Abstract
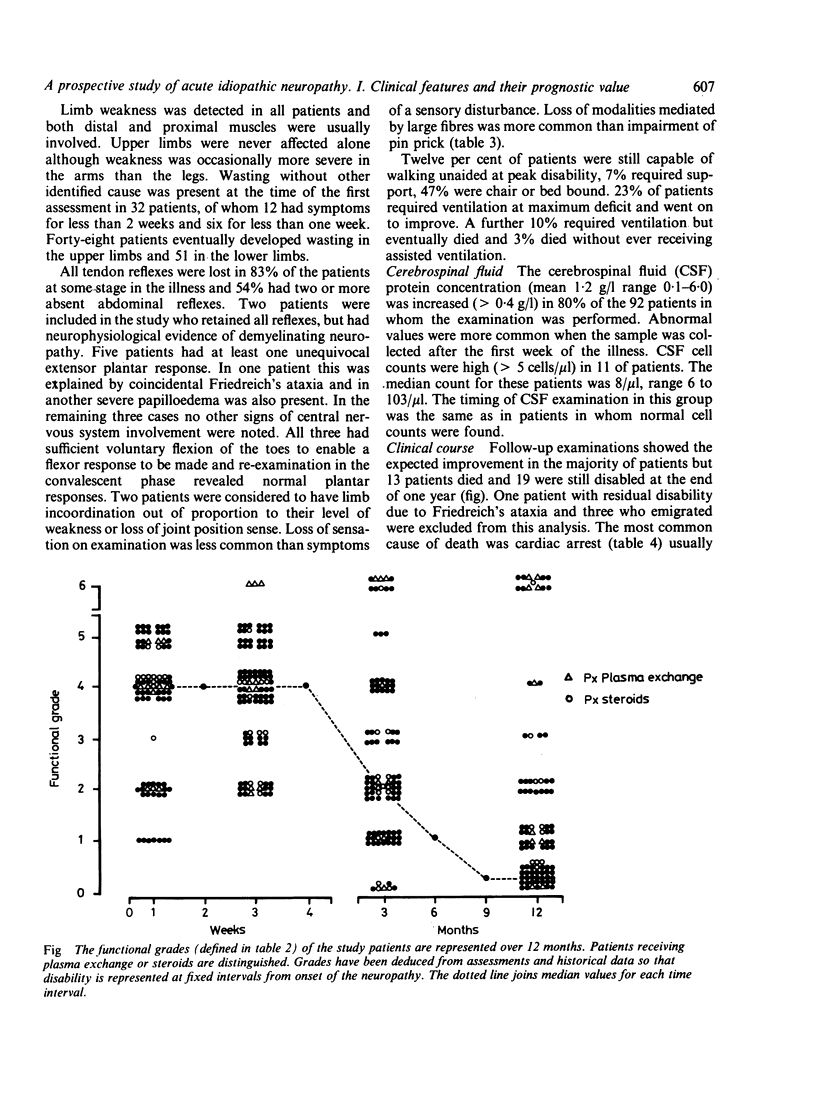
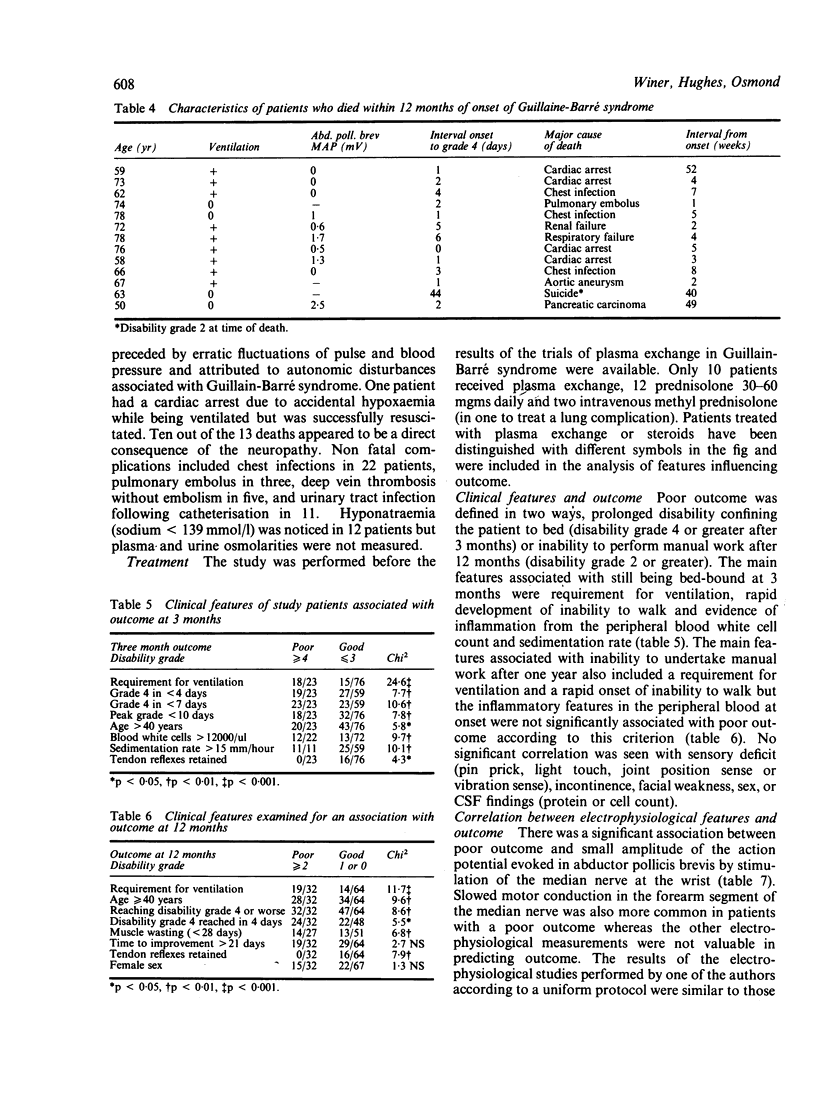
A prospective study in South-East England during 15 months in 1983-1984 recruited 100 patients with acute idiopathic neuropathy. After 12 months 67% had recovered completely, 20% were still significantly disabled and 13% had died. Ten of the 13 deaths were attributable to the neuropathy. The major features in the initial assessment which were associated with persistent disability were the time taken to become bedbound, requirement for ventilation, age greater than 40 years, and small or absent compound abductor pollicis brevis muscle action potentials elicited by stimulation of the median nerve at the wrist. These four variables have been combined in a statistical model to predict outcome for individual patients with acute idiopathic neuropathy.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. W., Donofrio P. D., McGonagle T. K. Sequential electrodiagnostic abnormalities in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Jul-Aug;8(6):528–539. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. F., Feasby T. E. Conduction block and denervation in Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):219–239. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchlow J. F., Seybold M. E., Jablecki C. J. The superficial radial nerve: techniques for evaluation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Oct;43(10):929–933. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.10.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle E., Brink J., Azen S., White D. Early predictors of incomplete recovery in children with Guillain-Barr'e polyneuritis. J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):356–359. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80962-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Humphreys P. The Guillain-Barré syndrome. A clinical and electrodiagnostic study of 25 cases. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jun;30(6):438–443. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490360014004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feasby T. E., Gilbert J. J., Brown W. F., Bolton C. F., Hahn A. F., Koopman W. F., Zochodne D. W. An acute axonal form of Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain. 1986 Dec;109(Pt 6):1115–1126. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.6.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiloff R. J. Peripheral nerve conduction in Miller Fisher syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Aug;40(8):801–807. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.8.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Emeryk B., Rowińska-Marcińska K., Jedrzejowska H. Nerve conduction in the Guillain-Barré-Strohl syndrome. J Neurol. 1979 May 2;220(3):169–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00705535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Butzer J. F. F-wave conduction velocity in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Assessment of nerve segment between axilla and spinal cord. Arch Neurol. 1975 Aug;32(8):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490500044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. P., Kvåle G., Nyland H. Epidemiology of the Guillain-Barré syndrome in the county of Hordaland, Western Norway. Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Jan;71(1):43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb03165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffel N. B., Rossi L. N., Mumenthaler M., Lütschg J., Ludin H. P. The Landry-Guillain-barré syndrome. Complications, prognosis and natural history in 123 cases. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Aug;33(1-2):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G. Electrophysiological studies in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1981;9 (Suppl):20–27. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Walsh J. C., Prineas J. W., Pollard J. D. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. A clinical and electrophsiological follow-up study. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):145–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSLER L. D., SIDELL A. D. The Guillain-Barre syndrome; the need for exact diagnostic criteria. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 12;262:964–969. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005122621905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W., McLeod J. G. Chronic relapsing polyneuritis. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Apr;27(4):427–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman P. T., Taori G. M. Prognostic significance of electrodiagnostic studies in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;39(2):163–170. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravn H. The Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A survey and a clinical report of 127 cases. Acta Neurol Scand. 1967;43(Suppl):1–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropper A. H. Severe acute Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology. 1986 Mar;36(3):429–432. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi L. N., Mumenthaler M., Lütschg J., Ludin H. P. Guillain-Barré syndrome in children with special reference to the natural history of 38 personal cases. Neuropadiatrie. 1976 Feb;7(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., SEARS T. A., GILLIATT R. W. The range of conduction velocity in normal motor nerve fibers to the small muscles of the hand and foot. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Aug;22:175–181. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi H., Takahashi M., Kang J., Ueno S., Yamada A., Miki H., Tarui S. The Guillain-Barré syndrome: clinical and electroneuromyographic studies. J Neurol. 1984;231(1):6–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00313644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDERHOLT W. C., MULDER D. W., LAMBERT E. H. THE LANDRY-GUILLAIN-BARR'E-STROHL SYNDROME OR POLYRADICULONEUROPATHY: HISTORICAL REVIEW, REPORT ON 97 PATIENTS, AND PRESENT CONCEPTS. Mayo Clin Proc. 1964 Jun;39:427–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


