isolate composition of each synthetic community treatment. NB, uninoculated (no bacteria); full, full synthetic community; −Burk, Burkholderia drop-out; −Vario, Variovorax drop-out; −Vario, −Burk, Burkholderia and Variovorax drop-out. b, Binarized image of representative seedlings inoculated or not with the full synthetic community or the Variovorax drop-out synthetic community. c, Primary root elongation of seedlings grown axenically (NB) or inoculated with the different synthetic community treatments outlined in a. Significance was determined via ANOVA, letters correspond to a Tukey post hoc test. n = 26, 26, 24, 37 and 29 (from left to right) biological replicates. d, Primary root elongation of seedlings inoculated with the full synthetic community or with the Variovorax drop-out synthetic community across different substrates: Johnson medium (JM) agar, Murashige and Skoog (MS) agar, sterilized clay or potting soil. n = 36, 47, 21, 24, 43, 48, 33 and 36 (from left to right) biological replicates across 2 independent experiments. e, Primary root elongation of seedlings inoculated with four subsets of the full synthetic community (module A, C, D or a previously described 35-member synthetic community with its single Variovorax strain removed (34-member)1), with (+Vario) or without (−Vario) Variovorax isolates. n = 40, 40, 15, 19, 22, 26, 25 and 29 (from left to right) biological replicates across 2 independent experiments. f, Primary root elongation of seedlings inoculated with the full synthetic community or with the Variovorax drop-out synthetic community across different abiotic stresses: low phosphate, high salt, high pH and high temperature. n = 43, 45, 37, 37, 43, 44, 44 and 43 (from left to right) biological replicates across 2 independent experiments. Significance was determined within each condition via ANOVA in d, f, and with a two-sided t-test in e. FDR-adjusted P values are displayed. g, Canonical analysis of principal coordinates (CAP) scatter plots comparing the compositions of the full synthetic community and Variovorax drop-out synthetic community (colour code as in a) across fractions (substrate (squares), root (circles) and shoot (triangles)). Permutational multivariate ANOVA (PERMANOVA) P value is shown. n = 7 (substrate + full), 8 (substrate + −Vario), 6 (root + full), 6 (root + −Vario), 5 (shoot + full) or 5 (shoot + −Vario). h, Relative abundance (RA) of the Variovorax genus within the full synthetic community across the agar, root and shoot fractions. n = 127, 119 and 127 biological replicates for agar, root and shoot, respectively, across 16 independent experiments.
