Fig. 3 |. Variovorax suppression of RGI is related to auxin and ethylene signalling.
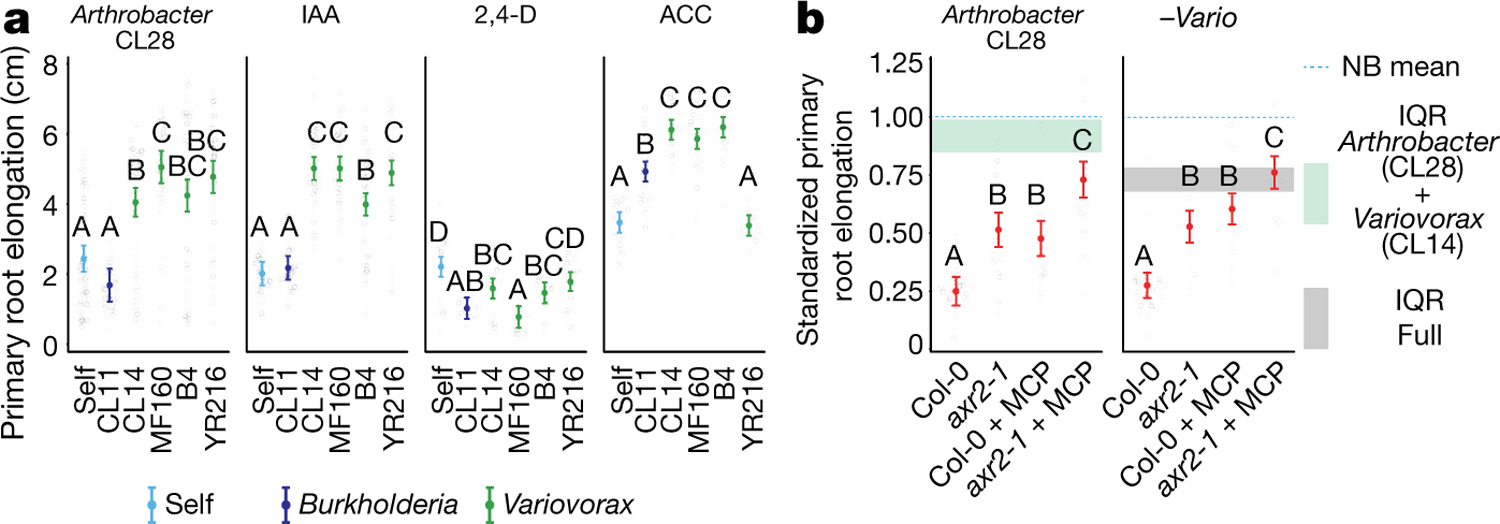
a, Primary root elongation of seedlings grown with RGI-inducing Arthrobacter CL28 or three hormonal treatments (100 nM IAA, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) or ACC), individually (self) or with Burkholderia CL11 or one of four Variovorax isolates (CL14, MF160, B4 or YR216). Significance was determined within each treatment via ANOVA; letters correspond to a Tukey post hoc test. n = 74, 46, 61, 48, 49, 49, 45, 44, 46, 43, 49, 40, 22, 19, 22, 19, 20, 25, 28, 30, 29, 29, 29 and 29 (from left to right) biological replicates across 2 independent experiments. b, Primary root elongation, standardized to axenic conditions, of wild-type (Col-0), auxin-unresponsive (axr2-1), ethylene-unresponsive (Col-0 + MCP) or auxin- and ethylene-unresponsive (axr2-1 + MCP) seedlings inoculated with RGI-inducing Arthrobacter CL28 or the Variovorax drop-out synthetic community (−Vario). The blue dotted line marks the relative mean length of uninoculated seedlings. Horizontal shading is the IQR of seedlings grown with Arthrobacter CL28 +Variovorax CL14 (aqua) or the full synthetic community (grey). Significance was determined via ANOVA; letters correspond to a Tukey post hoc test. n = 37, 25, 24, 23, 35, 21, 22 and 20 (from left to right) biological replicates across 2 independent experiments. In a, b, data represent the mean ± 95% confidence interval.
