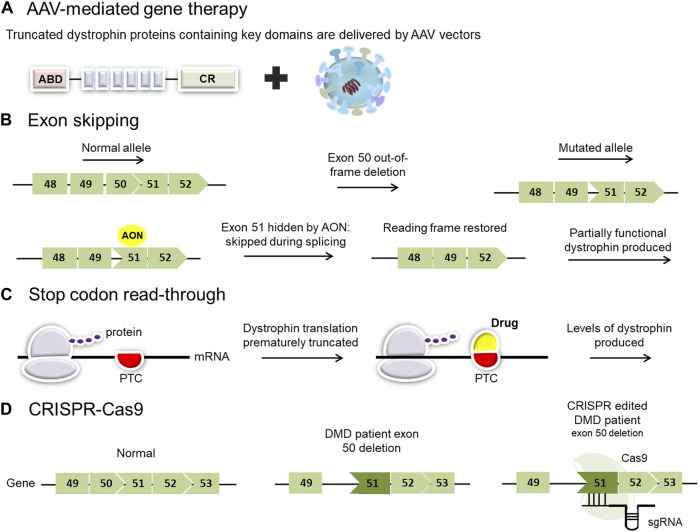
FIGURE 2.
Overview of current and proposed experimental therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). (A) AAV-mediated gene therapy employs viral vectors to deliver micro- or mini-dystrophin genes. Clinical trials using different adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotypes have shown promise for the treatment of patients with DMD. (B) Exon-skipping strategies seek to mask exons adjacent to others that have been deleted. This results in the restoration of the reading frame and permits the translation of a slightly smaller dystrophin product. (C) Stop codon read-through is a small molecule therapy aimed at reducing ribosomal sensitivity to mRNA stop codons, thus promoting ongoing dystrophin translation in those patients with nonsense mutations. (PTC: premature termination codon). (D) Genome editing, employing a CRISPR/Cas9 platform, has the potential to target specific pathogenic variants in the DMD gene but carries a risk of off-target effects.